














Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Wk 3 Lecture 1 - The National Territory - Provisions in the Constitution Relevant to Tourism and Hospitality
Typology: Lab Reports
1 / 22

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!















PROVISIONS IN THE PHILIPPINE CONSTITUTION RELEVANT
Nature & Purpose of the Constitution
Constitution is a legislation direct from the people
Constitution states the merely general framework of the law
Constitution is intended not merely to meet existing conditions but to govern the future
Constitution is the supreme or fundamental law
WHAT ARTICLES IN THE PHILIPPINE CONSTITUTION IS RELEVANT TO THE TOURISM & HOSPITALITY INDUSTRY?
Article 1: THE NATIONAL TERRITORY The national territory comprises the Philippine archipelago, with all the islands and waters embraced therein, and all other territories over which the Philippines has sovereignty or jurisdiction, consisting of its terrestrial, fluvial and aerial domains, including its territorial sea, the seabed, the subsoil, the insular shelves, and other submarine areas. The waters around, between, and connecting the islands of the archipelago, regardless of their breadth and dimensions, form part of the internal waters of the Philippines.
PHILIPPINE NATIONAL TERRITORY
Terrestrial Domain (Land territory) - The territorial domain refers to the land mass, which may be integrate or dismembered, or partly bound by water or consist of one whole island. It may also be composed of several islands, like the Philippines, which are also known as mid-ocean archipelagos
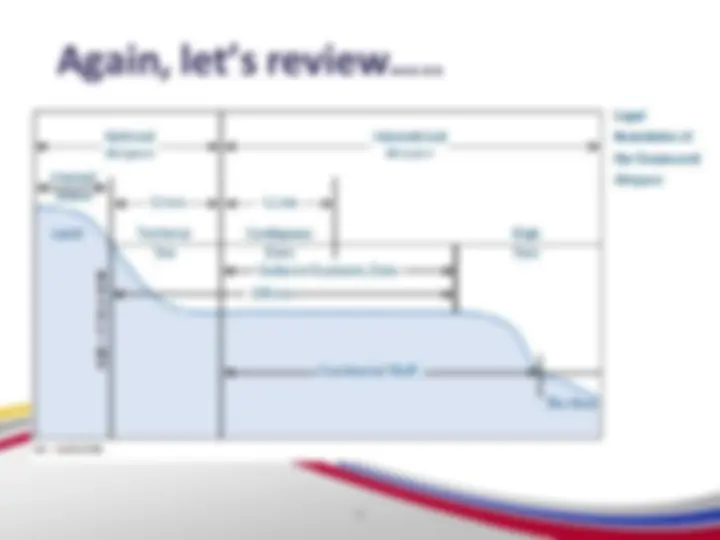
Fluvial Domain (Maritime Territory) – which covers internal waters, territorial sea, contiguous zone, exclusive economic zone, continental shelf
Aerial Domain (Airspace) – It includes the air directly above the state's terrestrial and fluvial domains, all the way up to where the outer space begins. The International Convention on Civil Aviation holds that every state has complete and exclusive sovereignty over the air space above its territory. It also regulates flight of civil aircraft over the territory of another state except by special agreement
PHILIPPINE NATIONAL TERRITORY
Innocent passage is a concept in the law of the sea that allows for a vessel to pass through the territorial waters of another state, subject to certain restrictions. The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea Article 19 defines innocent passage as:
Right of involuntary entrance is the right of any foreign merchant vessel to enter the territorial waters of a state in case of emergency such as lack, of provision, unseaworthiness of the vessel, inclement weather, pursuit of pirates, or other force majeure.
PHILIPPINE NATIONAL TERRITORY
Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) States may claim an EEZ that extends 200 nautical miles from the baseline as per UNCLOS. In this zone, a coastal State has the exclusive right to exploit or conserve any resources found within the water, on the sea floor, or under the sea floor’s subsoil. These resources encompass both living resources, such as fish, and non-living resources, such as oil and natural gas.^4 States also have exclusive rights to engage in offshore energy generation from the waves, currents, and wind within their EEZ.
PHILIPPINE NATIONAL TERRITORY
Continental Shelf The continental shelf is a natural seaward extension of a land boundary. This seaward extension is geologically formed as the seabed slopes away from the coast, typically consisting of a gradual slope (the continental shelf proper), followed by a steep slope (the continental slope), and then a more gradual slope leading to the deep seabed floor. These three areas, collectively known as the continental margin, are rich in natural resources, including oil, natural gas and certain minerals.
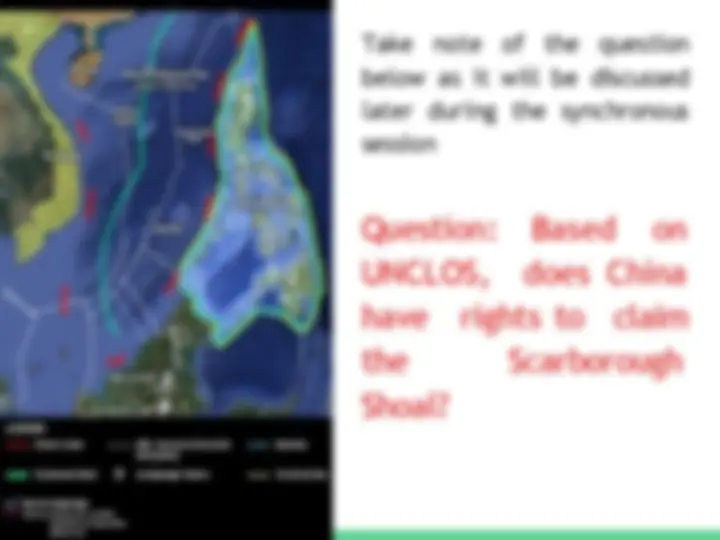
Question: Based on UNCLOS, does China rights to claim Scarborough have the Shoal?
For the purpose of tourism planning, development and marketing, having an idea of what constitutes the national territory of the Philippines is highly significant.
Take note of the question as it will be discussed later during the synchronous session