Download vietnam business somehow got this and more Summaries Business Statistics in PDF only on Docsity!
Lecture 12
Models for leading change
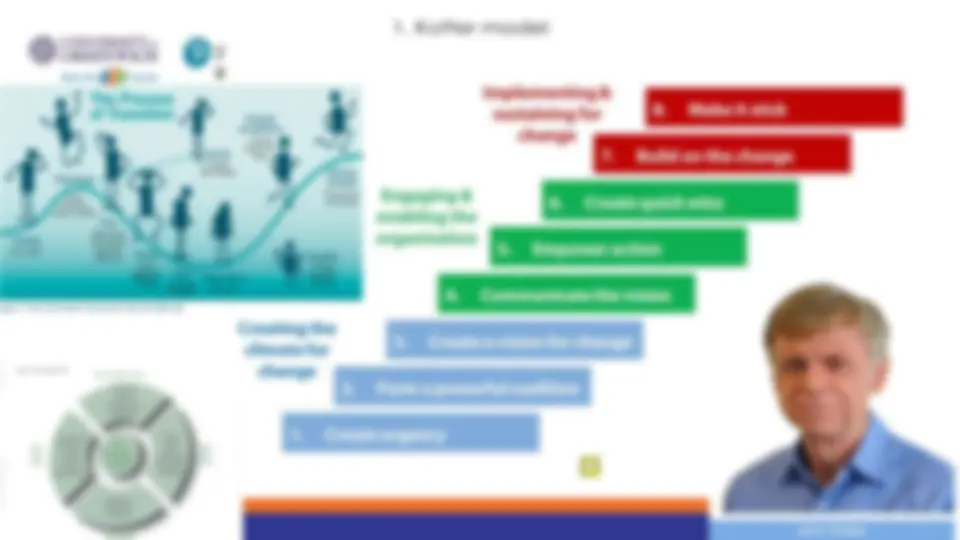
1. Kotter model
9 - 2 Discussion : Article 9 - Effective organizational change management Article 10a - Why Transformation Efforts Fail Article 10b - The 8 steps for leading change
The consequences of failure
- Financial expenditures
- Lost productivity
- Lost time in training and retraining workers
- Confusion, fatigue, and resentment for workers, clients, customers, suppliers, and other key stakeholders
- Damage to the brand
- Disruption in workflow
- Loss of high value stakeholders including workers, supporters, and clients/customers, among others.
STEP 2:
Creating the
Guiding
In putting together a Guiding Coalition, the team as a^ Coalition
whole should reflect:
- Position Power:
- Expertise:
- Credibility:
- Leadership:
STEP 3: Developing a Change Vision Effective visions have six key characteristics:
- Imaginable: They convey a clear picture of what the future will look like.
- Desirable: They appeal to the long-term interest of those who have a stake in the enterprise.
- Feasible: They contain realistic and attainable goals.
- Focused: They are clear enough to provide guidance in decision making.
- Flexible: They allow individual initiative and alternative responses in light of changing conditions.
- Communicable: They are easy to communicate and can be explained quickly.
- Examples:
STEP 5:
Empowering
Broad-Based
Action
- Remove
obstacles
Removing as many barriers as possible, including:
- Structural Barriers
- Troublesome Supervisors
STEP 6:
Generating Short-
term Wins
- Such wins provide evidence that the sacrifices that people are making
are paying off ;
- serve to reward the change agents by providing positive feedback that
boosts morale and motivation
- serve the practical purpose of helping to fine tune the vision and the
strategies
- tend to undermine the credibility of cynics and self-serving resistors
- building momentum that turns neutral people into supporters, and
reluctant supporters into active helpers
STEP 8: Make It Stick – Anchor the change (Institutionalizing new approaches) Some general rules about cultural change include:
- Cultural change comes last, not first
- You must be able to prove that the new way is superior to the old
- The success must be visible and well communicated
- You must reinforce new norms and values with incentives and rewards – including promotions
- Reinforce the culture with every new employee
Inspiring people
to change their
behaviour
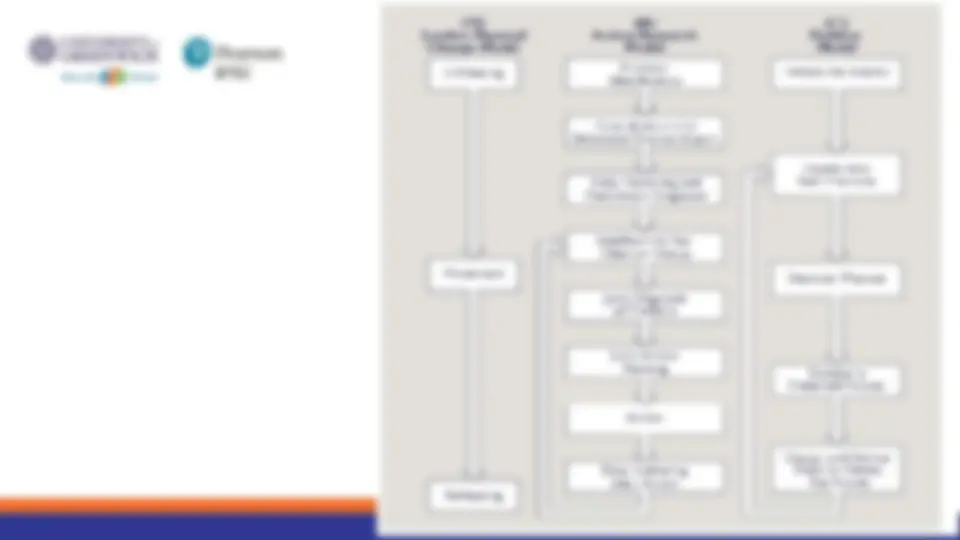
2.1. Lewin model: a general framework for understanding organizational change. 9 - 16
- This step usually involves reducing those forces maintaining the organization’s behavior at its present level. Unfreezing is sometimes accomplished through a process of “psychological disconfirmation Unfreezing
- This step shifts the behavior of the organization, department, or individual to a new level Moving Refreezing^ •^ This step stabilizes the organization at a new state of equilibrium. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qZH1cPaR--c
Changing employee behaviours in Vinmart
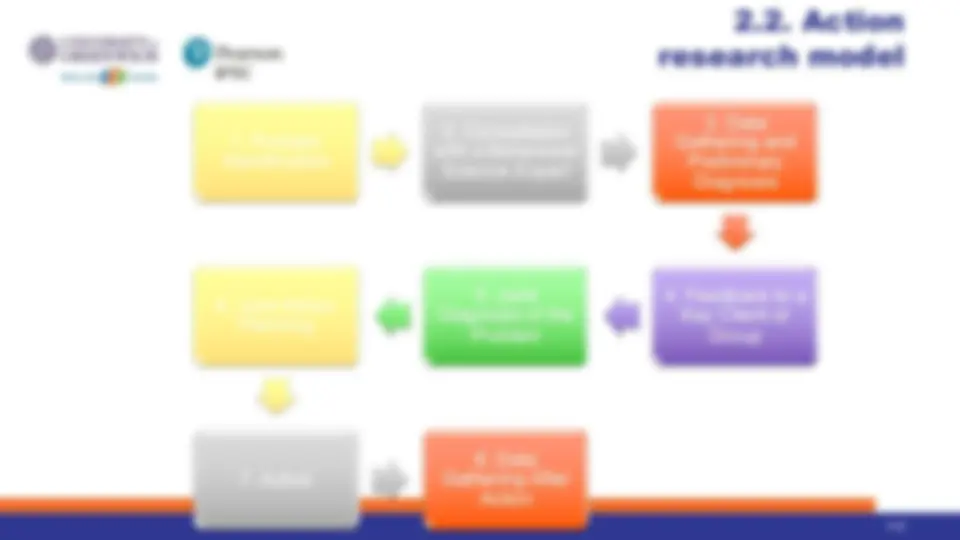
2.2. Action research model 9 - 19 v Action research is traditionally aimed both at helping specific organizations implement planned change and at developing more general knowledge that can be applied to other settings. v There are 8 main steps of action research model
2.2. Action research model 9 - 20
- Problem Identification
- Consultation with a Behavioral Science Expert
- Data Gathering and Preliminary Diagnosis
- Feedback to a Key Client or Group
- Joint Diagnosis of the Problem
- Joint Action Planning
- Action
- Data Gathering After Action