








Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Technical drawing mga men pucha may ma download Lang ako para makakuha Ng doc dito daming Alam may pa points pa
Typology: Lecture notes
1 / 16

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!










Rough Sketches are the most common recording method. The term “rough” describes the state of the design ideas. It suggests that the designs are incomplete and unrefined. Refined Sketches are refined design ideas. They may not look anything like the original rough sketches. Detailed Sketches communicate size, in addition to the shape and proportion communicated in the first two drawings. It also communicates the information needed to build a model of the product or structure.
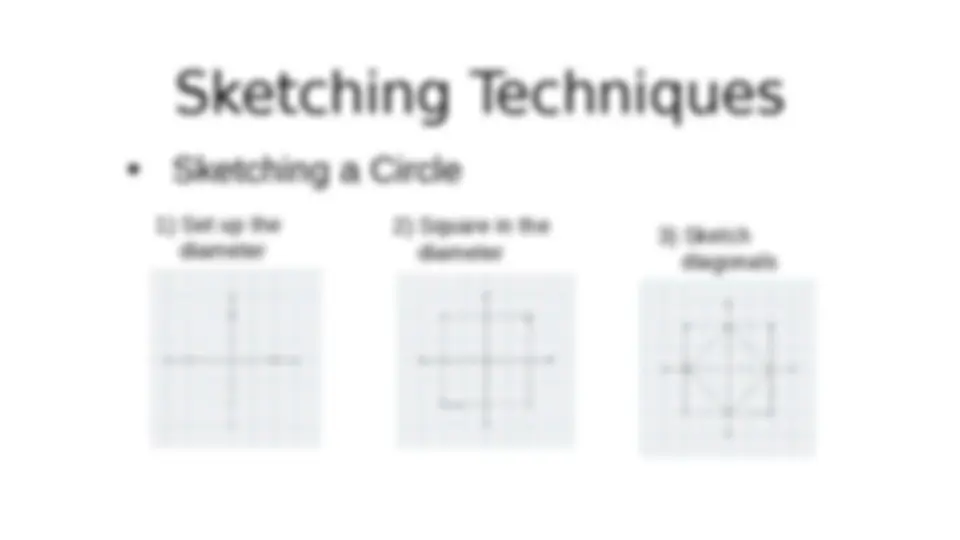
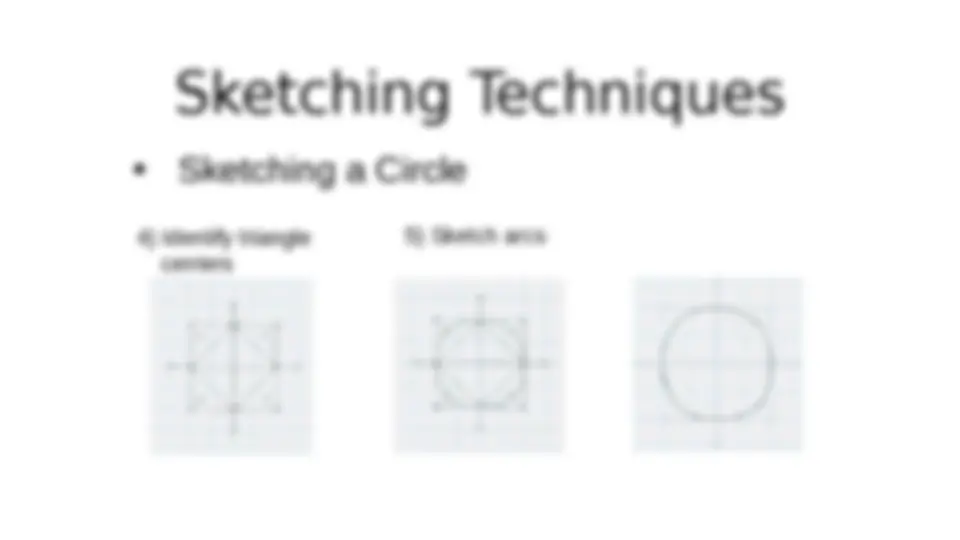
Sketching Techniques
Sketching Techniques
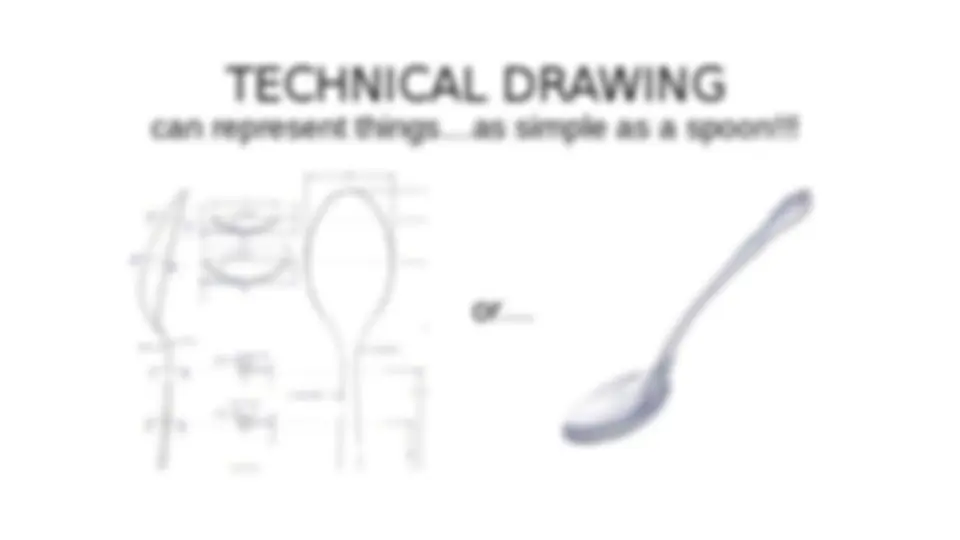
TECHNICAL DRAWING
TECHNICAL DRAWING
TECHNICAL DRAWING
TECHNICAL DRAWING
?DIFFERENCE: