






























Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Detailed information about Taenia saginata and Taenia solium, two tapeworm species that infect humans. the morphology of adult worms and their eggs, the life cycle of each species, and their modes of infection and pathogenicity. It also mentions diagnostic methods and treatment options.
What you will learn
Typology: Lecture notes
1 / 39

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!
































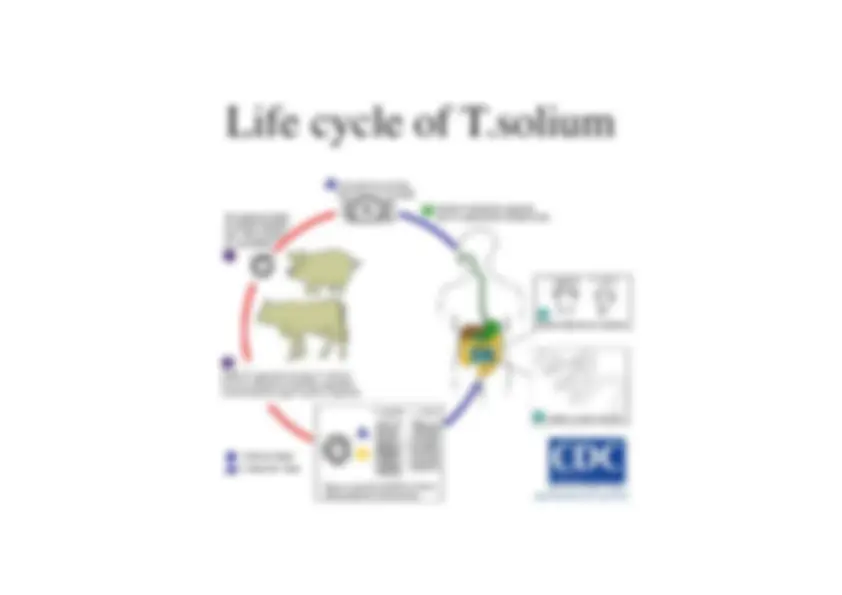
-^ The common name for Taenia solium is pork tapeworm i.e the armedtapeworm of man. •^ The restellum resembles the conventional figures of the sun, hence the name“solium”. •^ It is worldwide in distribution •^ The infection is common amongst those eating raw or insufficiently cookedmeasly pork. •^ It is uncommon in Jews and Mohammeedans who are not generally porkeaters.
-^ The neck is short,measuring from 5 to 10 mm in length. •^ Proglottides- The total number is less than a thousand. •^ A gravid segment measures 12mm by 6mm. •^ The gravid uterus consists of a median longitudinal stem with 5 to 10compound lateral branches on each side. •^ The gravid segments are expelled passively, in chains of 5 to 6 at atime, and not singly.
-^ The worm has a life span of as much as 25 years. •^ EGGS-
The characterstics of eggs are as follows:
1.^ Spherical and brown in colour. 2.^ Measures 31-43μm in diameter. 3.^ The thin, outer transparent shell, when present, represents theremnant of the yolk mass; it causes the eggs to clump together. 4.^ The inner embryophore is brown,thick walled and radially striated. 5.^ It contains an oncosphere(14 to20μm in diameter) with 3 pairs ofhooklets. 6.^ Does not float in saturated solution of common salt. 7.^ Eggs are resistant and may remain viable for 8 weeks. 8.^ Eggs are infective to pig as well as to man.
-^ The common name is beef tapeworm;the unarmed tapeworm of man. •^ It is worldwide in distribution. •^ In India, it is particularly prevalent amongst Mohammedans. •^ But is not generally found amongst Hindu community who do not as arule eat beef. •^ Adultworm lives in the small intestine of man.
-^ Morphology-
Adult worm
-^ It is white and semitransparent,measuring 5 to 10 meters in length butit may be upto 24 metres. •^ The scolex measure 1 to 2 mm in diameter, is quadrate in outline andhas 4 circular suckers. •^ The head is not provided with any rostellum or hooklets. •^ Adult worm moves against the peristaltic movement in the host’sintestine.
-^ The neck is fairly long and narrow. It is fragile. •^ Proglottides- The number varies 1,000 to 2,000. •^ The length of a gravid segment is 3 to 4 times its breadth. •^ When relaxed, the terminal gravid segment measures about 2 cms inlength by 0.5 cm in breadth. •^ The gravid segments are expelled singly and may force their waythrough the anal sphincter often showing great activity outside.
-^ The life span of the adult worm is considerable, it may live forupwards of 10 years. •^ Eggs – As there is no uterine opening , the eggs are liberated by therupture of ripe proglottides. •^ Eggs are infective to cattle only. •^ Rest of the characterstics of the egg are same as those for T.solium.
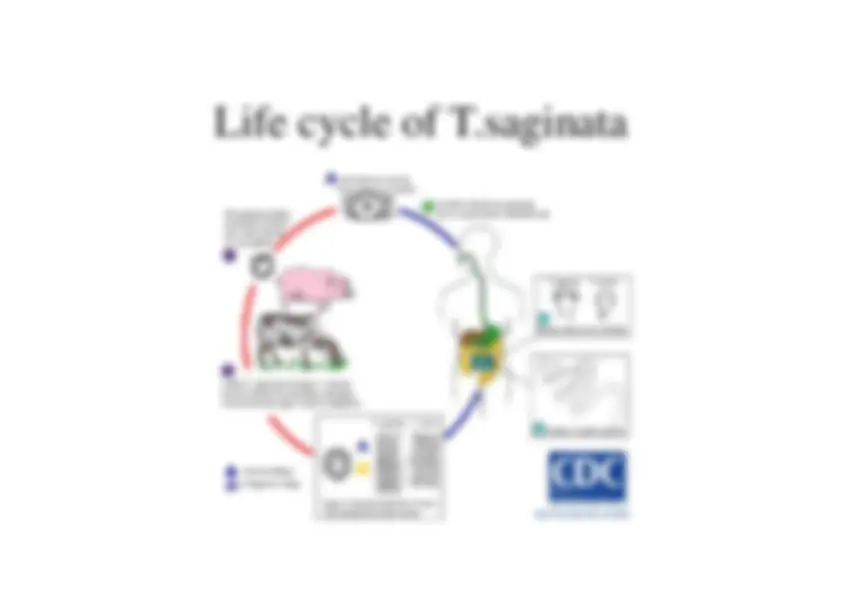
-^ Life cycle of T.saginata
-The worm passes its life cycle in two hosts: 1. The definitive host:man which harbours the adult worm. 2. The intermediate host: Cattle which harbours the larval stage. • The adult worm lives in the small intestine of man. • The eggs or gravid segments are passed out with the faeces on theground. • The animals swallow these eggs while grazing in the field. • On reaching the alimentary canal of the intermediate host, theradially striated walls of the eggs rupture and oncosheres areliberated.
-^ These penetrate the gut wall with the aid of their hooks and gainentrance into the portal vessels or mesenteric lymphatics then to thesystemic circulation. •^ The naked oncospheres are filtered out from the circulating blood intothe muscular tissues. •^ Ultimately they settle down in the muscular tissue and undergoesfurther development. •^ The oncospheres lose their hooks on reaching their destination. •^ It takes about 60 to 70 days for the oncospheres to metamorphose intothe cysticercus stage.