





















































































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An in-depth analysis of the shareholder rights, industrial partner profits and losses, and corporate structures in stock corporations. It covers topics such as the use of misleading names, parent/holding and subsidiary corporations, share types, and the process of issuing and transferring shares. It also discusses the minimum capital stock not required of stock corporations, the power to invest in shares of other corporations, and the declaration and issuance of dividends.
Typology: Slides
1 / 210

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!





























































































- 1. Consensual – there must be meeting of minds. - 2. Nominate – it has name/designation. - 3. Bilateral/Multilateral – there must be 2/more persons. - 4. Onerous – the services/business of partnership has something in return; it is not gratuitous in character.
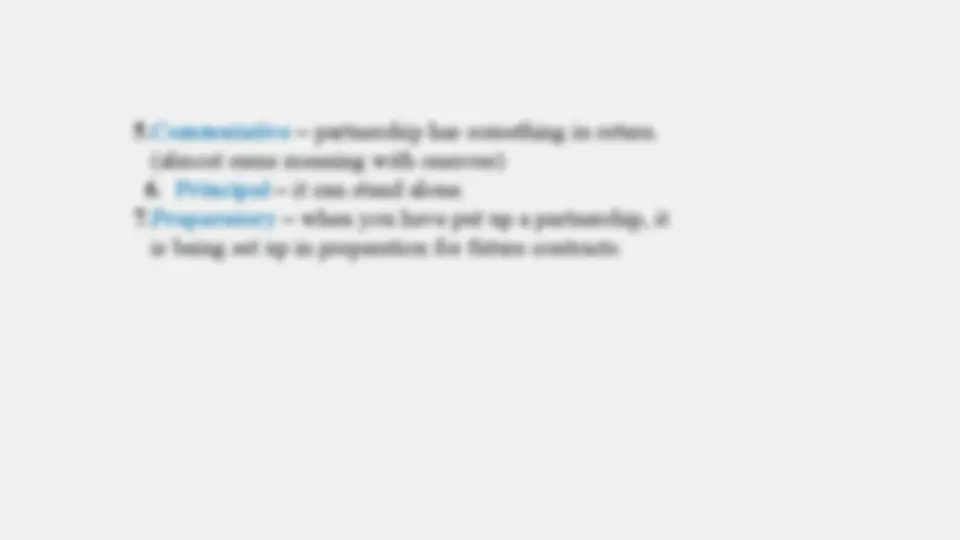
5.Commutative – partnership has something in return. (almost same meaning with onerous)
6. Principal – it can stand alone. 7.Preparatory – when you have put up a partnership, it is being set up in preparation for future contracts.
whom he wants to be associated with in partnership.
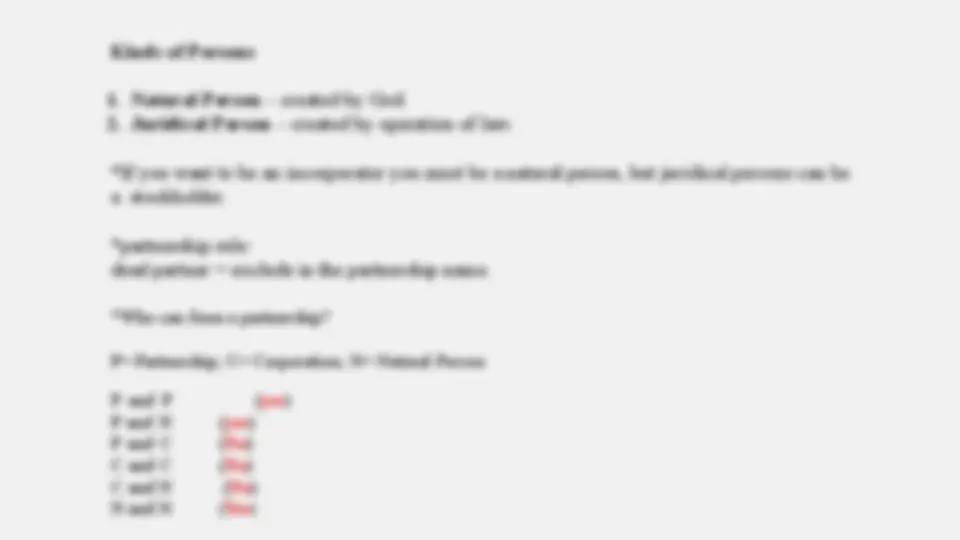
Kinds of Persons
1. Natural Person – created by God. 2. Juridical Person – created by operation of law.
*If you want to be an incorporator you must be a natural person, but juridical persons can be a stockholder.
*partnership rule: dead partner = exclude in the partnership name.
*Who can form a partnership?
P= Partnership; C= Corporation; N= Natural Person P and P ( yes ) P and N P and C C and C C and N N and N
( yes ) ( No ) ( No ) ( No ) ( Yes )
Under Art 1772
Partnership still acquires personality despite failure to comply with the requirements of execution of public instrument and registration of name in SEC.
Under Arts 1773 and 1775
Partnership with immovable property contributed, if without requisite inventory, signed and attached to public instrument, shall not acquire any juridical personality because the contract itself is void. This is also true for secret associations or societies.
3.The sharing of gross returns does not of itself establish a partnership, whether or not the persons sharing them have a joint or common right or interest in any property from which the returns are derived.
4.The receipt by a person of a share of the profits of a business is prima facie evidence that he is a partner in the business, but no such inference shall be drawn if such profits were received in payment:
a. As a debt by installments or otherwise.
b. As wages of an employee or rent to a landlord.
c. As an annuity to a widow or representative of a deceased partner.
d. As interest on a loan, though the amount of payment vary with the profits of the business.
e.As the consideration for the sale of a goodwill of a business or other property by installments or otherwise.
Effects of an unlawful partnership
- Art. 1771. A partnership may be constituted in
- ART 1173.
three thousand pesos or more (P3000 or more)
Exchange Commission (SEC).
partnership & members to the 3rd persons.
Art 1773.
- Where immovable property contributed, failure to comply w/ the following requisites will render the partnership contract void: