



Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
some first year nursing notes, might have inacuracies
Typology: Lecture notes
1 / 7

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!





On special offer
Consists of:
Occurrence in blood (per mm3) 4-6 million Cell anatomy Salmon- colored biconcave disks; anucleate; literally, sacs of hemoglobin; most organelles have been ejected Function Transport oxygen bound to hemoglobin molecules; also transport small amount of carbon dioxide Cell type Leukocytes (white blood cells, or WBCs) Occurrence in blood (per mm3) 4000-11, Granulocytes Cell type Neutrophils Occurrence in blood (per mm3) 3000- (40- 70% of WBCs) Cell anatomy Cytoplasm stains pale pink and contains fine granules, which are difficult to see; deep purple nucleus consists of three to seven lobes connected by thin strands of nucleoplasm Function Active phagocytes; number increase rapidly during short- term or acute infections Cell type Eosinophils Occurrence in blood (per mm3) 100- (1-4% of WBCs) Cell anatomy Red coarse cytoplasmic granules; figure- or bilobed nucleus stains blue- red Function Kill parasitic worms; increase during allergy attacks; might phagocytize antigen- antibody complexes and inactivate some inflammation chemicals Cell type Basophils Occurrence in blood (per mm3) 20- 50 (0-1% of WBCs) Cell anatomy Cytoplasm has a few large blue- purple granules; U- or S- shaped nucleus with constrictions, stains dark blue Function Granules contain histamine (vasodilator chemical), which is discharged at sites of inflammation Agranulocytes Cell type Lymphocytes Occurrence in blood (per mm3) 1500- (20-45% of WBCs) Cell anatomy Cytoplasm pale blue and appears as thin rim around nucleus; spherical (or slightly indented) dark purple- blue nucleus Function Part of immune system; one group (B lymphocytes) produces antibodies; other group (T lymphocytes) involved in graft rejection, fighting tumors and viruses, and activating B lymphocytes Cell type Monocytes Occurrence in blood (per mm3) 100- (4-8% of WBCs) Cell anatomy Abundant gray-blue cytoplasm; dark blue- purple nucleus often kidney-shaped Function Active phagocytes that become macrophages in the tissues; long- term “clean- up team”; increase in number
A condition in which the oxygen-carrying capacity of blood is reduced due to decreased RBC or low hemoglobin a. Iron deficiency anemia b. Megaloblastic anemia
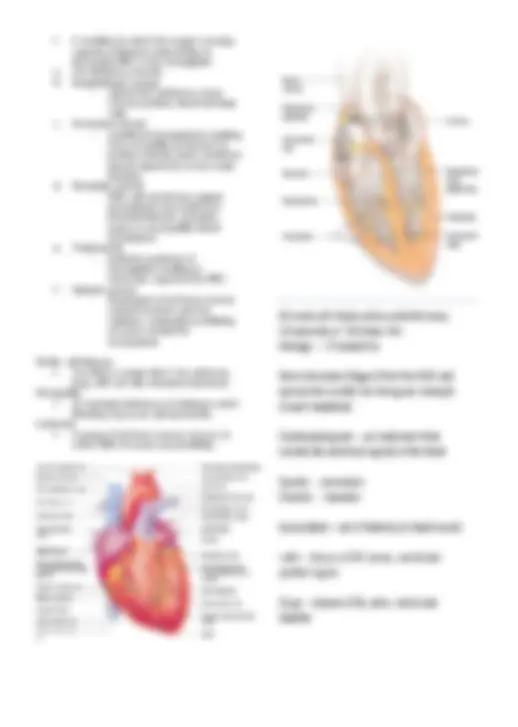
Abnormal conditions Tachycardia - elevated beating of the heart Bradycardia - slow beating of the heart Arryhythmia - irregular heart beat Congestive heart failure - loss of pumping efficiency by the heart Ischemia - reduced blood flow to the myocardium Angina pectoris - severe pain that usually accompanies ischemia Myocardial infarction - complete obstruction to blood flow in a coronary artery Rheumatic fever - acute systemic inflammatory disease after Streptococcal infection Cardiomegaly - enlargement of the heart Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) A printout recording of the electrical activity of the heart Echocardiography Using ultra high frequency sound waves (beyond human hearing), similar to “sonar,” to form an image of the inside of the heart. This procedure can demonstrate valve damage, congenital (before birth) defects and other abnormalities
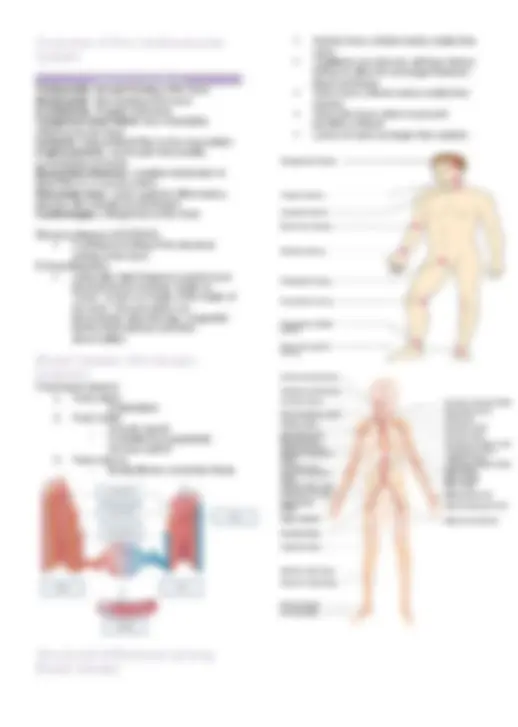
Three layers (tunics)
Arteries have a thicker tunica media than veins Capillaries are only one cell layer (tunica intima) to allow for exchanges between blood and tissue Veins have a thinner tunica media than arteries Veins also have valves to prevent backflow of blood Lumen of veins are larger than arteries
macrophages- help clear out debris of dead and dying cells Lymph nodes- bean- shaped located along lymph vessels, functions as a type of filter Spleen- a large single mass of lymph tissue located in the left hypochondriac region between the stomach and diaphragm contains T cells and macrophages. It also stores platelets and produce blood cells during fetal life
Ability to resist damage from foreign substances Innate Immunity First line of Defense Skin and mucous membranes, lysozyme from tears and saliva, urine Second line of Defense