








































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
MPLS overview,MPLS Concepts and Label assignment and distribution
Typology: Lecture notes
Uploaded on 09/27/2017
1 / 66

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!



























































V1.
(^) MPLS overview (^) MPLS Concepts (^) LSRs and labels (^) Label assignment and distribution (^) Label Switch Paths (^) Loops and TTL (^) LDP overview (^) Day in the Life of a Packet
(^) MPLS is developed by integrating IP switching protocols of different manufactures (^) IP Switching (Ipsilon) (^) Tag Switching (Cisco) (^) Aggregate RouteBased IP Switching (IBM) (^) Cell Switch Router (Toshiba) IP Navigator (Ascend)
(^) MPLS is developed by the combination of ATM and IP at 1990s. In 1996 , Ipsilon proposed IP switching protocol which solve the problem of better supporting IP on ATM switch, this makes an ATM switch a router and at the same time having the high performance of an ATM switch , breaking the performance bottleneck on the router (can not achieve wire speed on POS3,POS12)
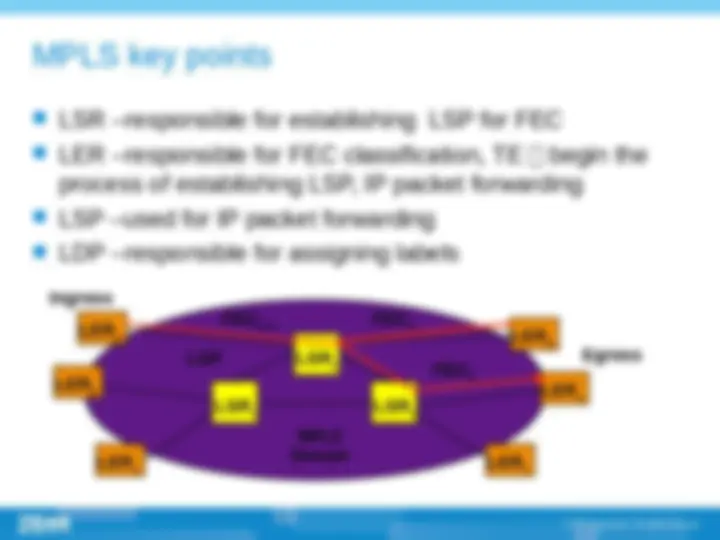
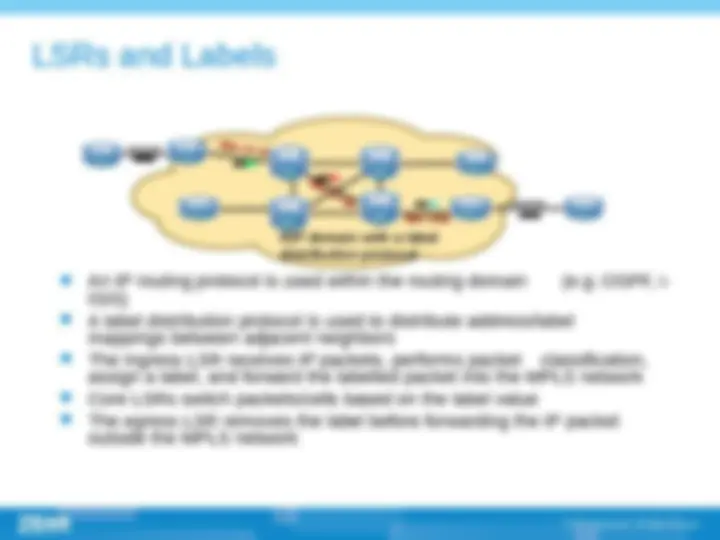
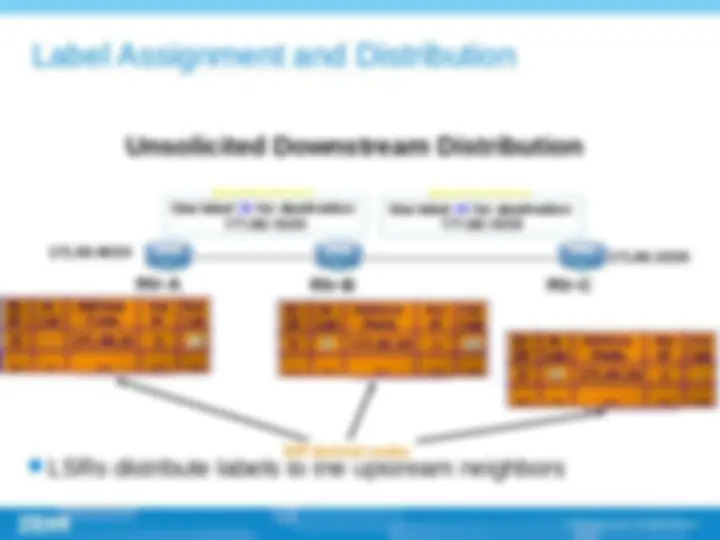
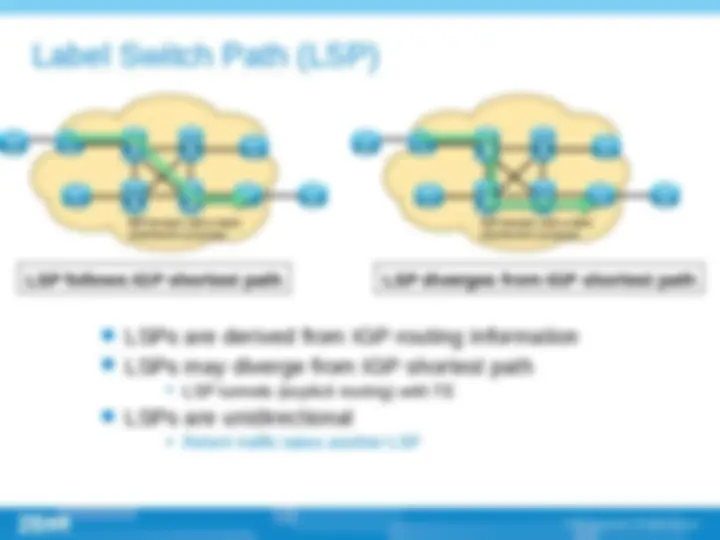
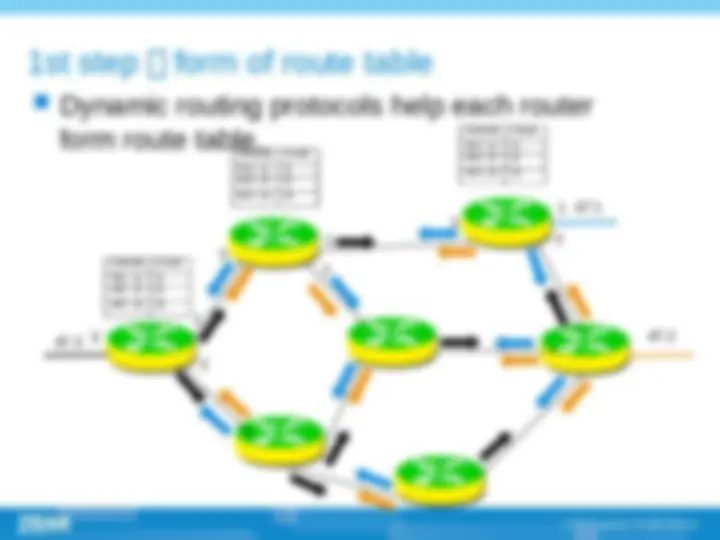
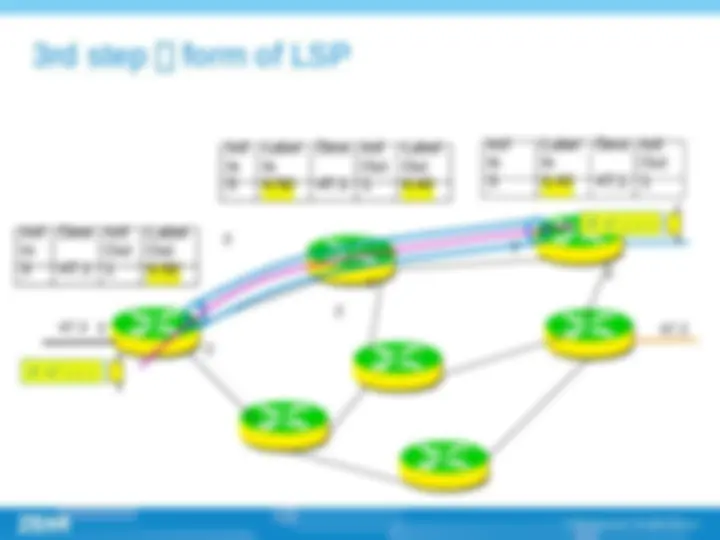
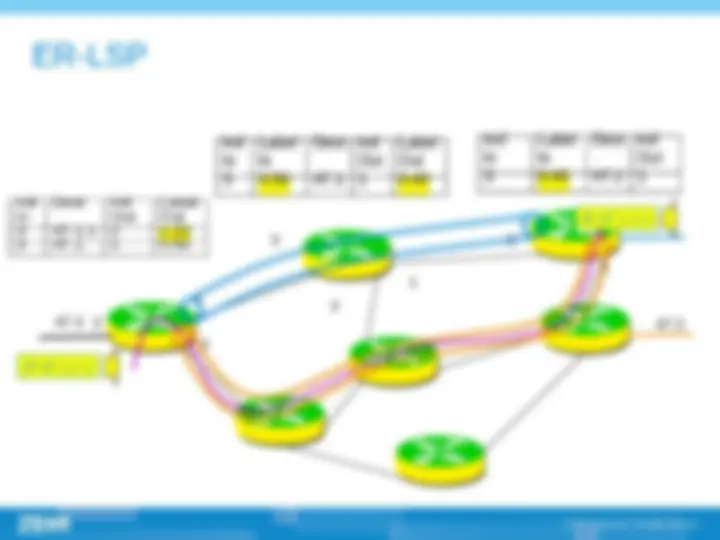
(^) Multi-protocol label switch (^) Label is at the layer 2.5, between link layer and network layer. This technology have the advantage of layer 2 switching and layer 3 routing. (^) The successful point of MPLS technology is that it introduced connection-oriented mechanism into IP network; (^) Core idea of MPLS is , routing on the edge and switching on the core part (^) Establishing of LSP , label switch path ,, LSP is established by topology not by data. The establishing of LSP can be done by LDP , CR-LDP , RSVP protocols.
(^) Current core network is made up of router and ATM switch (^) Core network based on MPLS is superior than core network based on router and ATM (^) This is the developing motion of MPLS.
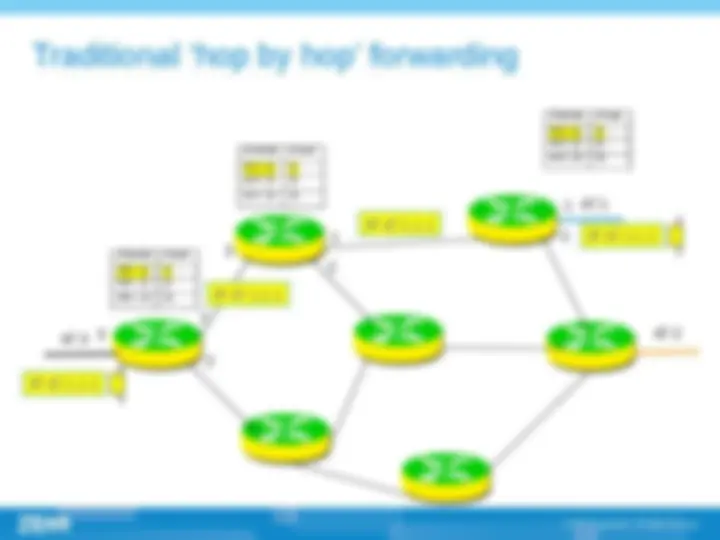
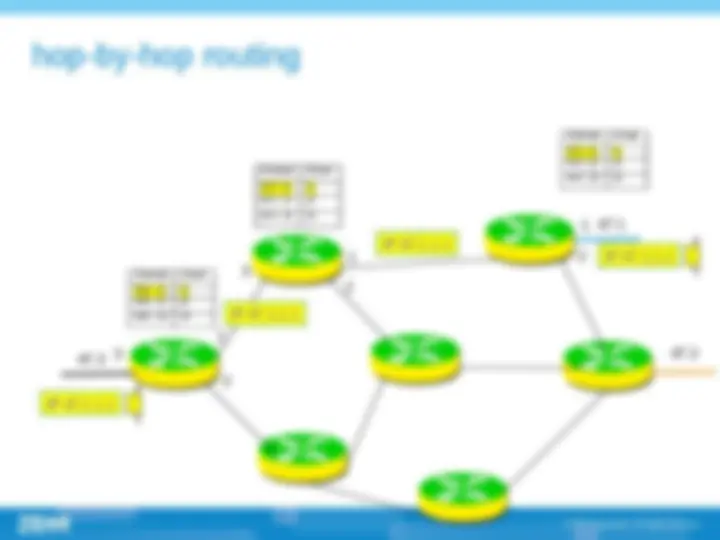
(^) Comparison of label switching and hop-by-hop forwarding based on destination IP address , (^) MPLS is implemented on switch, thus taking full advantage of high speed of switch. Traditional switch can search label and replace them, but can not analyze network header or at least not fast enough to analyze it, so it is difficult to implement forwarding based on network header information on traditional switch When packet comes into MPLS network, ingress router will decide which FEC it belongs to, it can use any information about the packet not only the network layer information. , for example the port information ,
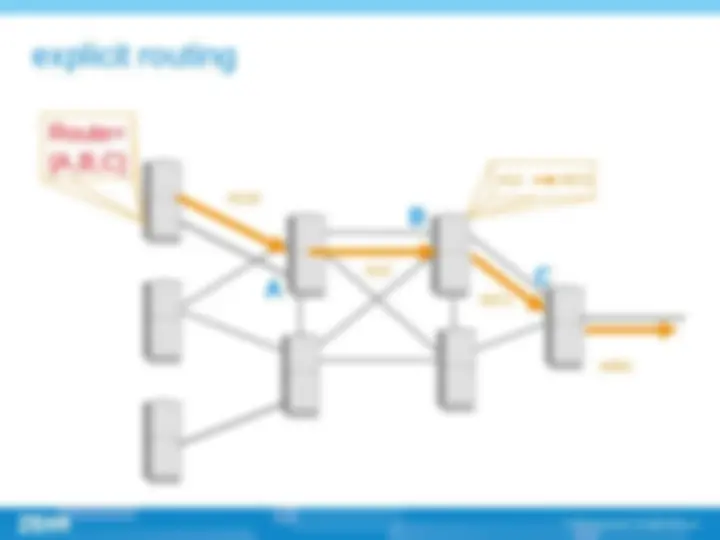
(^) MPLS can assign different labels to packet coming from different routers, thus making it easy to implement routing based on ingress routers. Because ingress router id can not be sent with the packet , so traditional routing patterns do not support this function. (^) Sometimes it is reasonable to designate a predefined route for the packets than hop-by-hop routing.
(^) Unlike IP, classification/label can be based on: Destination Unicast address Traffic Engineering VPN QoS (^) FEC: Forwarding Equivalence Class (^) A FEC can represent a: Destination address prefix, VPN, Traffic Engineering tunnel, Class of Service.
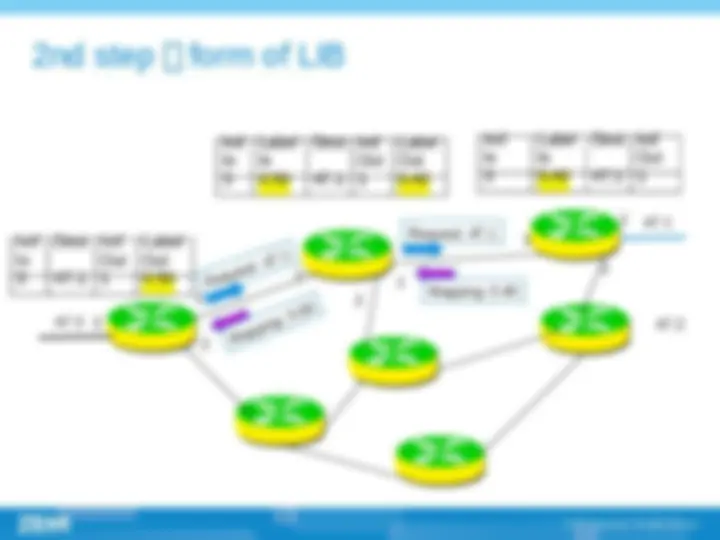
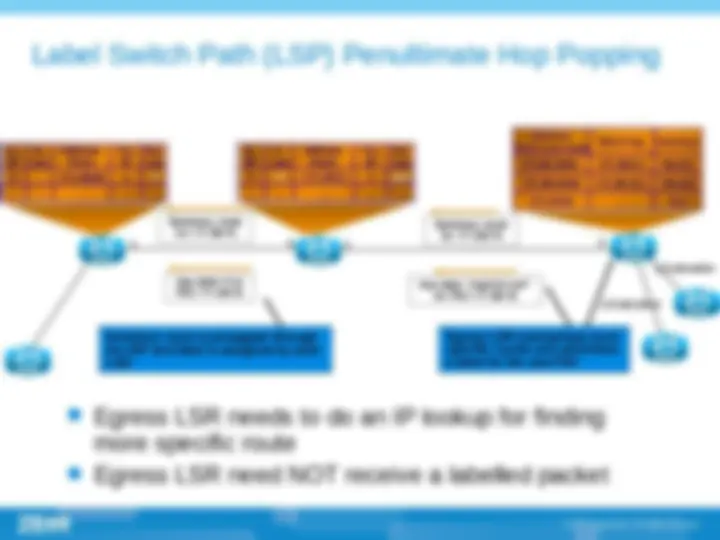
(^) Label (^) FEC (Forwarding equivalence class) (^) LSR (Label switching router) (^) LER (Label edge router) (^) LSP (Label switching path) (^) LDP (Label distribution path)
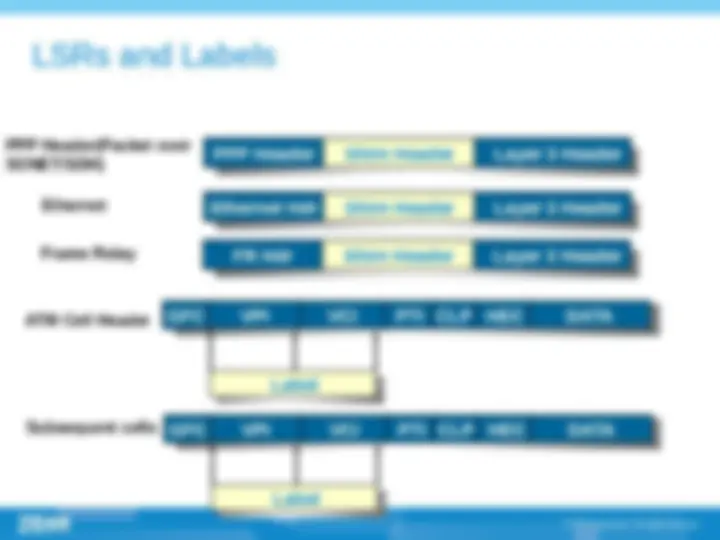
(^) MPLS label is an integer ranged between 0 to 1048575,it is used to identify specific FEC. (^) This label is encapsulated in layer 2 header.
(^) Two or more MPLS labels, encapsulated after link layer header and before network header. (^) Top label in the stack appear earliest. (^) Network layer header follow the last label in the stack
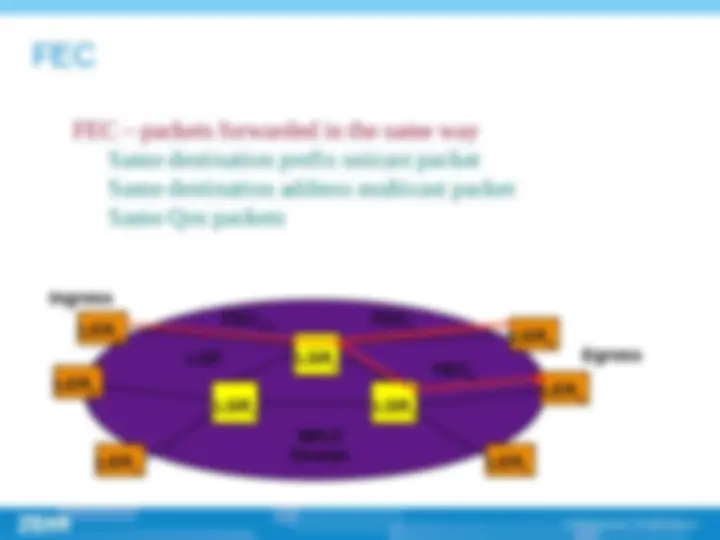
(^) Forwarding Equivalence Class (FEC) , A group of packets that have common attributes. These packets will be forwarded in the same way by LSR in the MPLS network , just because they are forwarded in the same way they are equivalence.
FEC – packets forwarded in the same way Same destination prefix unicast packet Same destination address multicast packet Same Qos packets MPLS Domain LERa LSRy LERb LERc LERd LERe LERf LSRx LSRz LSP Ingress Egress FECp FECq FECp+q