













Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Kohlberg's Moral Development Theory
Typology: Slides
1 / 22

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!















Quick Facts
Born : October 25, 1927 (Bronxville, New York)
(^) Died : January 17, 1987 (aged 59) (Boston, Massachussets)
(^) Subjects of Study:
A Jewish American Psychologist^ Child Development
WORDS TO REMEMBER
Moral is a lesson that is learn from
something
Morality principles concerning the
distinction between right and wrong or good and bad behavior.
The Heinz Dilemma
Question:Question:
YES NO
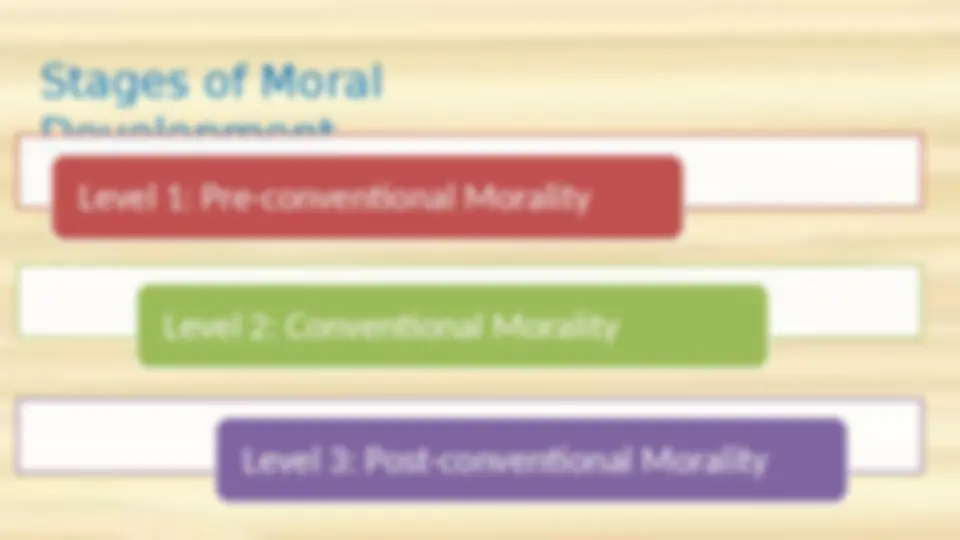
Sub-stages of Moral Development
How advance is your moral reasoning?
A. (^) B. C.
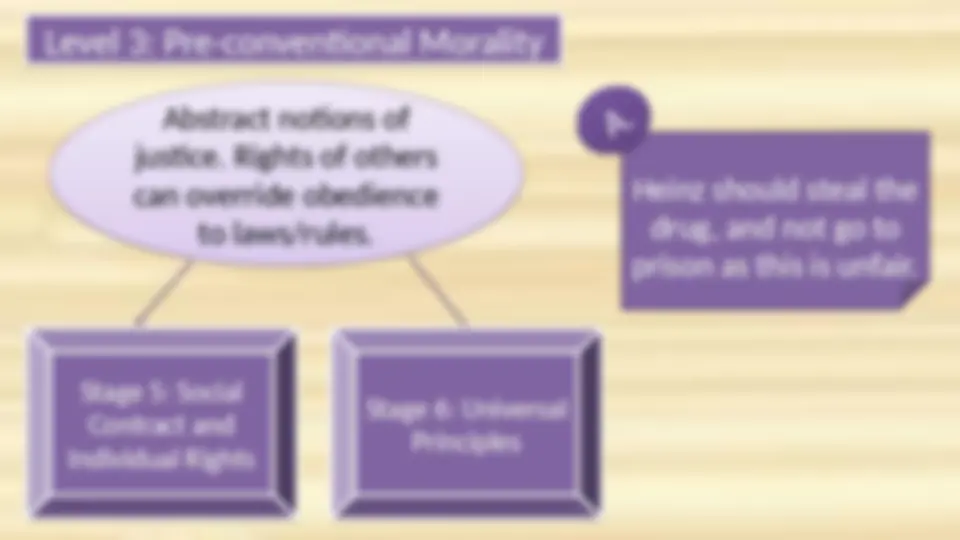
Heinz should steal the drugs and not go to prison as this is unfair.
Heinz should not steal the drugs, since he would be breaking the law.
Heinz should steal the drug and accept any prison sentence.
Choose one^ Choose one
Children desire to obey rules and avoid being punished, if they are punished, it gives them signal that their act is morally wrong.
Children desire to obey rules and avoid being punished, if they are punished, it gives them signal that their act is morally wrong.
Example: A young girl or boy is on her/his best behaviour at the mall to avoid beaten up by his mother or father.
Example: A young girl or boy is on her/his best behaviour at the mall to avoid beaten up by his mother or father.
Children act like give and take strategy, In this stage, children take some incentives return to do work.
Children act like give and take strategy, In this stage, children take some incentives return to do work.
Example: A child studies hard knowing that his/her parents will give him/her a present if he/she pass the exam.
Example: A child studies hard knowing that his/her parents will give him/her a present if he/she pass the exam.
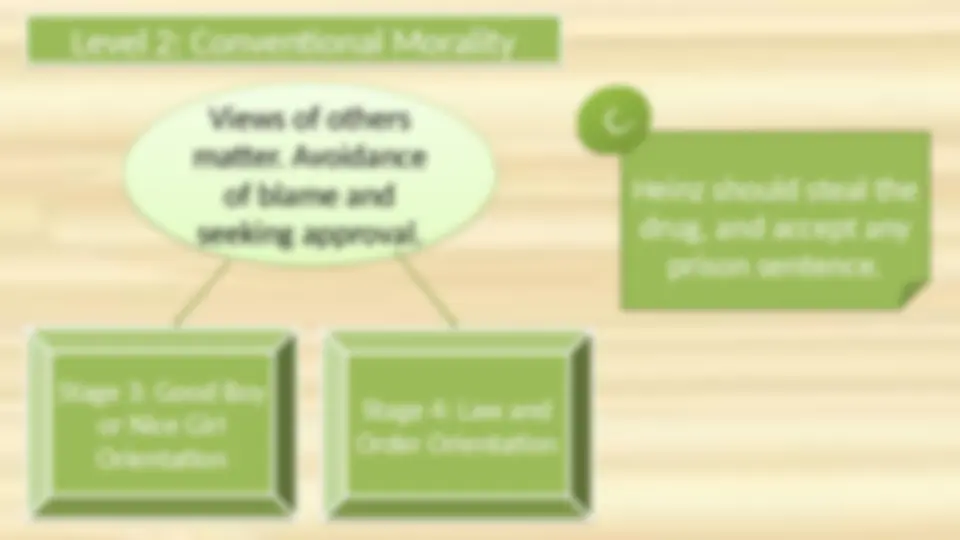
People want to be praised and want to be seen as a good boy or nice girl by others. People want to attain good social status and recognition.
People want to be praised and want to be seen as a good boy or nice girl by others. People want to attain good social status and recognition.
Example: A child does not talk to his classmates during the test because his teacher doesn’t like it.
Example: A child does not talk to his classmates during the test because his teacher doesn’t like it.
People become aware of wider rules of society and follow the law to avoid guilt.
People become aware of wider rules of society and follow the law to avoid guilt.
Example: If you drink and drive, you are endangering the lives of others on the road, not just yourself.
Example: If you drink and drive, you are endangering the lives of others on the road, not just yourself.
Some people think that rules are good for human beings but sometime they should disobeyed, depending on the situation and interest of an individual.
Some people think that rules are good for human beings but sometime they should disobeyed, depending on the situation and interest of an individual.
Example: People are protesting against abortion whether to legalize it or not.
Example: People are protesting against abortion whether to legalize it or not.
People develop their own guidelines and these laws sometimes fit and sometimes do not fit with the law.
People develop their own guidelines and these laws sometimes fit and sometimes do not fit with the law.
Example: Some people refuse to obey a law which treats a large portion of the population as second class citizens.
Example: Some people refuse to obey a law which treats a large portion of the population as second class citizens.