















































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
A comprehensive lecture on the structure of crystalline solids, focusing on metals. It covers topics such as crystal structure, crystallographic points, directions, and planes, crystalline and non-crystalline materials, and metallic crystal structures like fcc, bcc, and hcp. The lecture also discusses atomic packing factor, density computation, and the relationship between crystallographic directions and planes to atomic linear and planar densities. Exercises and examples using matlab for calculations and visualizations.
Typology: Summaries
1 / 65

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!


























































Page 1
International University
National University – HCMC
Dr. Nguyen Dinh Uyen
Page 2
The Structure of Crystalline Solids
Dr. Uyen Nguyen
Page 4
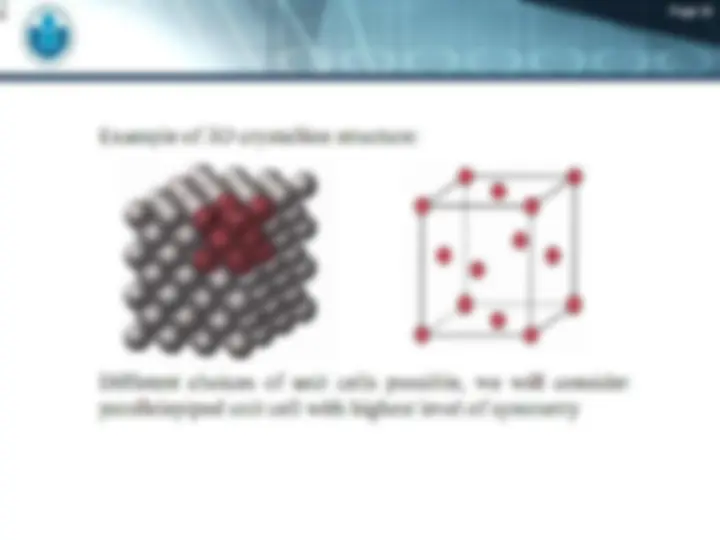
Crystal Structure
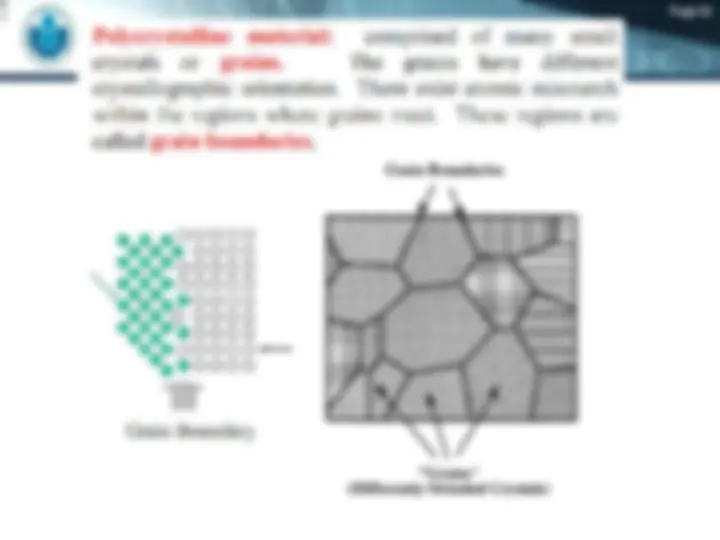
(^) A crystalline material is one in which the atoms are situated in a repeating or
periodic array over large atomic distances;
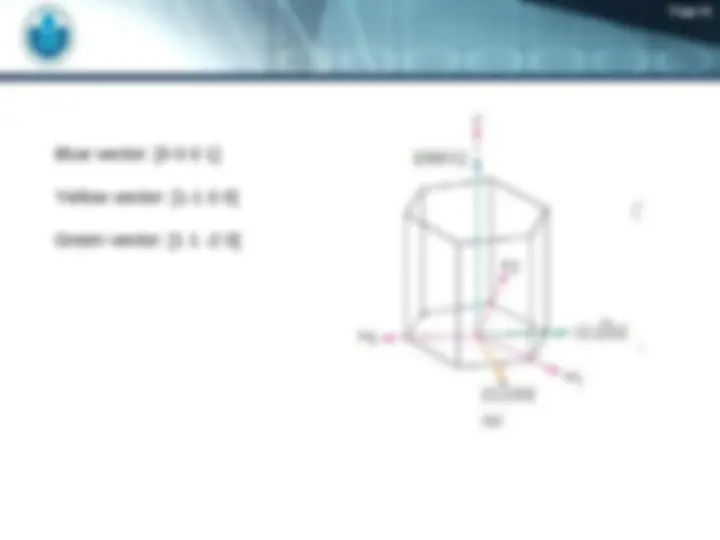
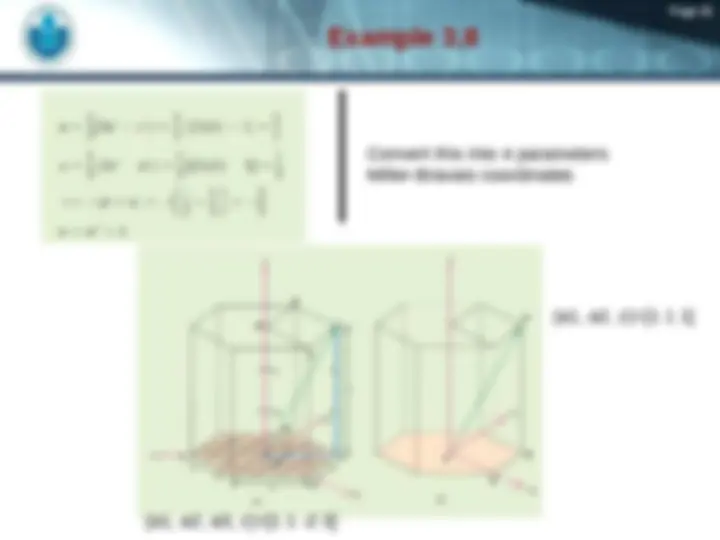
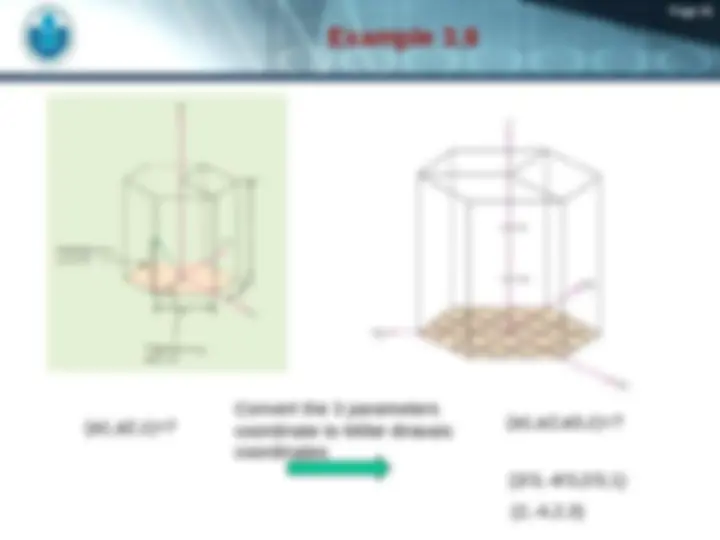
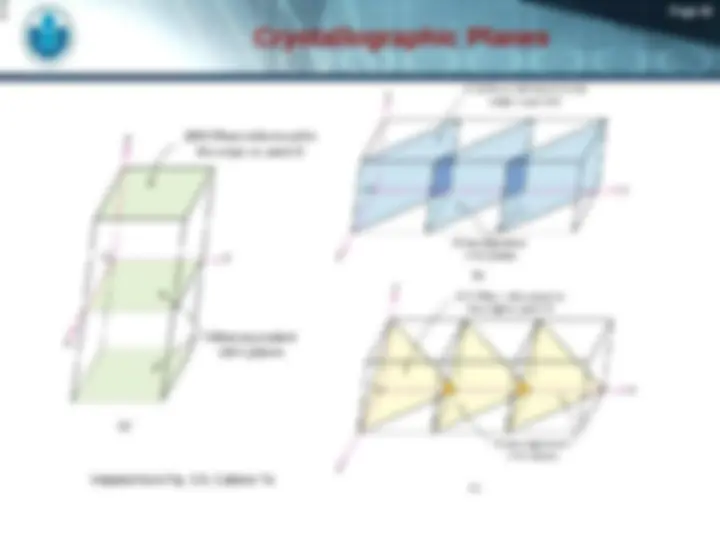
(^) Crystallographic Points, Directions, and Planes
(^) A specific points, direction, and planes of the crystal.
(^) Crystalline and Non-crystalline Material
(^) Explore different type of crystalline and non-crystalline materials
Page 7 7
Page 8 8
Crystalline materials... -metals -many ceramics -some polymers
Noncrystalline materials... -complex structures -rapid cooling crystalline SiO 2 "Amorphous" = Noncrystalline noncrystalline SiO^2 Adapted from Fig. 3.22(b), Callister 7e. Adapted from Fig. 3.22(a), Callister 7e. Materials and Packing Si Oxygen
Page 10 1 0
Page 11 1 1
Structures
empty space? 2-dimensions
vs. Now stack these 2-D layers to make 3-D structures https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F4Du4zI4GJ
Page 13 1 3
Page 14 1 4
radii are the same.
order to lower bond energy.
We will examine three such structures...
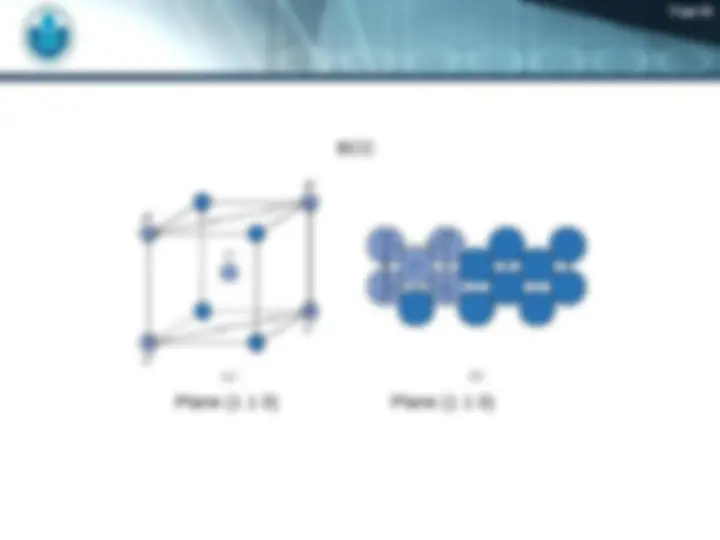
FCC – Face Centered Cubic BCC – Body Centered Cubic HCP – Hexagonal Closed Packet https:// www.youtube.com/watch?v=HC WwRh5CXYU
Page 16 1 6
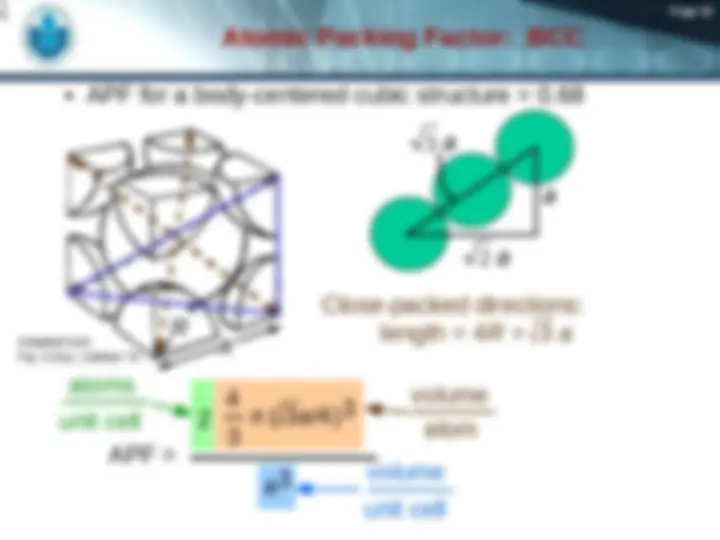
maximum achievable APF
4 3
( 2 a /4)
atoms unit cell atom volume a
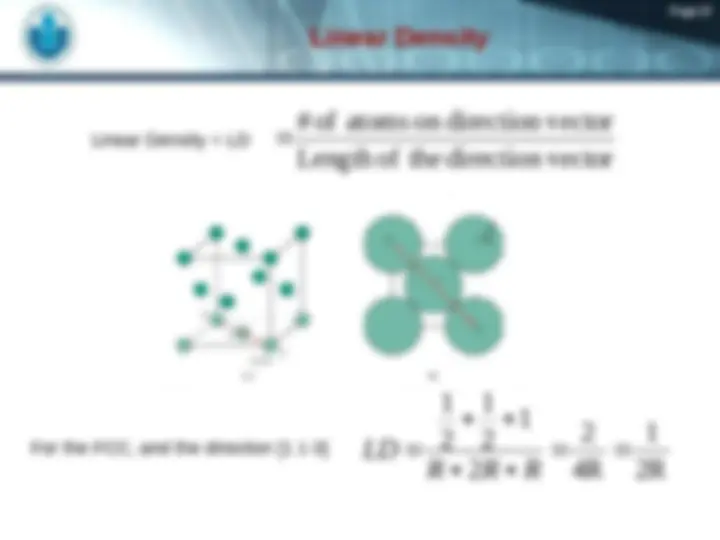
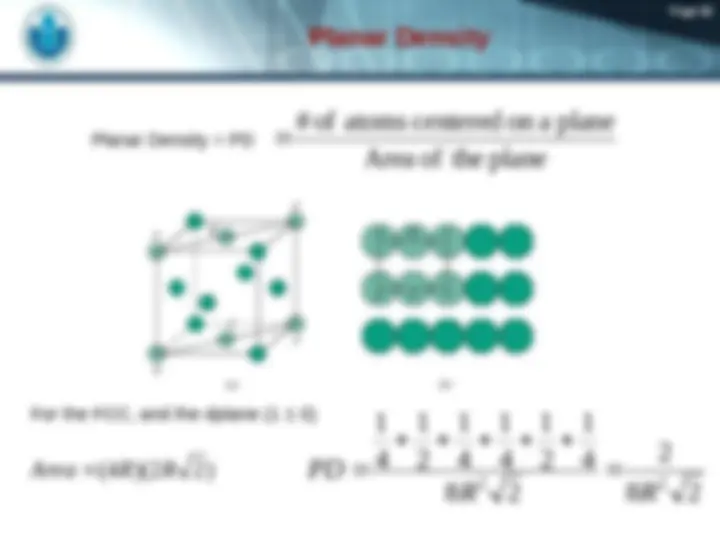
unit cell volume Close-packed directions: length = 4 R = 2 a Unit cell contains: 6 x 1/2 + 8 x 1/ = 4 atoms/unit cell a 2 a Adapted from Fig. 3.1(a), Callister 7e.
Page 17
Use Matlab to
calculate the Unit Cell
Volume for the
followings:
1- Gold
2- Iron
Page 19 1 9
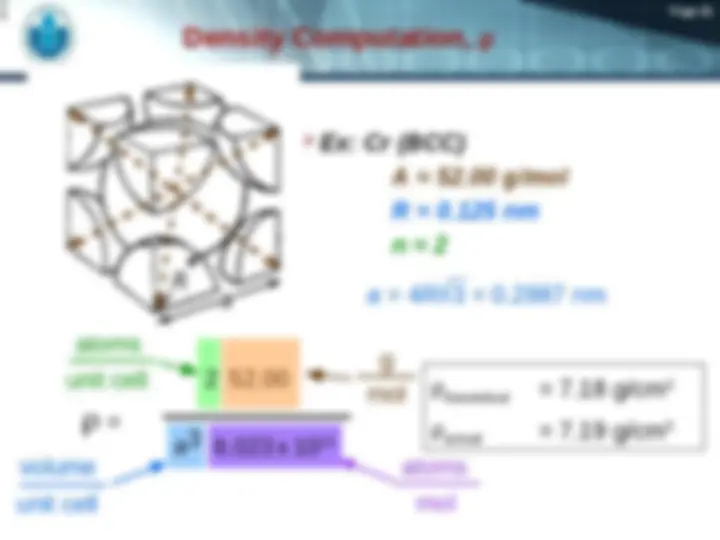
a
4 3
(^) ( 3 a /4)
atoms unit cell atom volume a
unit cell volume length = 4 R = Close-packed directions: 3 a
a
Adapted from Fig. 3.2(a), Callister 7e. 2 a 3^ a
Page 20
Calculate the
Atomic Packing
Factor for BCC
structure