Download Manufacturing Processes II: Casting Methods, Defects, and Troubleshooting and more Study notes Engineering Dynamics in PDF only on Docsity!
MANUFACTURING PROCESSES II
PROCESS CHARACTERISTICS
IN CASTING METHODS,
DEFECTS AND
TROUBLESHOOTINGS
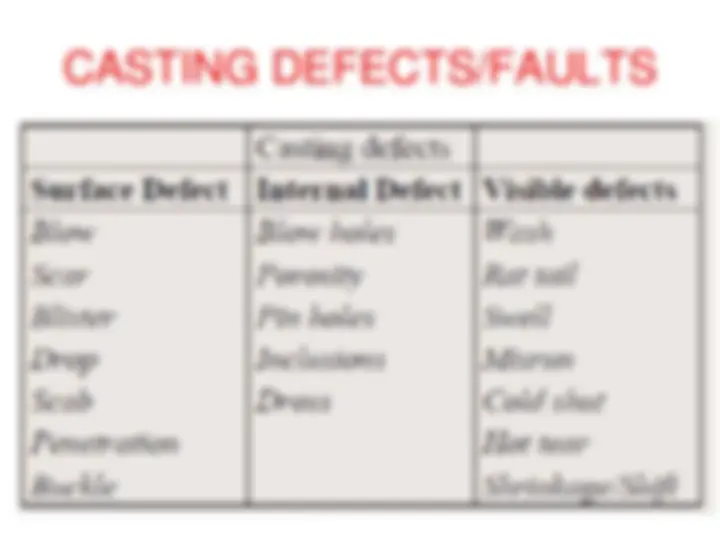
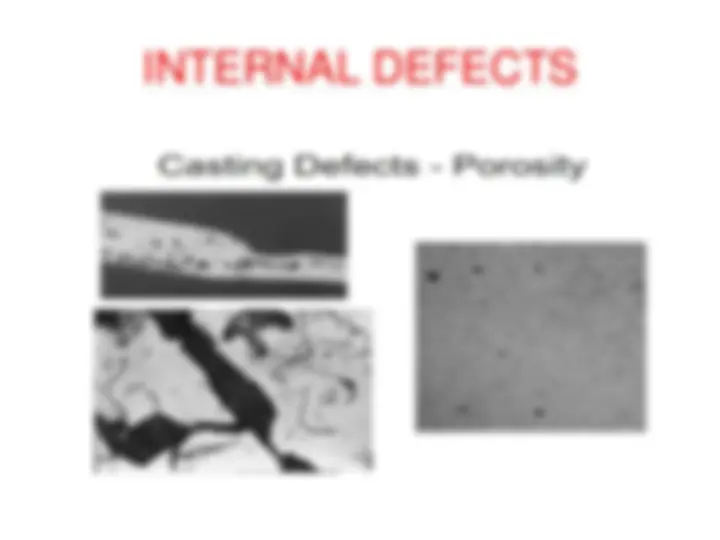
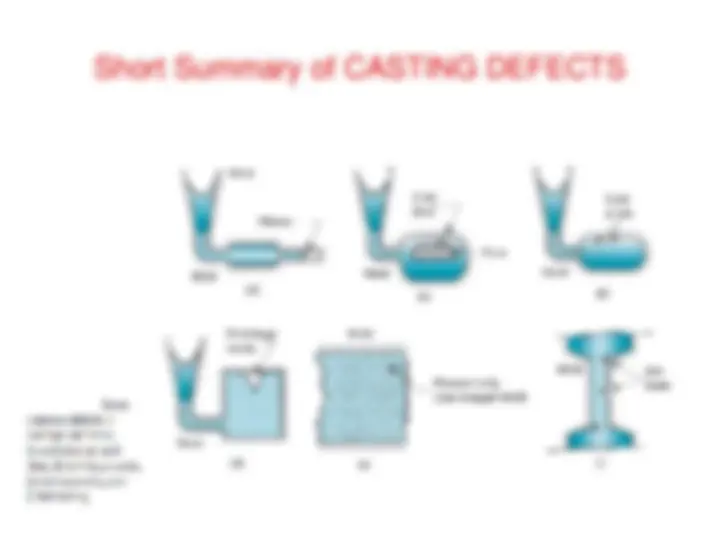
CASTING
Advantages
- Molten material can flow into very small sections so that intricate shapes can be made by this process. As a result, many other operations, such as machining, forging, and welding, can be minimized.
- Possible to cast practically any material: ferrous or non-ferrous.
- The necessary tools required for casting molds are very simple and inexpensive. As a result, it is the ideal process for production of a small lot.
- There are certain parts (like turbine blades) made from metals and alloys that can only be processed this way. Turbine blades: Casting + Machining.
- Size and weight of the product is not a limitation for the casting process.
Cast Products
- SAND CASTING
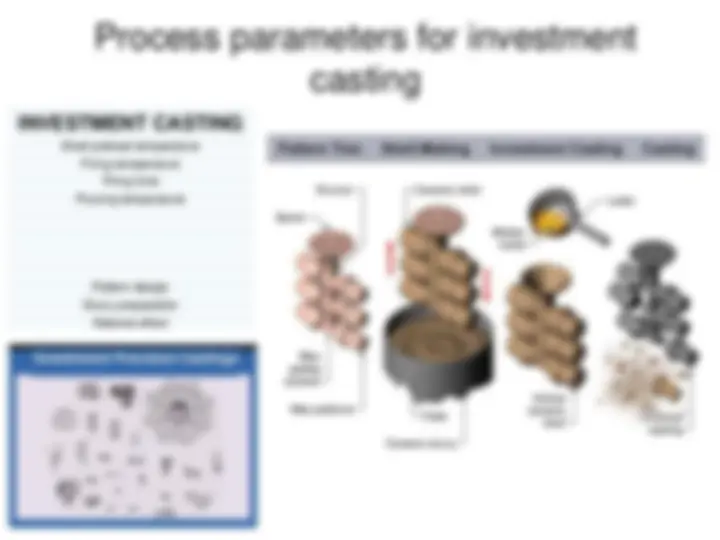
- INVESTMENT CASTING
- SHELL MOLDING
- DIE CASTING
- CENTRIFUGAL CASTING
- INGOT CASTING CASTING METHODS 14:47 5
Process parameters for sand casting
SAND CASTING
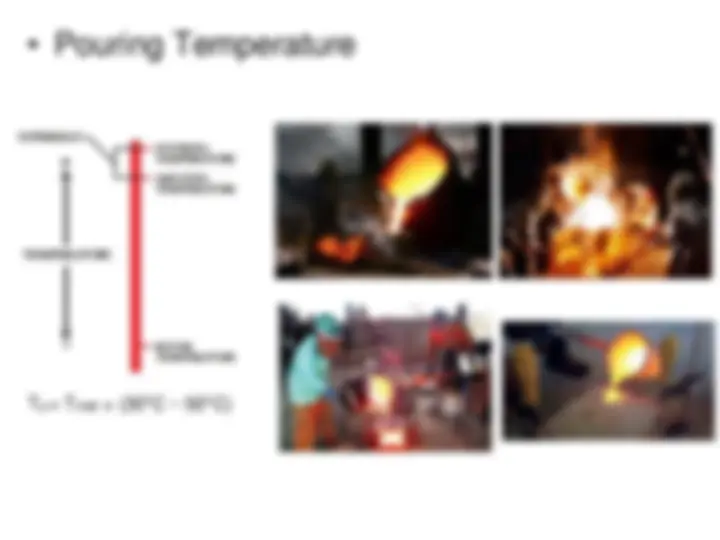
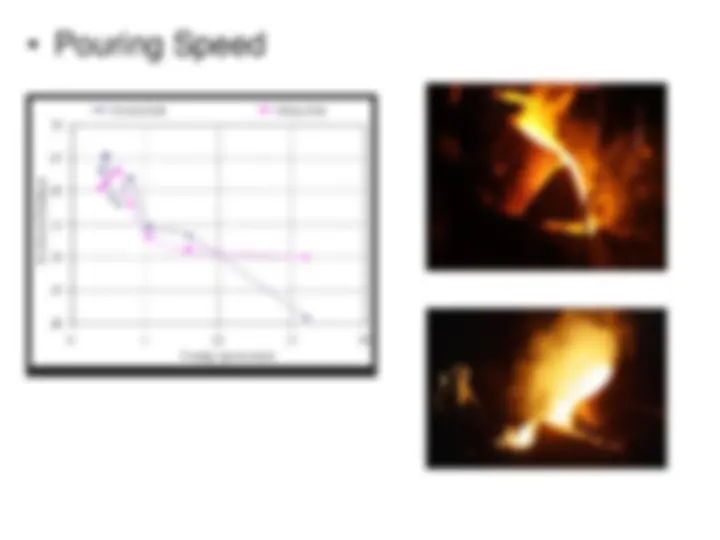
Pouring temperature Pouring speed Solidification time Mold hardness Moisture content Permeability Mold design Material effect
- Pouring Temperature Tp = Tmelt + (30°C ~ 50°C)
Problem 1: Solidification Time If the diameter (D) is 40 mm and the thickness of the casting (x) is 3 mm, please calculate the volume, surface area, and solidification time of this cylindrical casting part (C= 22 and n= 2).
- Directional solidification
Directional solidification is solidification that occurs from farthest
end of the casting and works its way towards the sprue.
The directional solidification rule is that "solidification of the
molten metal in a casting should occur in such a manner that liquid
feed metal is always available for that portion that is just
solidifying."
Another way to describe directional solidification is
that the casting should -- "cool and solidify
progressively from thin sections to heavy sections with
constant metal feed into the heavy sections."
In the figure, the heaviest section is the 2.5" diameter
center hub. The mold should be designed so that the
hub section will solidify last and have good metal feed
through the entire cooling process.
- Directional solidification
Process parameters for die casting
DIE CASTING
Pouring temperature Injection pressure Die temperature Plunger velocity Die cooling system Filling time Flow rate Die design Die surface coating Material effect
- Die Temperature
- Low die temperature produce misruns
- High die temperature results the mold erosion
- Pouring Temperature
- High pouring temperature reduces the die life
- High pouring temperature increases shrinkage problems
- High pouring temperature induces longer cycle time
- High pouring temperature increases the rate of gas
solubility in the metal