






































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
he content of "Living in the Era" would typically encompass various aspects of contemporary life, including: Societal Changes: Discussions on how society has evolved in terms of values, norms, demographics, and social structures. Technological Advancements: Exploration of the impact of technology on daily life, such as the proliferation of smartphones, social media, artificial intelligence, and automation. Cultural Trends: Examination of current cultural phenomena, including pop culture, fashion, music, art, and entertainment. Global Challenges: Coverage of global issues like climate change, pandemics, geopolitics, and economic developments shaping the present era. Lifestyle and Well-being: Insights into modern lifestyles, health and wellness trends, work-life balance, and personal development.
Typology: Slides
1 / 55

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!
















































Contents
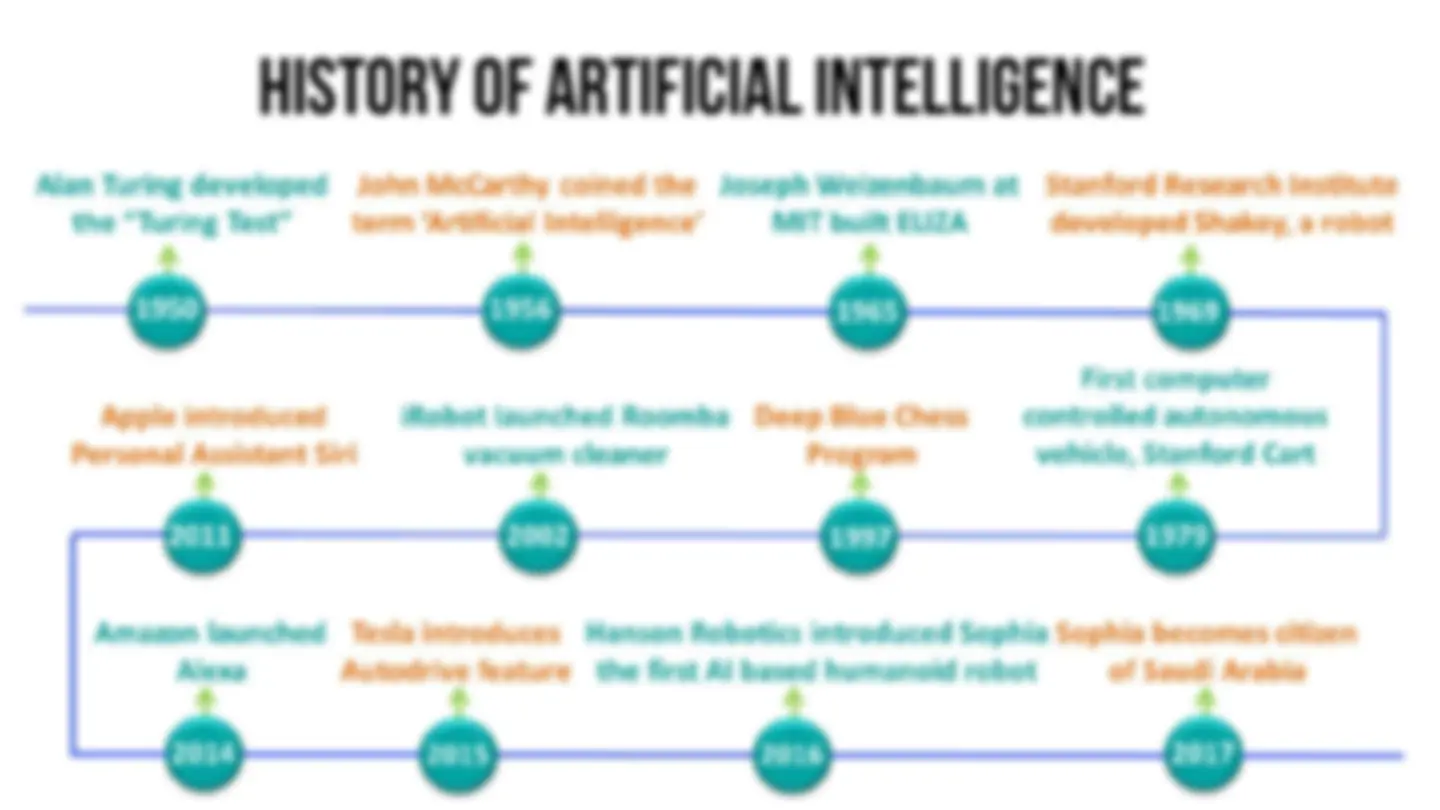
It was first coined by John McCarthy in 1956 at the Dartmouth Conference, where he defined it as " the science and engineering of making intelligent machines". What is Artificial Intelligence?
Automation is about setting up robots to follow a set of pre-defined rules. Artificial Intelligence is about setting up robots to make their own decisions (though still based on human input). AI can be used in automation, but most automation uses conventional software to transfer data from one location to another. difference between AI and automatic machine
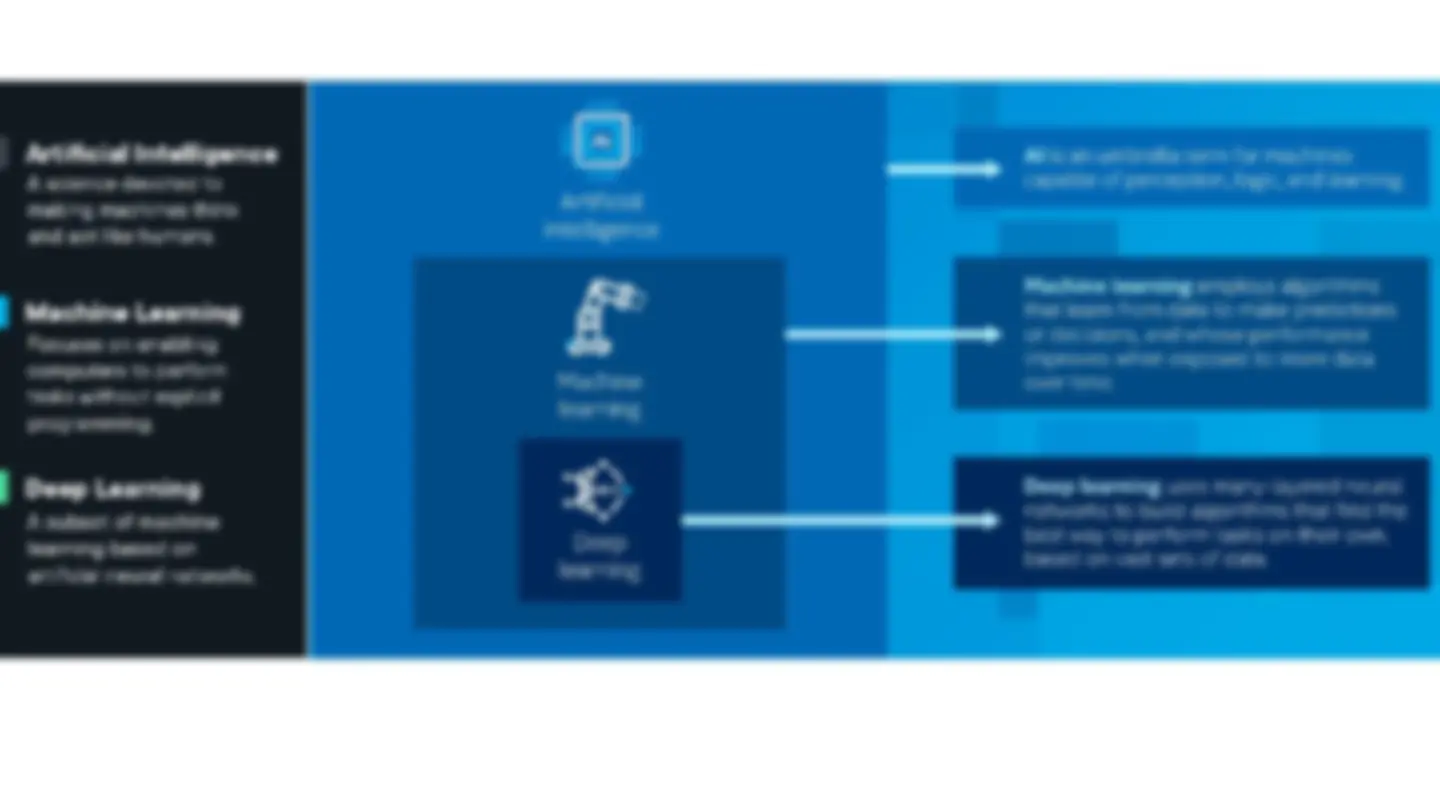
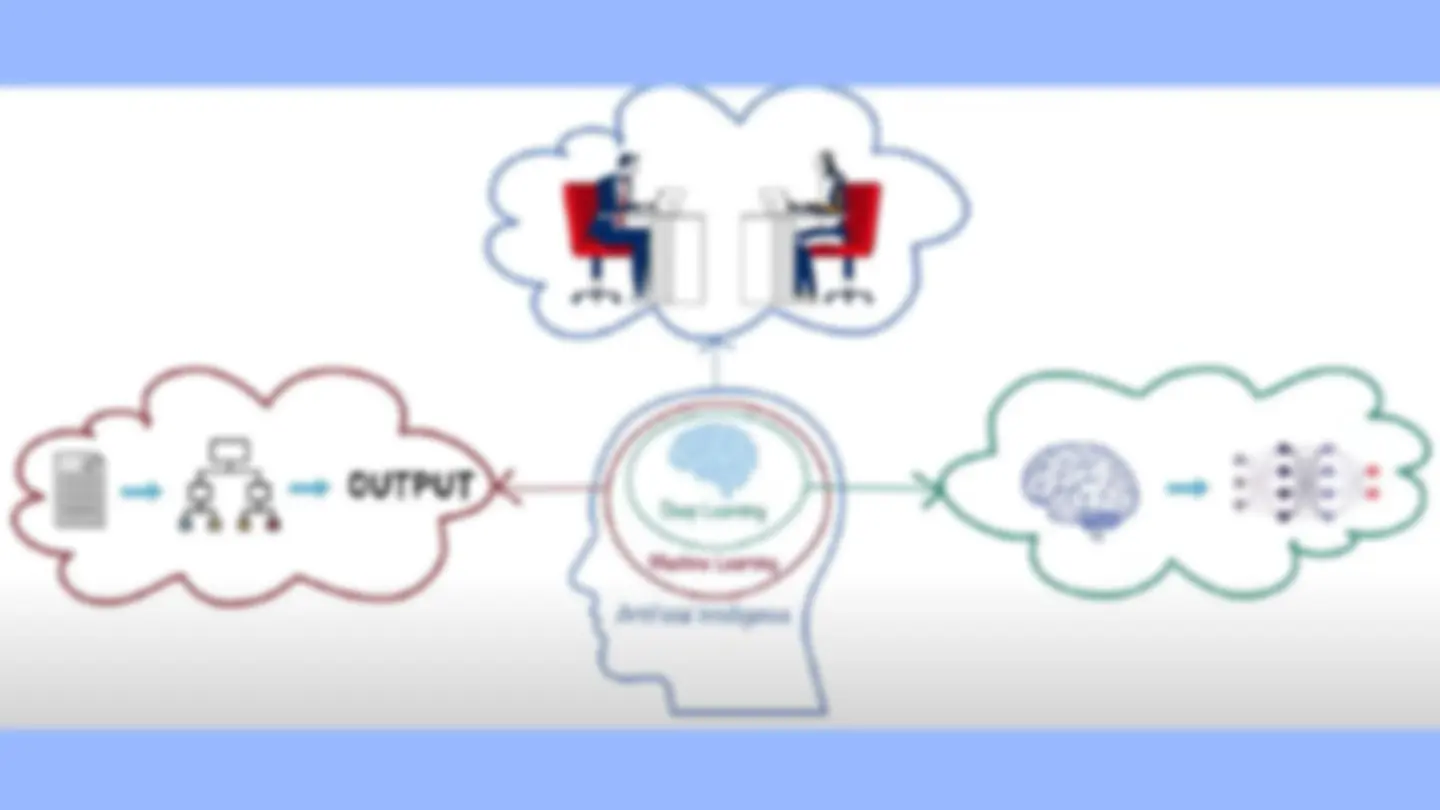
STRUCTURE OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE Kahkashan, Rehman & Ahirwar, Dr. Anamika. (2020). Depiction the Artificial Intelligence with Machine Learning. Solid State Technology. 63. 4734-4739.
In order for the software to learn automatically from patterns or features in the data, artificial intelligence (AI) combines massive amounts of data with quick, iterative processing and intelligent algorithms. AI is a broad field of study that includes many theories, methods and technologies, as well as the following major subfields: Machine Learning, and Deep Learning. HOW Artificial intelligence works
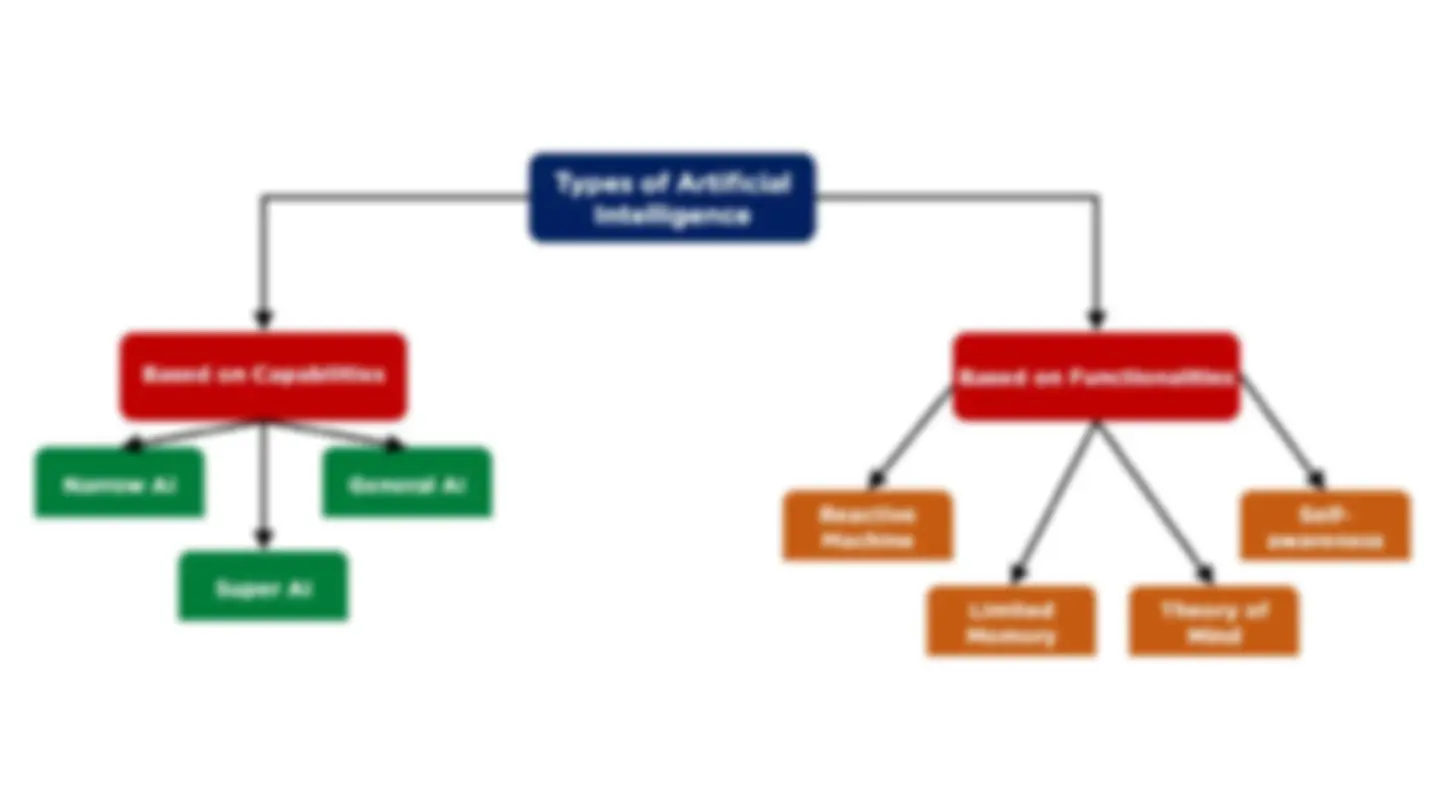
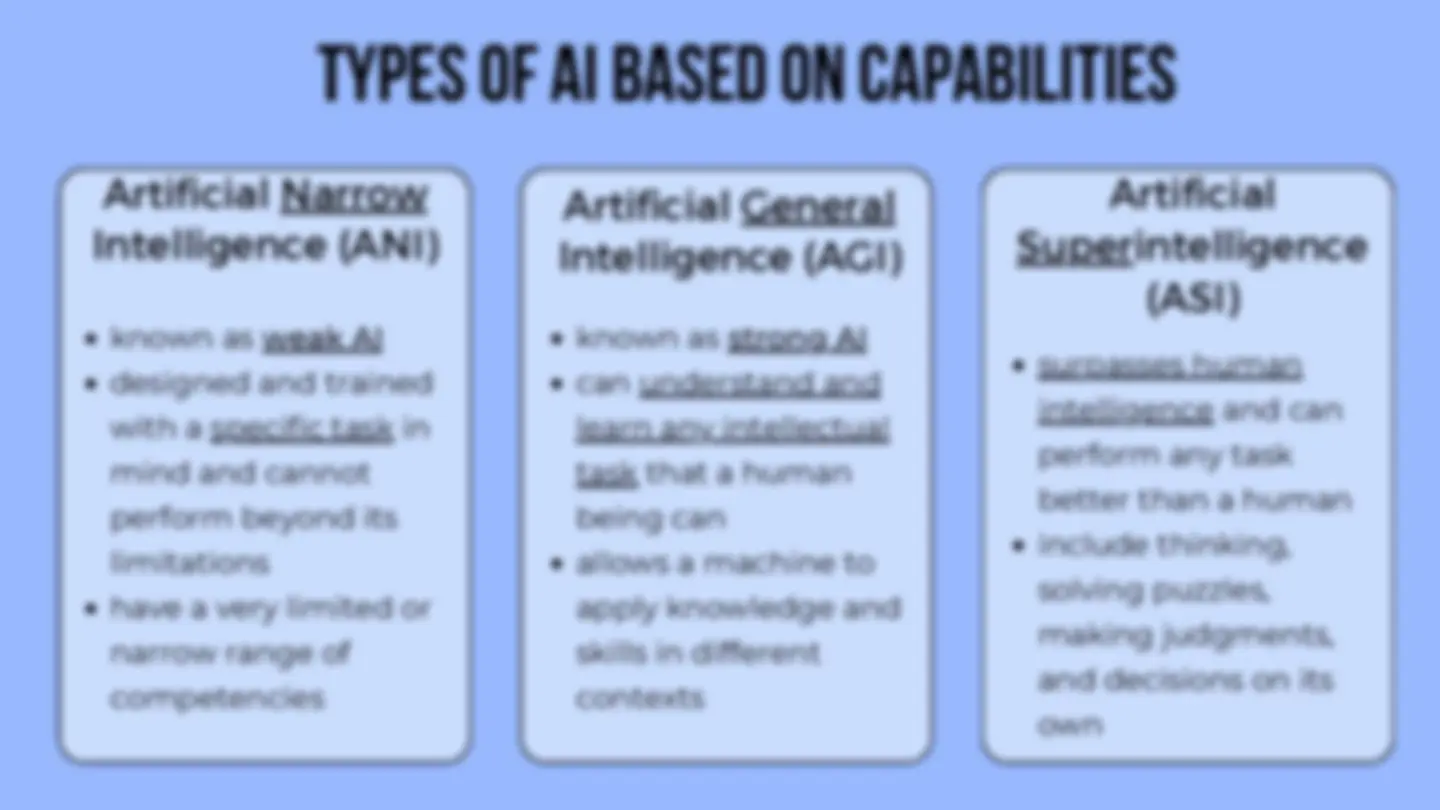
a subset of AI the science of programming machines to think and act like humans without being explicitly programmed to aims to enable computers to learn automatically without human intervention and adjust actions uses algorithms that can make predictions through pattern recognition mACHINE LEARNING
SUPERVISED Learning
REINFORCEMENT Learning
mACHINE LEARNING CategorieS UNSUPERVISED Learning
self-driving cars speech recognition pattern recognition computer programming image recognition contextual recommendations fact checking Applications are: DEEP LEARNING
Banking Healthcare Human Resources (HR) Marketing and Sales Supply Chain Applications are: Predictive Analytics
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a subfield of AI that focuses on enabling machines to understand and interpret human language. NLP is used in applications such as chatbots, virtual assistants, and language translation. Natural Language Processing With NLP, PCs can decode, display and generate human language and communicate. Its ultimate aim is to make predictable organized attempts with the computers we use every day by teaching systems to understand the human language and to react intelligently.
Expert Systems a computer program that uses artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to simulate the judgment and behavior of a human or an organization that has expertise and experience in a particular field relies on having a good knowledge base. Experts add information to the knowledge base, and nonexperts use the system to solve complex problems that would usually require a human expert.
CaDet (Cancer Decision Support Tool) is used to identify cancer in its earliest stages. DENDRAL helps chemists identify unknown organic molecules. DXplain is a clinical support system that diagnoses various diseases. MYCIN identifies bacteria such as bacteremia and meningitis, and recommends antibiotics and dosages. PXDES determines the type and severity of lung cancer a person has. R1/XCON is an early manufacturing expert system that automatically selects and orders computer components based on customer specifications. Examples of expert systems