











Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
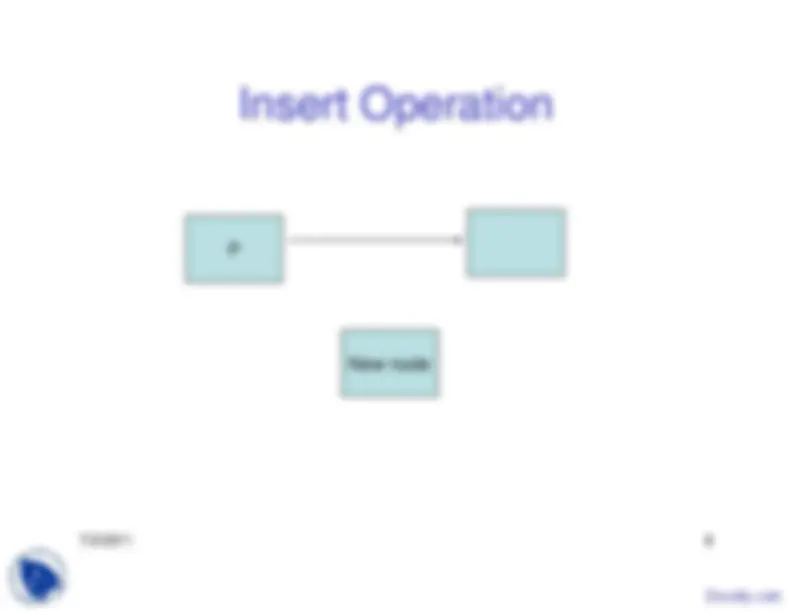
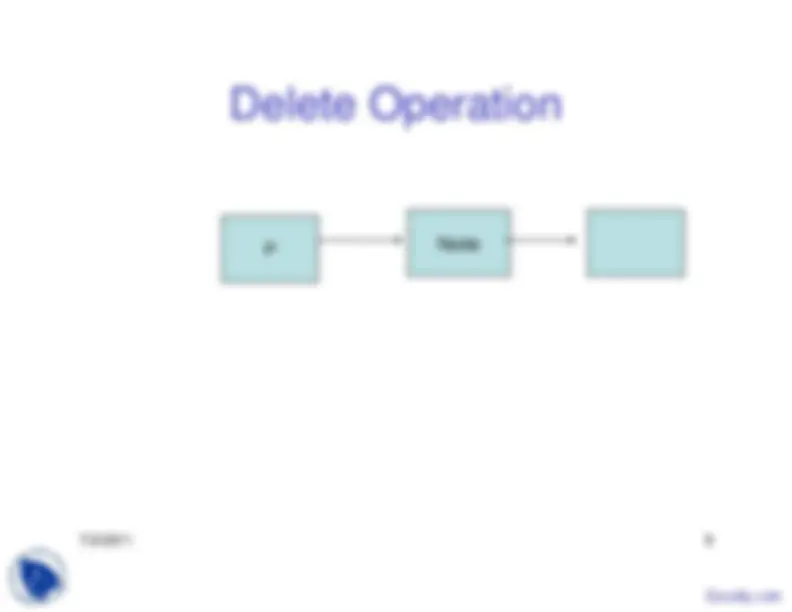
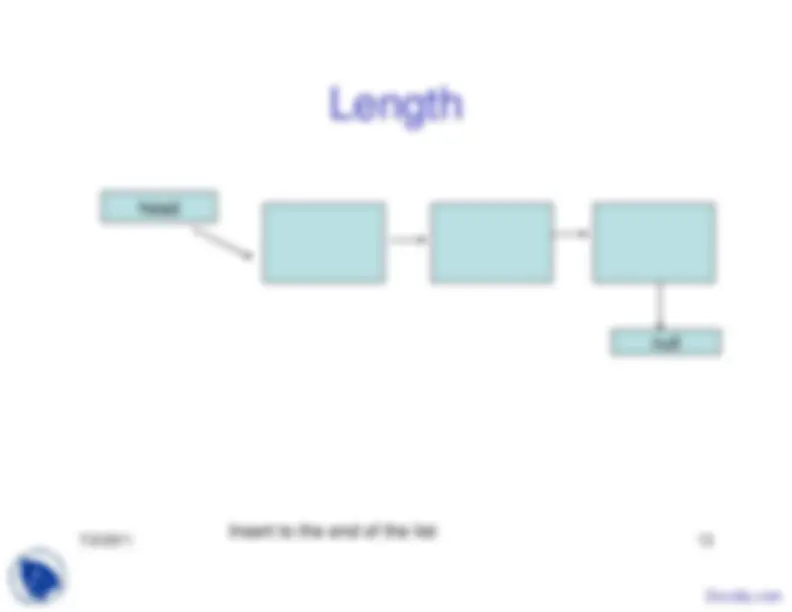
The advantages and disadvantages of linked lists, focusing on their ease of insertions and deletions, and the extra space required for pointers. It also covers basic operations on a linked list, such as insertion, deletion, building a list, appending and prepending, empty list check, length calculation, and list traversal. The document also introduces doubly linked lists and their insertion and deletion operations.
Typology: Slides
1 / 20

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!













Inserting into a Doubly Linked List
Deleting from a Doubly Linked List
Make it a Circular Doubly Linked List