














Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An in-depth analysis of common acquired and congenital anomalies in infants, focusing on Colic, Failure to Thrive, and Hydrocephalus. It covers causes, assessments, therapeutic management, and diagnostic evaluations for each condition. Parents and healthcare professionals can use this information to better understand these conditions and provide appropriate care.
Typology: Summaries
1 / 36

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!





























Elsie P. Miguel, RN MN
ASSESSMENT
THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT
FAILURE TO THRIVE (FTT)
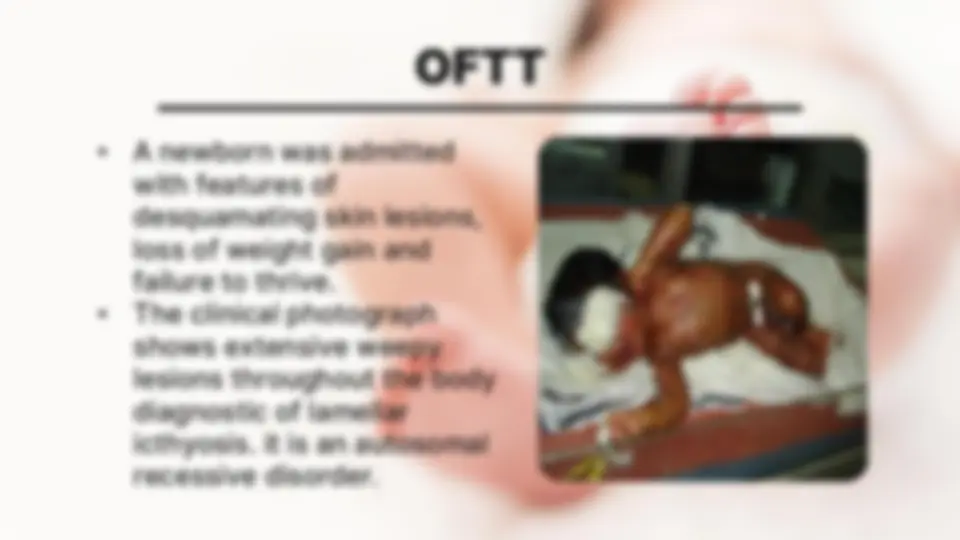
OFTT
FACTORS LEADING TO INADEQUATE FEEDING
THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT
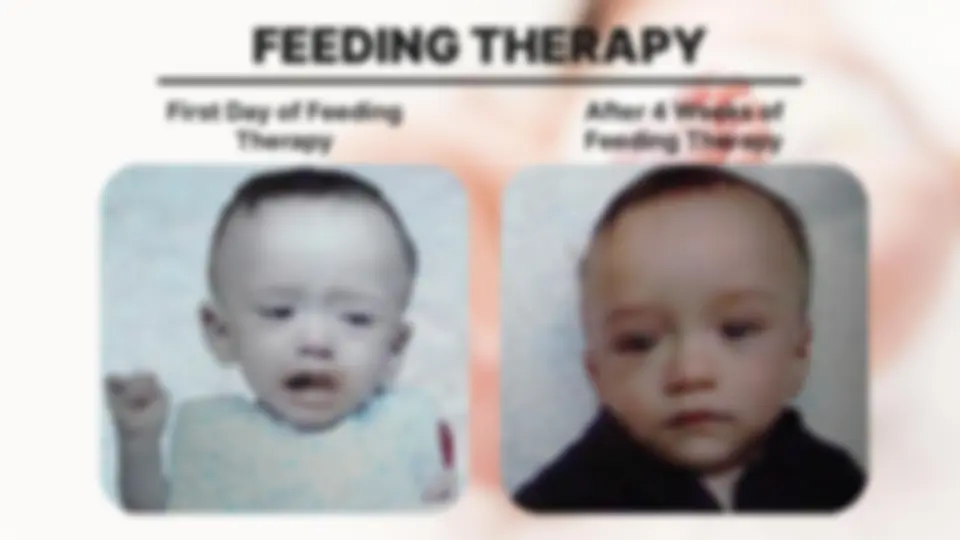
FEEDING THERAPY First Day of Feeding Therapy After 4 Weeks of Feeding Therapy
NURSING DIAGNOSIS (NFTT)
Elsie P. Miguel, RN MN
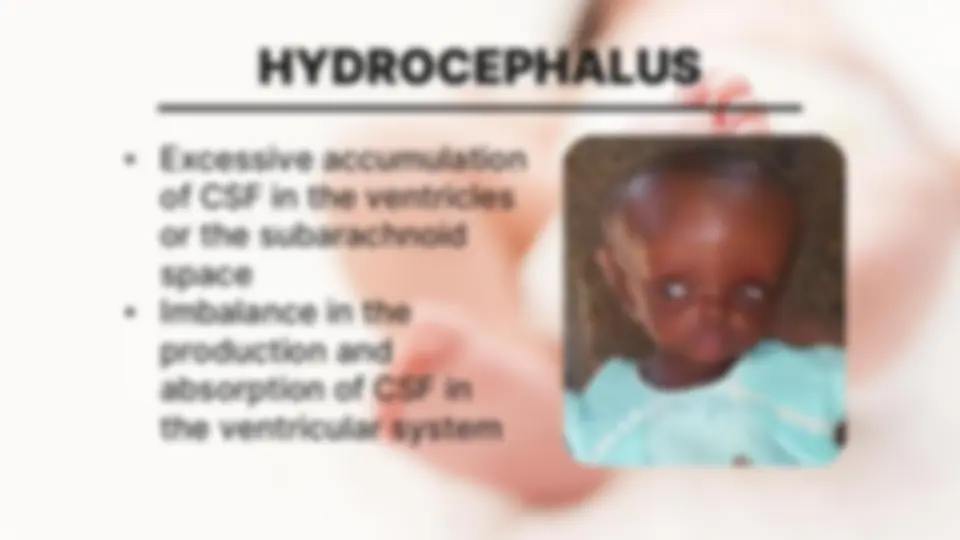
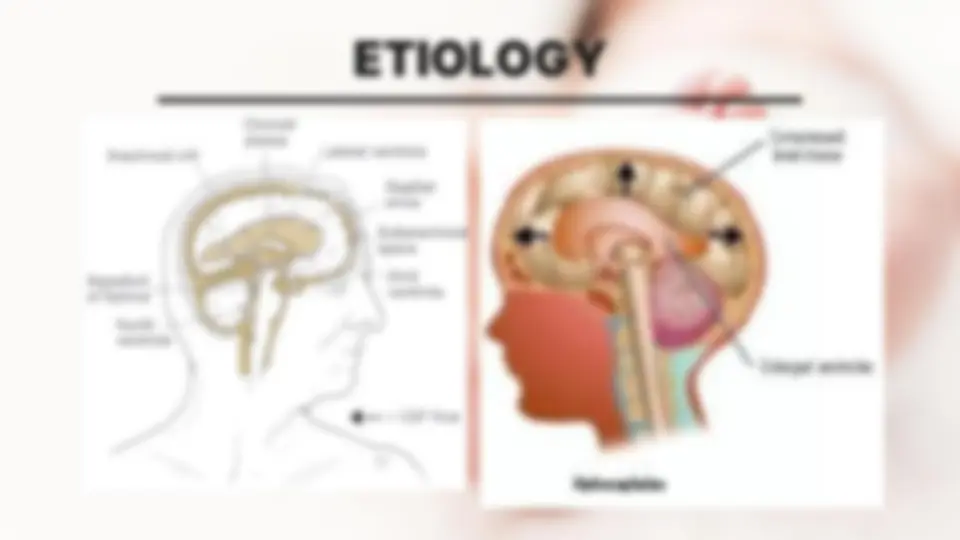
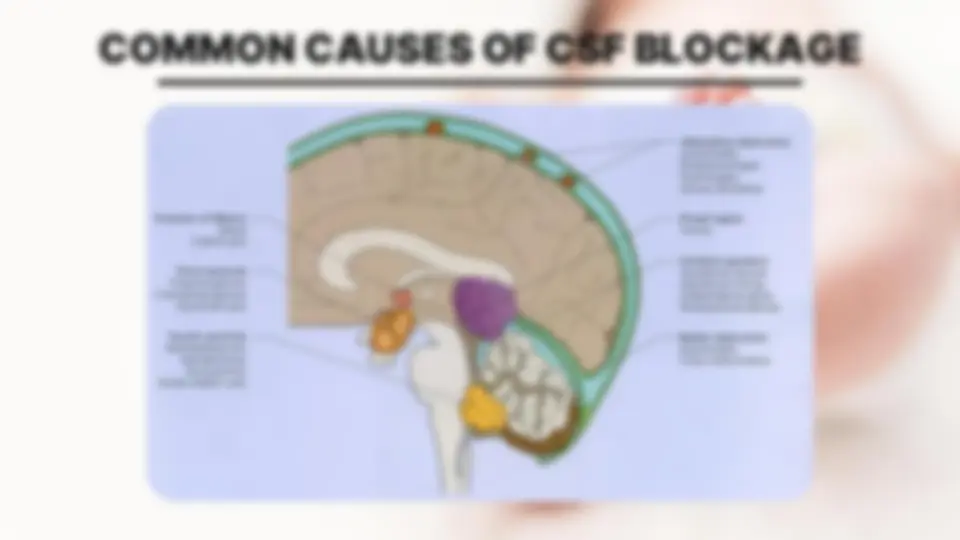
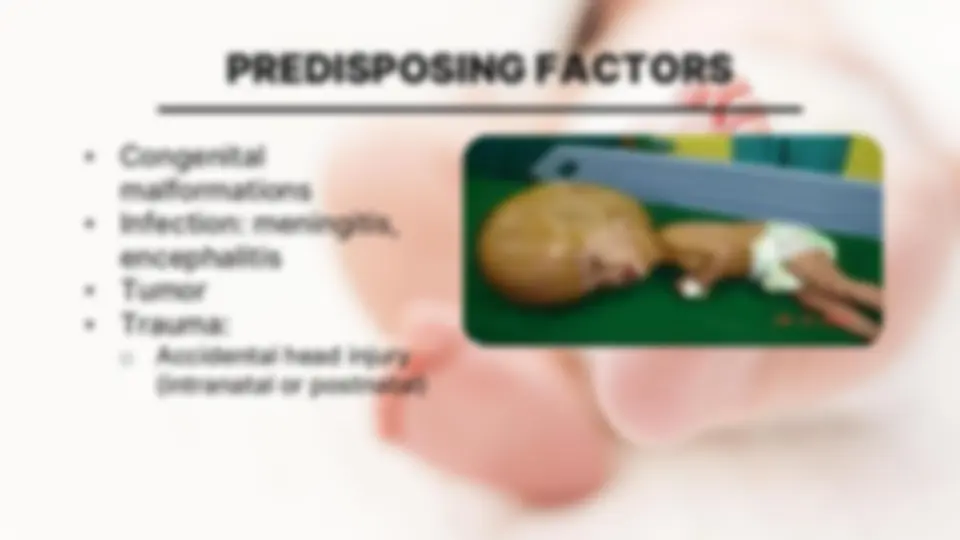
EXCESS IN CSF IN NB OCCURS FOR 1 IN 3 REASONS