










Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
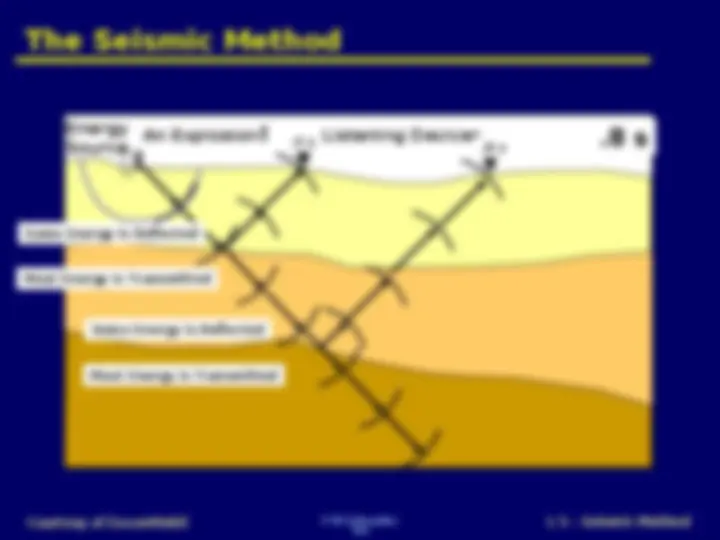
Seismic reflection is a method of exploration geophysics that provides information about the sub-surface structure of the seafloor. The general principle involves sending artificially generated acoustic waves down the water column and into the seafloor, where the different structures and objects within the Earth's crust reflect this energy back according to their acoustic impedance.
Typology: Lecture notes

Limited-time offer
Uploaded on 04/15/2021
5 documents
1 / 21

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!















On special offer
F W Schroeder Courtesy of ExxonMobil L 5 – Seismic Method
Mitchum et al., 1977b AAPG©1977 reprinted with permission of the AAPG whose permission is required for further use.
F W Schroeder Courtesy of ExxonMobil L 5 – Seismic Method
To D/P Drop Prospect Drill Wildcats Confirmation Well Identify Opportunities Process Seismic Data Capture Prime Areas Interpret Seismic Data Acquire Seismic Data Success Success Failure Uneconomic Economic Analysis Assess Prospects
F W Schroeder Courtesy of ExxonMobil L 5 – Seismic Method
Device
Device
Listening device #1 records a reflection starting at 0.4 seconds Listening device #2 records a reflection starting at 0.8 seconds
Time
F W Schroeder Courtesy of ExxonMobil L 5 – Seismic Method
Vibrators Generate a Disturbance Geophones Detect Motion
Air Guns Generate a Disturbance Hydrophones Detect Pressure
F W Schroeder Courtesy of ExxonMobil L 5 – Seismic Method
Field Record (marine)
F W Schroeder Courtesy of ExxonMobil L 5 – Seismic Method
Source Receivers R1 R2 R3 R4 R S Direct Arrival Reflections 2 Way Travel Time Offset (Distance) R1 R2 R3 R4 R Direct Arrival Reflection For each shot, reflections are recorded in 5 receivers There are 5 ‘bounce’ points along interface 3 1 2 3
F W Schroeder Courtesy of ExxonMobil L 5 – Seismic Method
The curvature of this hyperbola is a function of the average velocity down to the depth of the reflection CMP Gather Offset Distance
F W Schroeder Courtesy of ExxonMobil L 5 – Seismic Method CMP Gather Offset Distance
Velocity Too Slow Velocity Correct Velocity Too Fast Flat Curves Down Curves Up
F W Schroeder Courtesy of ExxonMobil L 5 – Seismic Method
Energy Source
0.2 s down 0.2 s up 0.4 s -
Bounce Point
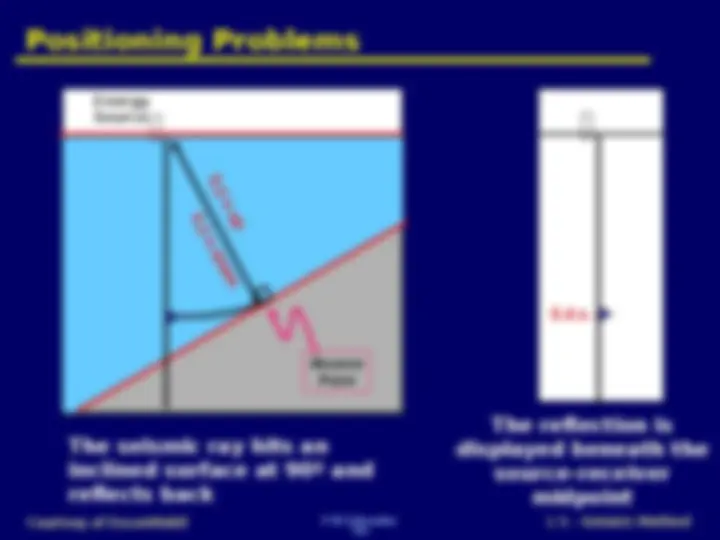
F W Schroeder Courtesy of ExxonMobil L 5 – Seismic Method
F W Schroeder Courtesy of ExxonMobil L 5 – Seismic Method
F W Schroeder Courtesy of ExxonMobil L 5 – Seismic Method
F W Schroeder Courtesy of ExxonMobil L 5 – Seismic Method
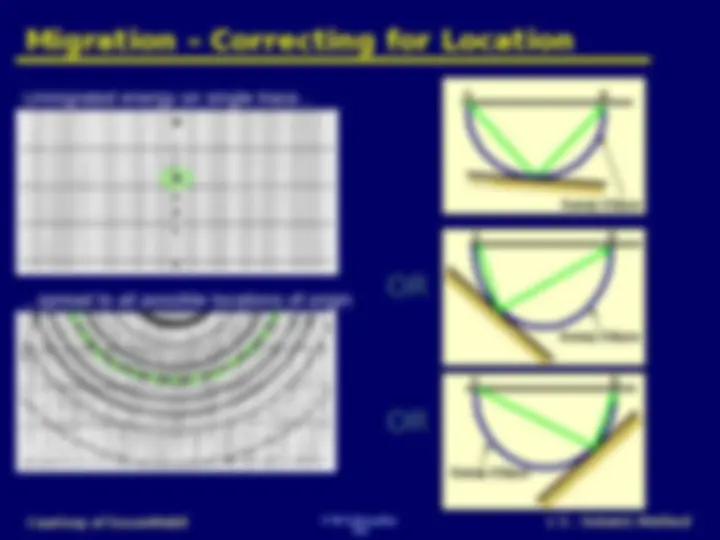
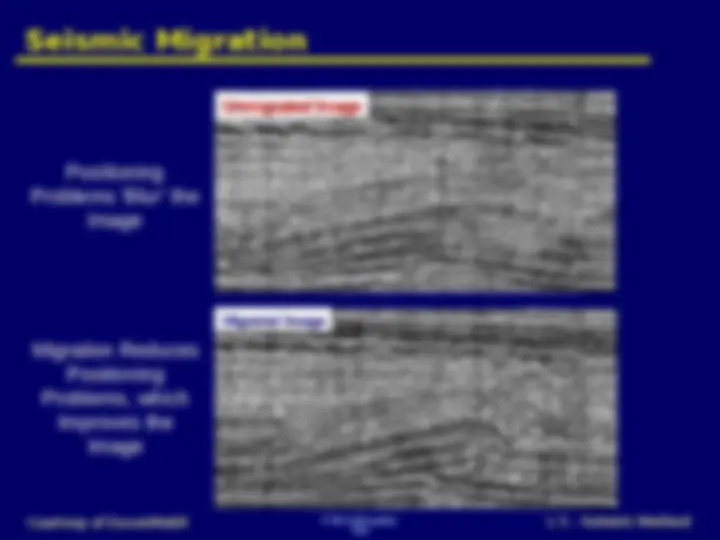
Two reflections on unmigrated data After spreading to all possible locations Reflections are not positioned in the subsurface correctly since they have dip Constructive interference occurs where the reflections are properly positioned Destructive interference dominates where the reflections are NOT properly positioned
F W Schroeder Courtesy of ExxonMobil L 5 – Seismic Method
Unmigrated ImageUnmigrated Image Unmigrated ImageUnmigrated Image Migrated ImageMigrated ImageMigrated ImageMigrated Image