

























Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
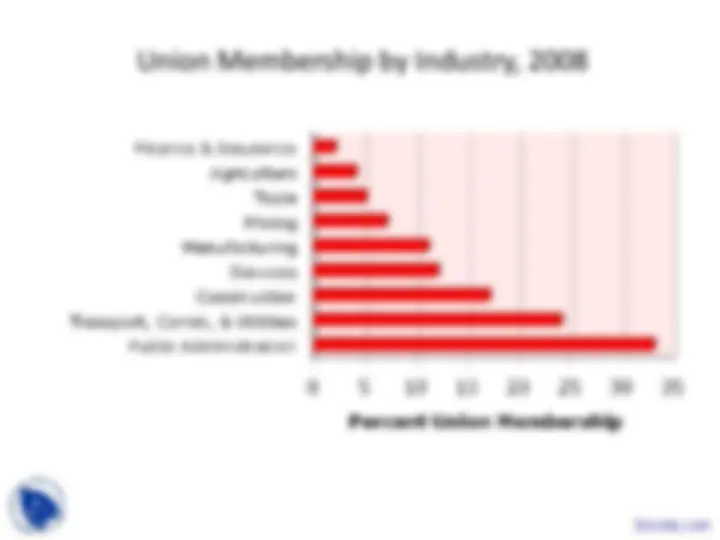
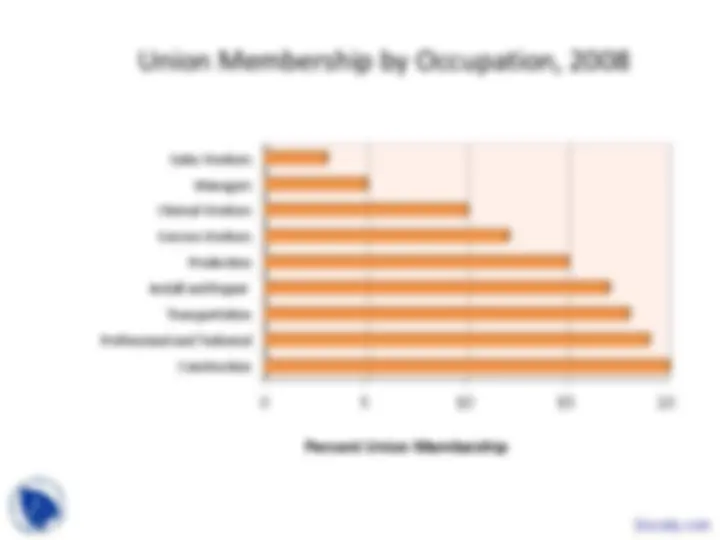
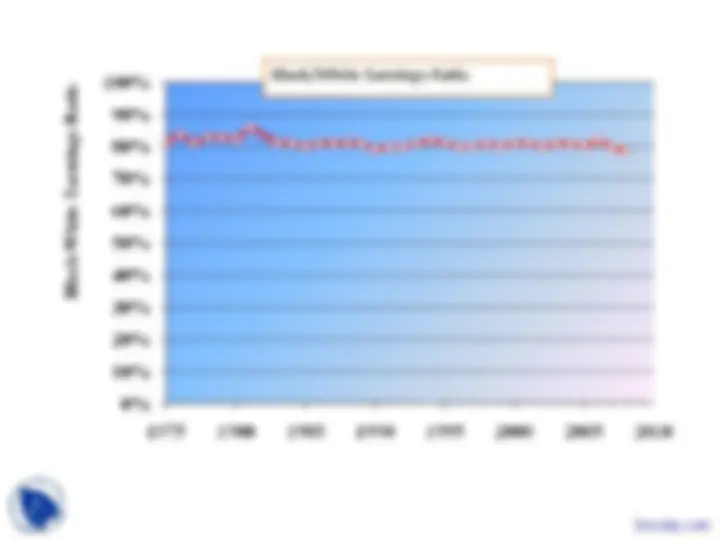
An in-depth analysis of labor unions, their membership statistics, the historical development of labor laws, and the economic impact of unions. It includes data on union membership by industry, occupation, and demographic group, as well as a timeline of key labor laws and their effects. Additionally, it explores the reasons for the rise and decline of unionism, and discusses strategies to raise union wages and models of union behavior.
Typology: Slides
1 / 35

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!




























Professional and Technical^ Install and Repair^ Transportation Construction^ Production 0 5 10 15 20 Clerical Workers Service Workers^ Sales Workers^ Managers Percent Union Membership Docsity.com
Unionism’s Rise and Fall (^101505)
Percent Union Membership (^1880 1900 1920 1940 1960 1980 2000) Docsity.com
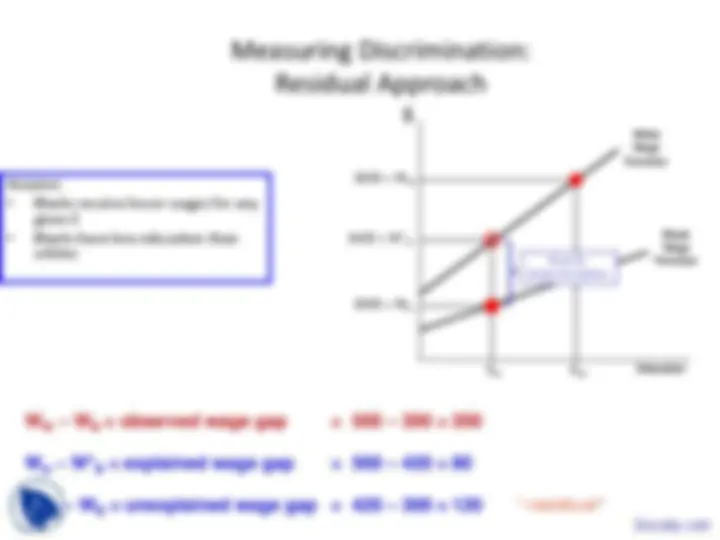
W^ $ t^ Employer Concession
W WN (^) U LU LN S^ U^ S^ N W WS (^) T LN LS^ S D^ N^ S^ spill Union sector Non-Union sector
-^ Voos and Mishell (1986): unionization causes 20% to 23% reduction in profits If unions reduce profits in competitive industries, then an efficiencyloss occurs since firms will leave the industry. (Output will be lower andprices higher) The empirical evidence is mixed on whether there is an efficiency loss.