


























Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
The functioning of the autonomic nervous system, focusing on the neurotransmitters and receptors involved in the transmission of signals. It covers the role of acetylcholine (ach) and adrenergic receptors, as well as the effects of various drugs on these receptors.
Typology: Exams
1 / 36

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!





























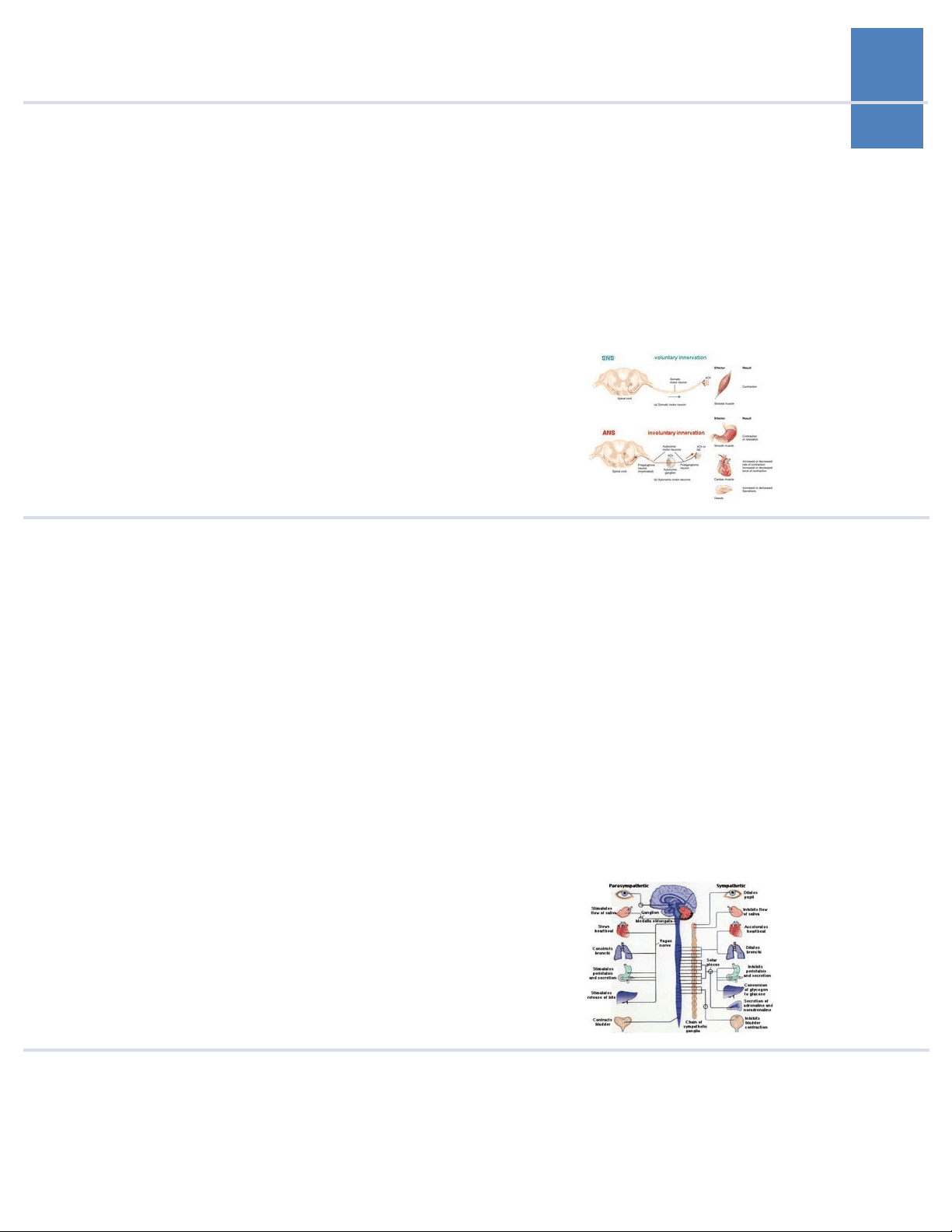
regions of the spinal cord. Most sympathet- ic ganglia are found in chains on each side of the spinal cord - "paravertebral ganglia".
ganglion. Innervated by preganglionic sym- pathetic fibers that release acetylcholine. Releases epinephrine (not NE) from chro-
maffin cells directly into the blood stream (Hence: epinephrine is a hormone not a neurotransmitter).
allows ACh to last longer in the synaptic cleft and exert its effects.
back inhibition. Activation of M3 receptors on target leads to increase in cell Ca2+.
sphincter, and prostate. It also causes ejaculation from penis.
- Mechanism: Leads to con- striction and results in an increase in cytosolic Ca2+ (cause contraction).
14
27. • Located in lungs, blood ves- sels, GI tract, uterus, and liver. - Where are ²2receptors located? - What is their mechanism?
35. M2, ± 2 a, nd D2 Receptors
Which receptors cause a decrease in cAMP?
nicotinic N and nicotinic M receptors. Ef- fects: CNS effects - mild, alerting action. Tremor, emesis, stimulation of respiratory center, convulsion, respiratory failure, and fatal coma. It has sympathomimetic effects on cardiovascular system - causes vaso- constriction, increased HR --> increases BP. It has parasympathetic effects in GI and urinary tracts - cause nausea, vom- iting, diarrhea, and urination. In skeletal muscle, depolarization blockade results in flaccid paralysis including respiratory mus- cles - the channel is kept open! Treatment in overdose: give anticonvulsant (e.g. di- azepam) for CNS effects, give atropine to antagonize muscarinic effects, and provide mechanical respiration. It is used in treat- ment of nicotine withdrawal symptoms as an aid to smoking cessation. It is also used as an insecticide. The mechanism of ac- tion limits potential use of drugs on these receptors because both the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems will be affected.
20