Download HISTOLOGY OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT and more Lecture notes Histology in PDF only on Docsity!
HISTOLOGY OF
GASTROINTESTINAL
TRACT
Content
1. Introduction
2. General Structure
3. Histology of:
- Oral Cavity
- Esophagus
- Stomach
- Small Intestine
- Large Intestine
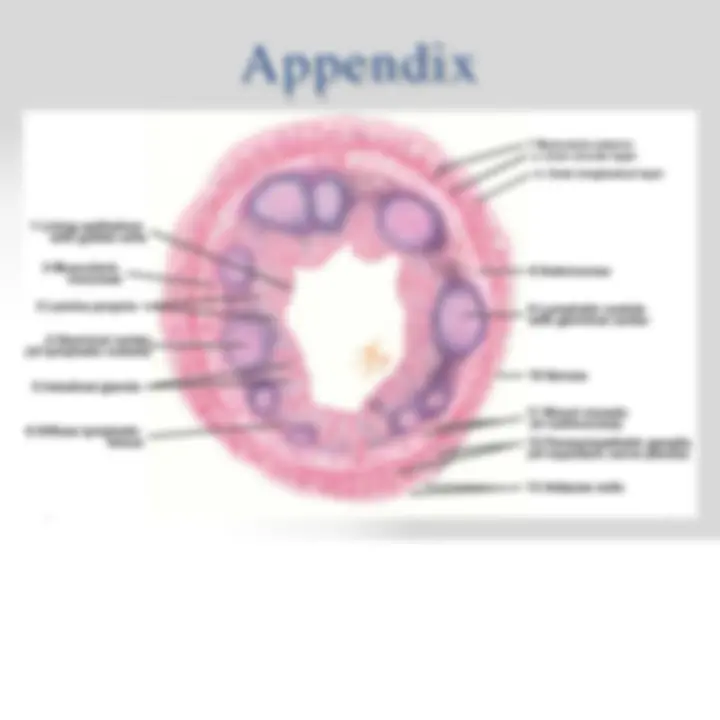
- Appendix
- Salivary Gland
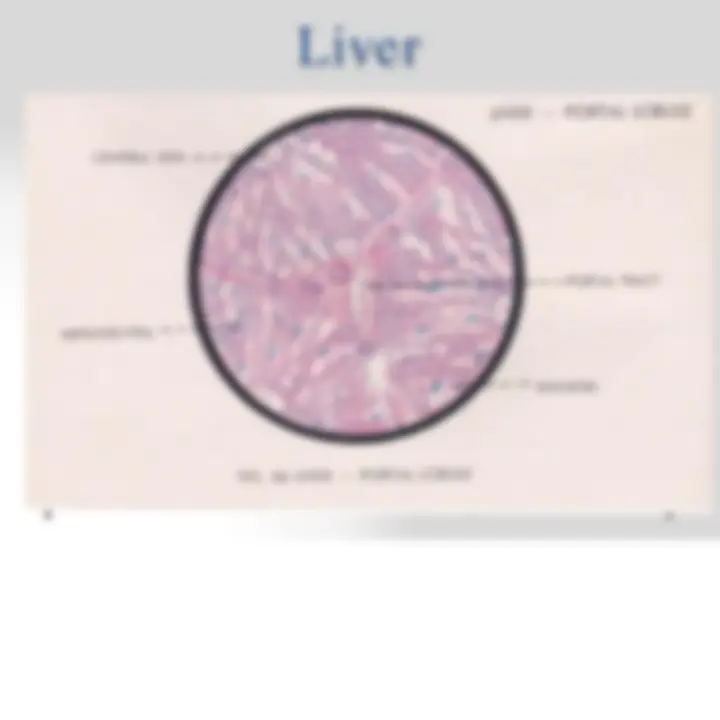
- Liver
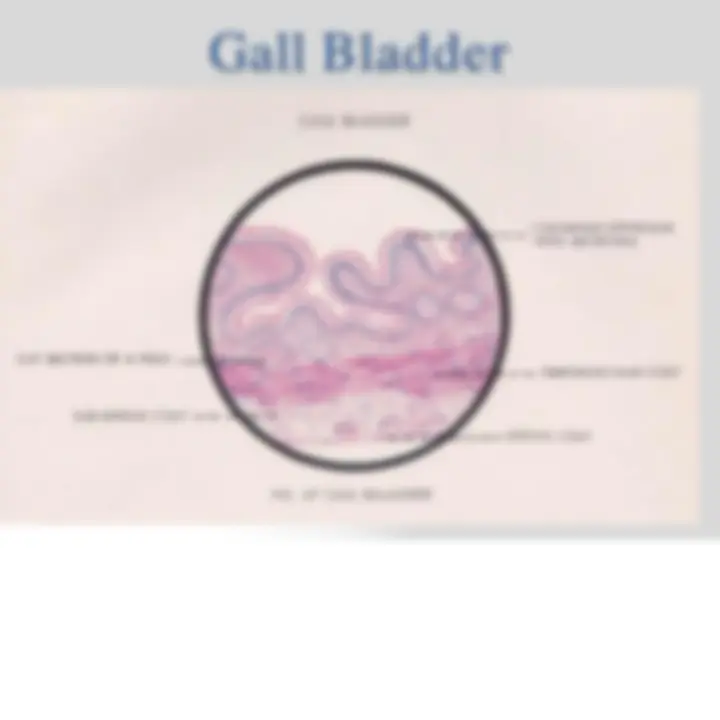
- Gall Bladder
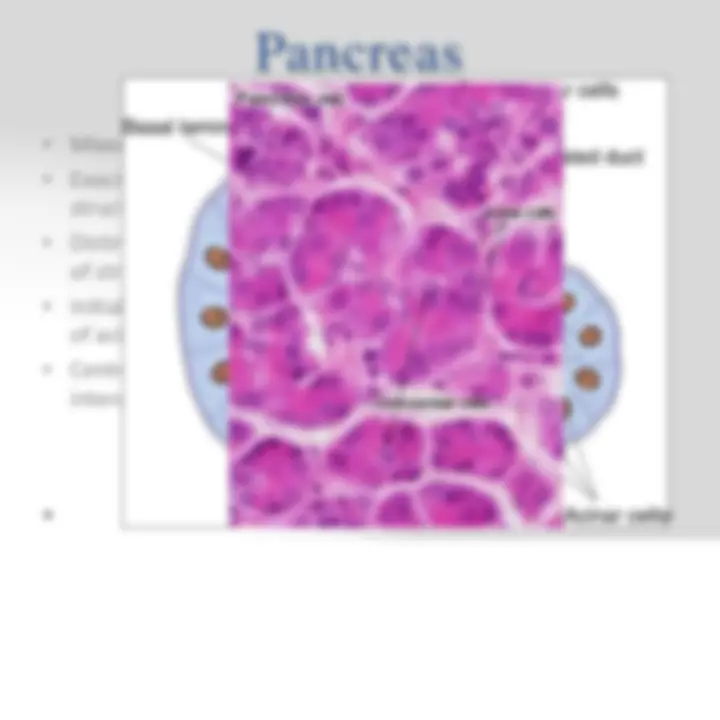
- Pancreas
4. Medical Application
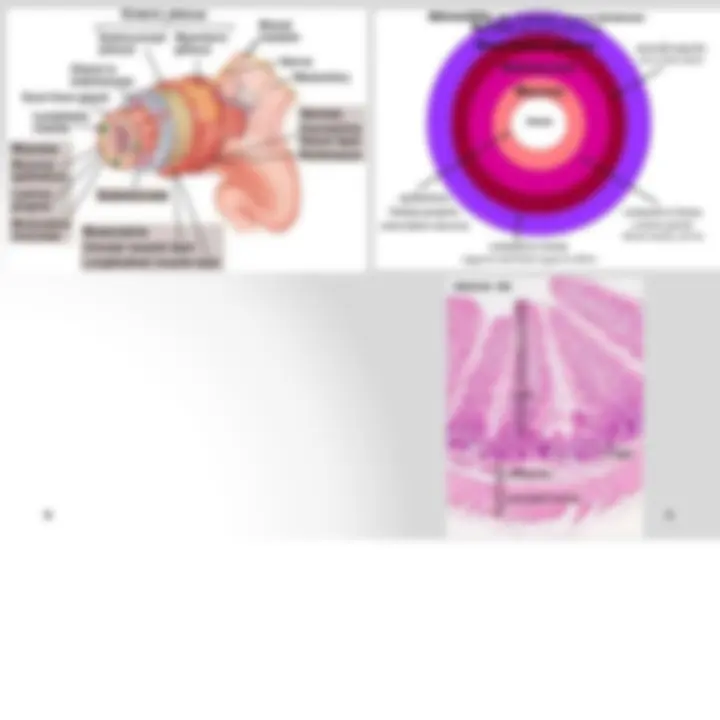
General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: o Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. o Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers:
- Mucosa o Epithelial lining; A lamina propria of loose connective tissues rich in blood, lymph vessels and smooth muscle cells; Muscularis mucosae.
- Submucosa o Dense connective tissues with many blood and lymph vessels.
- Muscularis o Contains smooth muscle cells, divide into 2 layers; internal (circular); external (longitudinal)
- Serosa o Thin layer of loose connective tissue rich in blood and lymph vessels and adipose and single squamous covering epithelium (mesothelium)
Oral Cavity
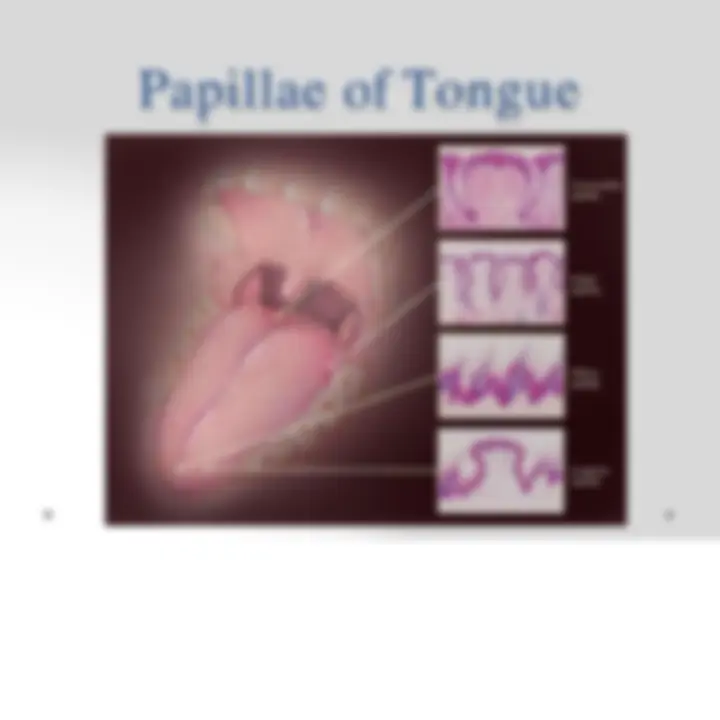
o Papillae
- Filiform
- Fungiform
- Foliate
- Circumvallate
- Pharynx
- Teeth and Associate Structures
o Dentin
o Enamel
o Pulp
o Periodontium
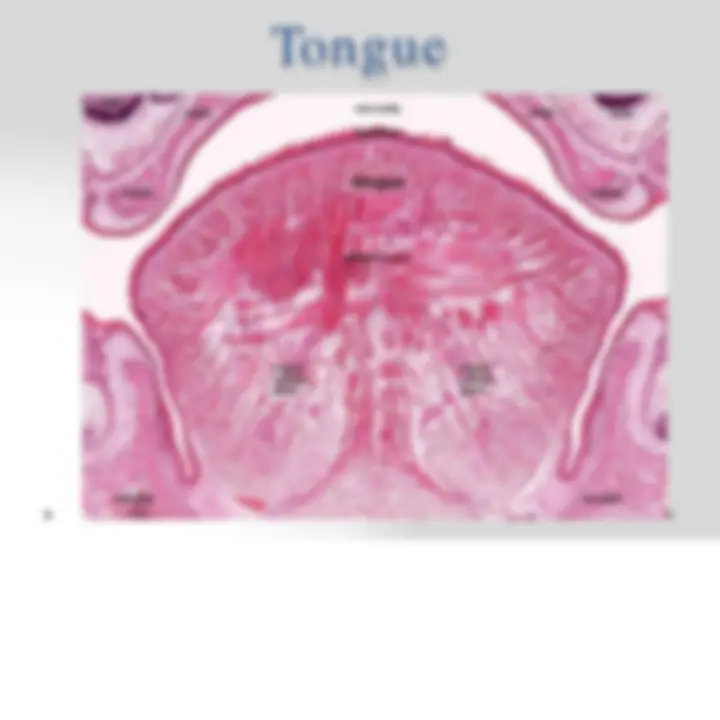
Tongue
- Mass of striated muscle covered by a mucous
membrane.
- Muscle fibers cross on another in 3 planes, they are
grouped in bundles, usually separated by connective tissue.
- Dorsal Surface → Irregular; Thicker epithelium; Covered
anteriorly by a great number of small eminences papillae;
Separated from anterior two thirds by a V-shaped
boundary.
- Ventral Surface → Epithelium on this surface is
thinner.
Papillae of Tongue
Papillae of Tongue
- Filiform Papillae o Conical Shape o Numerous and present over entire surface of tongue o Their epithelium does not contain taste bud and is Keratinized.
- Fungiform Papillae o Resemble mushrooms (narrow stalk and smooth surface, dilated upper part) o Contain scattered taste buds on upper surfaces o Irregularly interspersed among filiform papillae.
- Foliate Papillae o Poorly developed in humans o 2 or more parallel ridges and furrows on the dorsolateral surface of tongue o Contain many taste buds
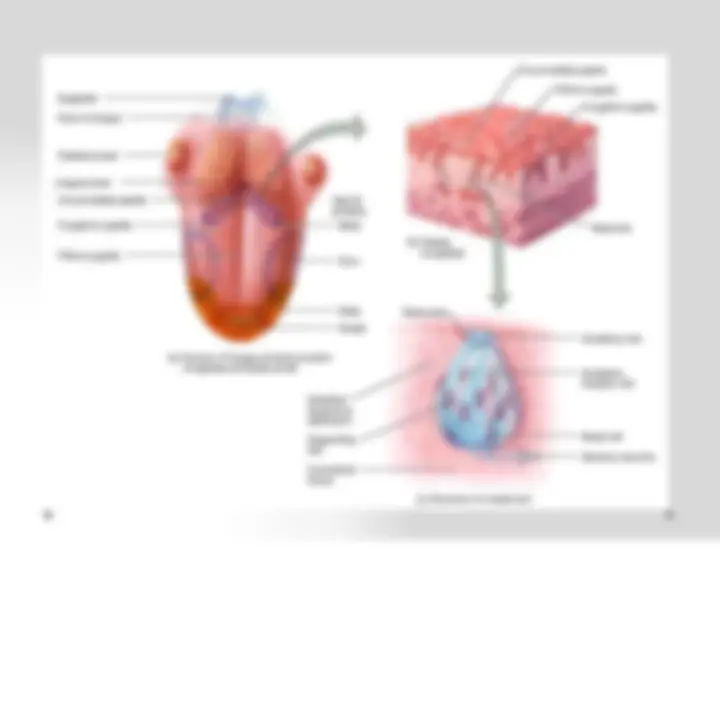
Taste Bud
• SUSTENTACULAR OR SUPPORTING CELLS
o Arranged peripherally, curved course, narrow at each end and broader in the centre appearing spindle shaped. o At both ends the cells surround small openings known as external and internal pores.
- NEUROEPITHELIAL OR GUSTATORY CELLS o Distributed between the sustentacular cells long narrow, having slender red shaped form with a nucleus in the middle. o On the free surface, these cells gives rise to short hair which project into the lumen of the pit. o The substances to be tasted gets dissolved in the saliva, stimulate the hairs in the neuroepithelial cells and the impulses is conducted along the nerves (sweet, bitter, sour, salty)
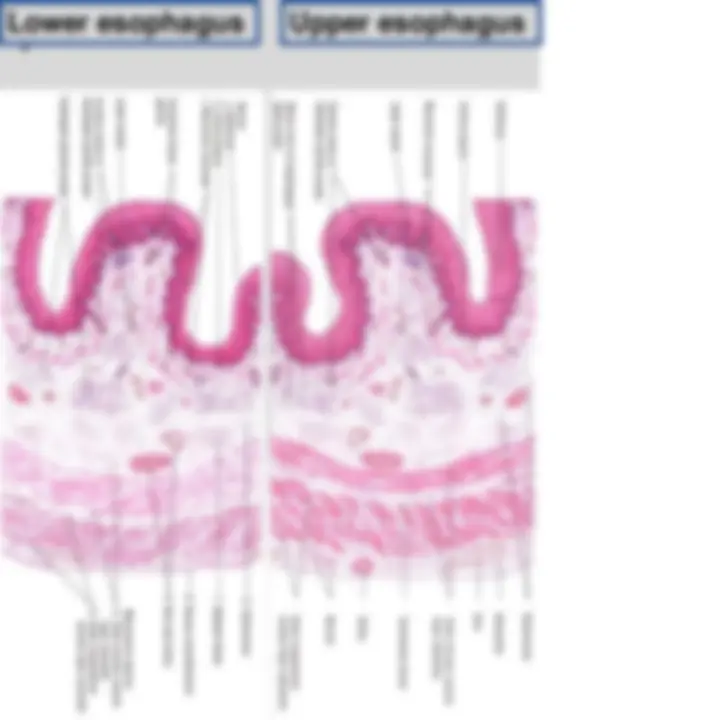
Esophagus
Esophagus
- Muscular Tube function to transport food stuffs from mouth to stomach
- Covered by non keratinized stratified squamous epithelium.
- In general same layers as rest of digestive tract.
- In submucosa → groups of small mucous secreting glands (esophageal glands) secretion facilitated transport of food stuff and protects mucosa.
- Lamina Propria near stomach → groups of gland (esophageal cardiac gland) secrete mucus
- Distal end muscular layer → Only smooth muscle
- Mid Portion → Mixture of striated and smooth muscle
- Proximal end → Only striated muscle cells
- Portion in peritoneal cavity covered by serosa
- The other portion covered by layer of connective tissue, adventitia that blends into surrounding tissue.
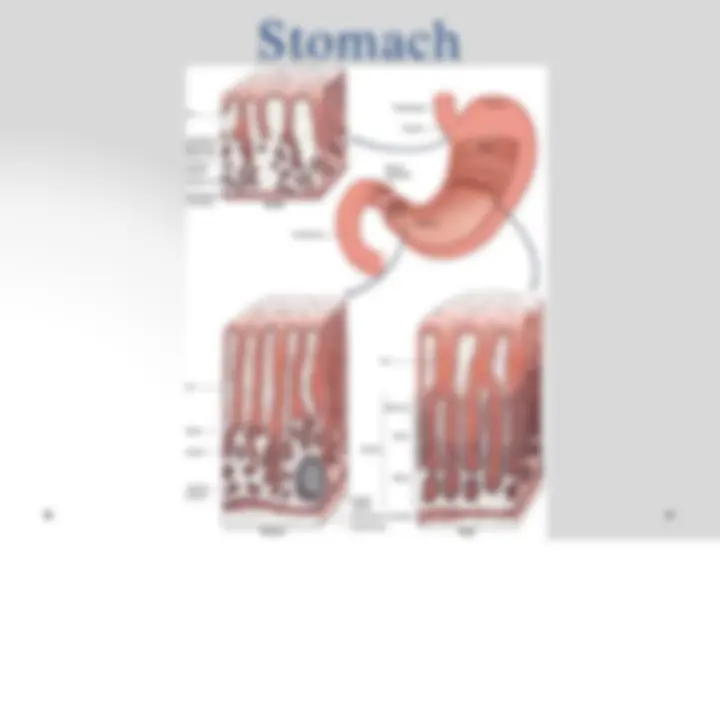
Stomach
Stomach
- Mixed exocrine endocrine gland.
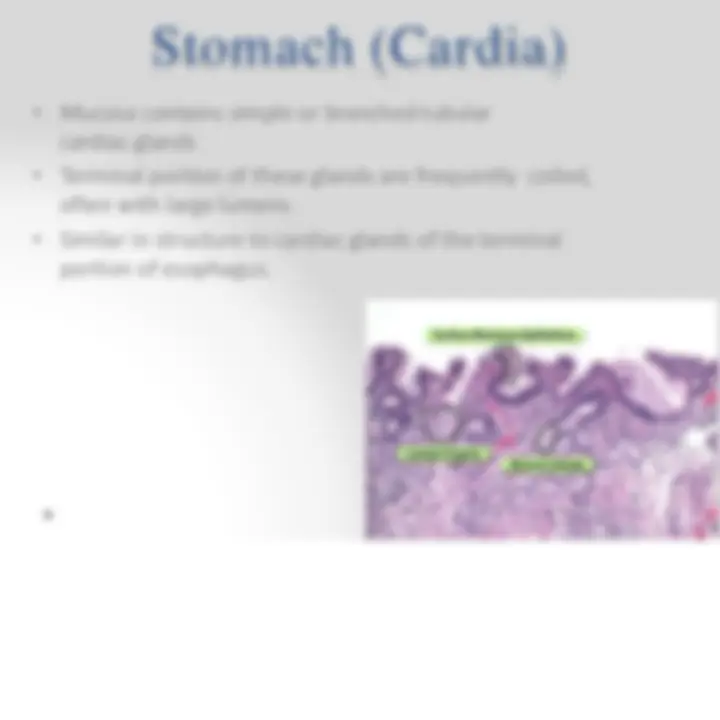
- Divides into 4 regions: o Cardia o Fundus o Body o Pylorus
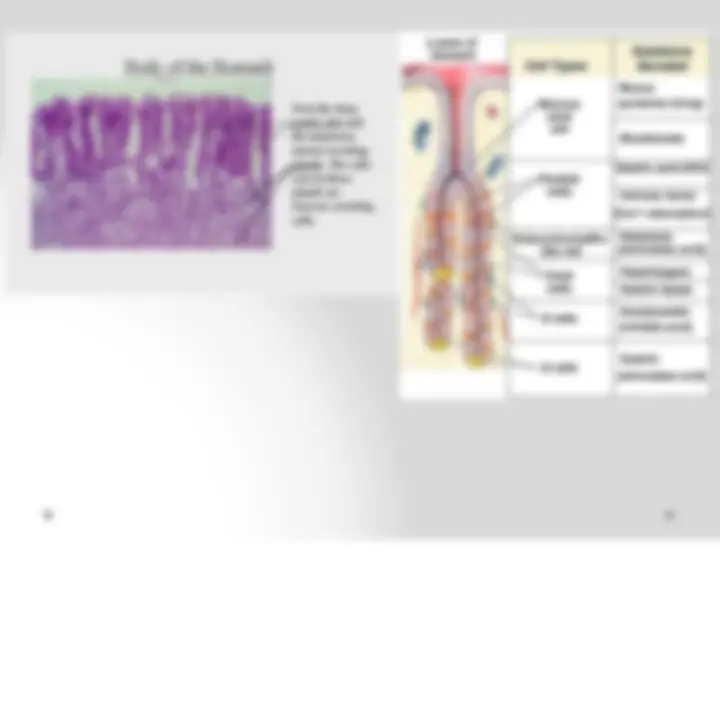
- Fundus and body are identical in microscopic
structure.
- Mucosa and submucosa of undistended stomach lie in
longitudinally directed folds known as rugae.