






















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
In the subject of the Data Structures, the key concept and the main points, which are very important in the context of the data structures are listed below:Heaps and Priority Queues, Full Binary Tree, Non-Leaf Node, Same Level, Leaves, Next-To-Last Level, Left to Right, Leaves, Different Types, Heap
Typology: Slides
1 / 32

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!

























Full Binary Tree
Examples of Different Types of Binary Trees 4
What is a Heap? A heap is a binary tree that satisfies these special SHAPE and ORDER properties:
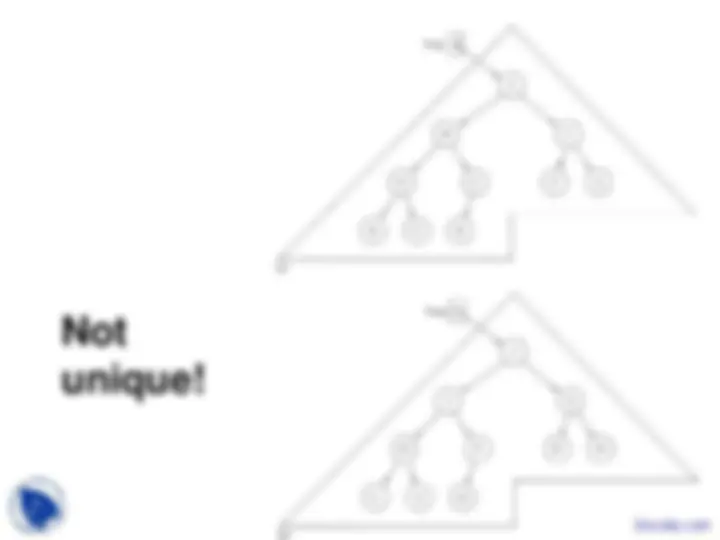
Is this a Heap?
Not unique!
We Can Number the Nodes Left to Right by Level This Way
And use the Numbers as Array Indexes to Store the Trees 70 0 60 1 40 3 30 4 12 2 8 5 tree [ 0 ] [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] [ 6 ] 70 60 12 40 30 8 tree.nodes
// HEAP SPECIFICATION // Assumes ItemType is either a built-in simple data // type or a class with overloaded relational operators. template< class ItemType > struct HeapType { void ReheapDown ( int root , int bottom ) ; void ReheapUp ( int root, int bottom ) ; ItemType* elements; //ARRAY to be allocated dynamically int numElements ; };
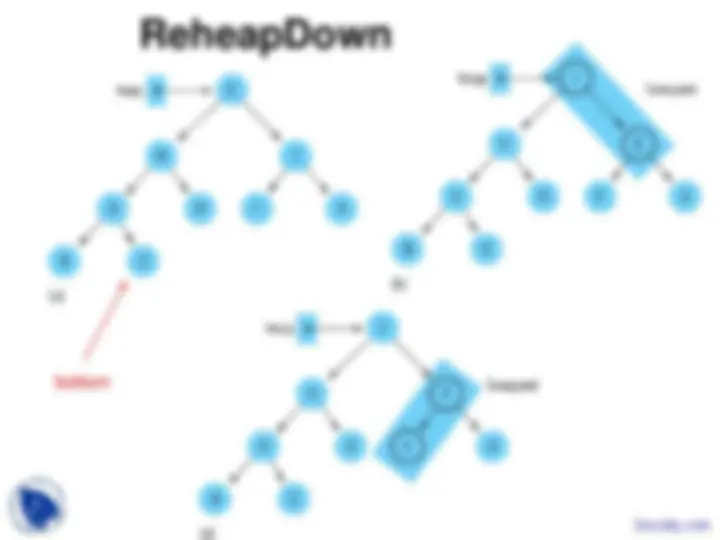
ReheapDown
ReheapDown (cont)
O(logN)
ReheapUp
Real-life Priority Queue