















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
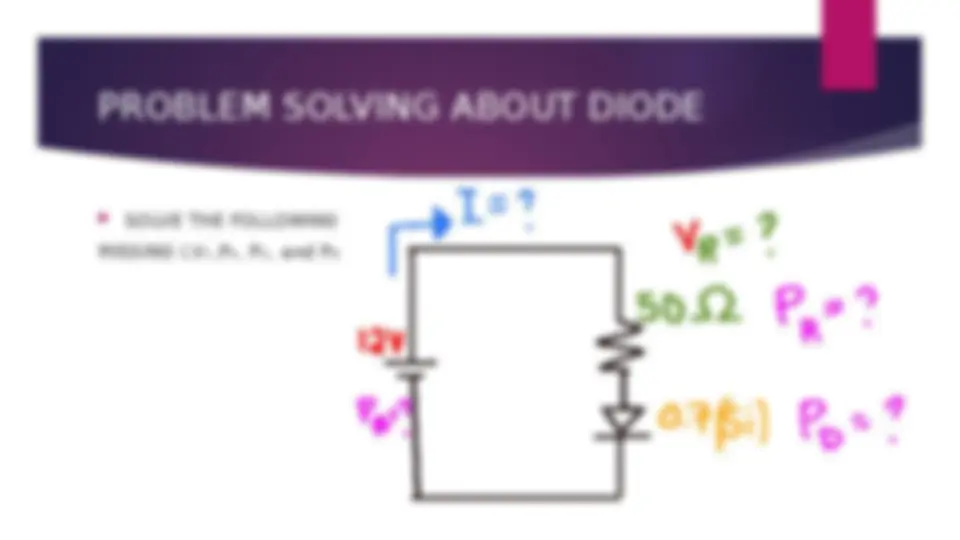
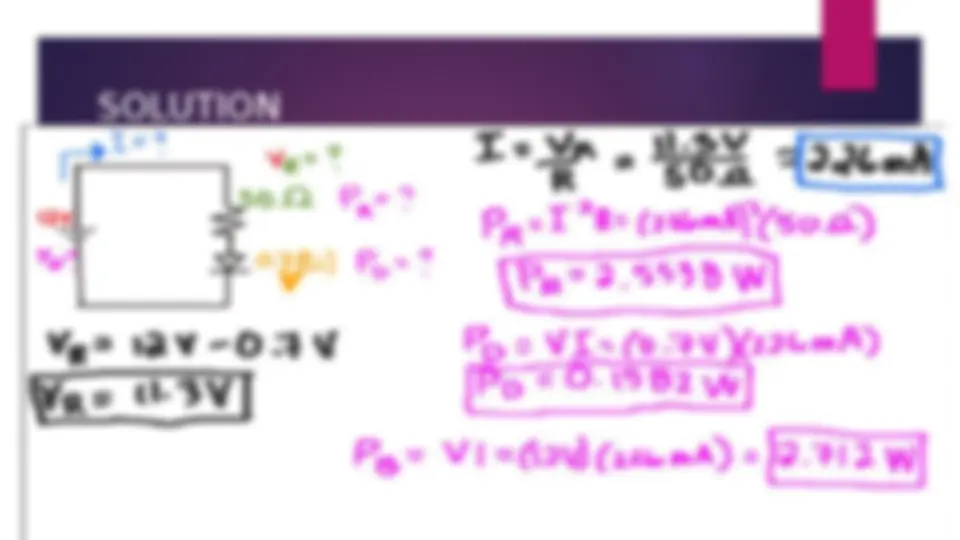
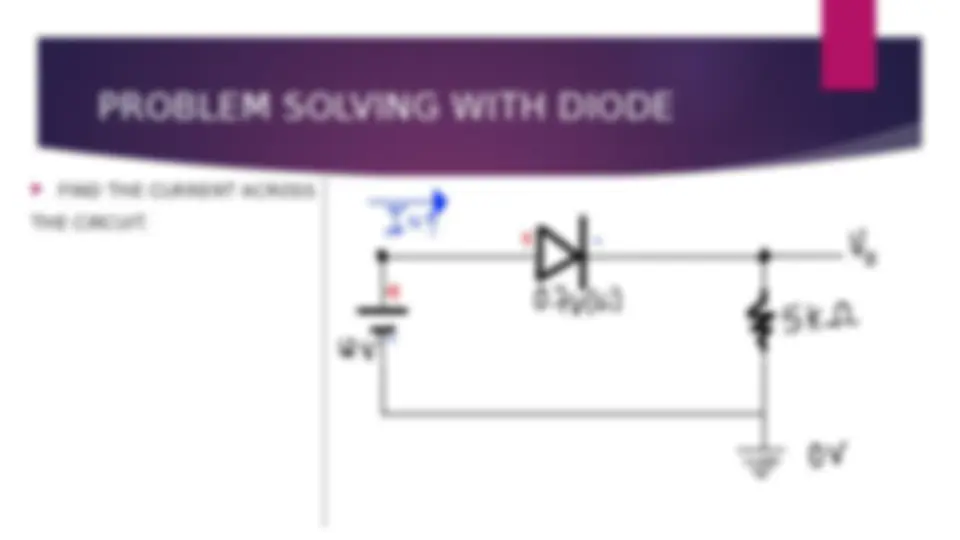
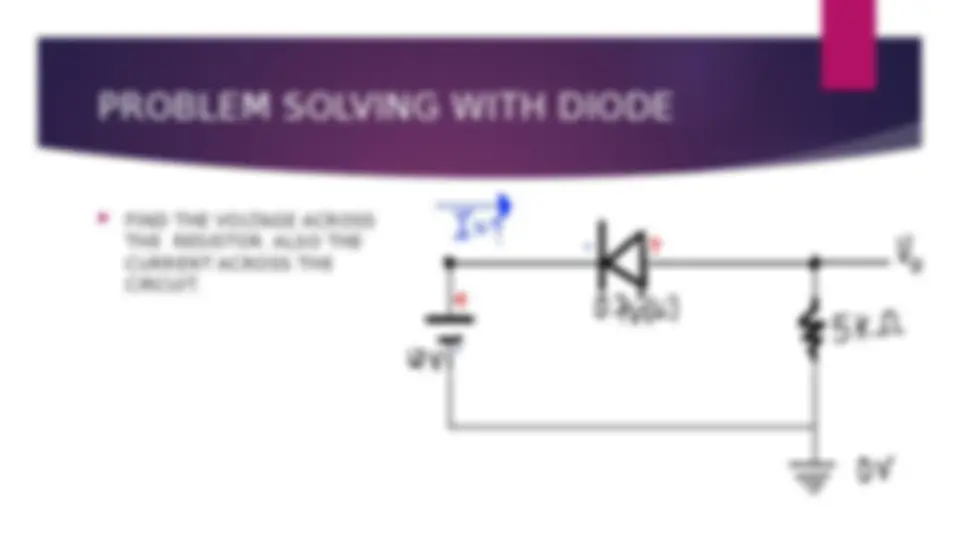
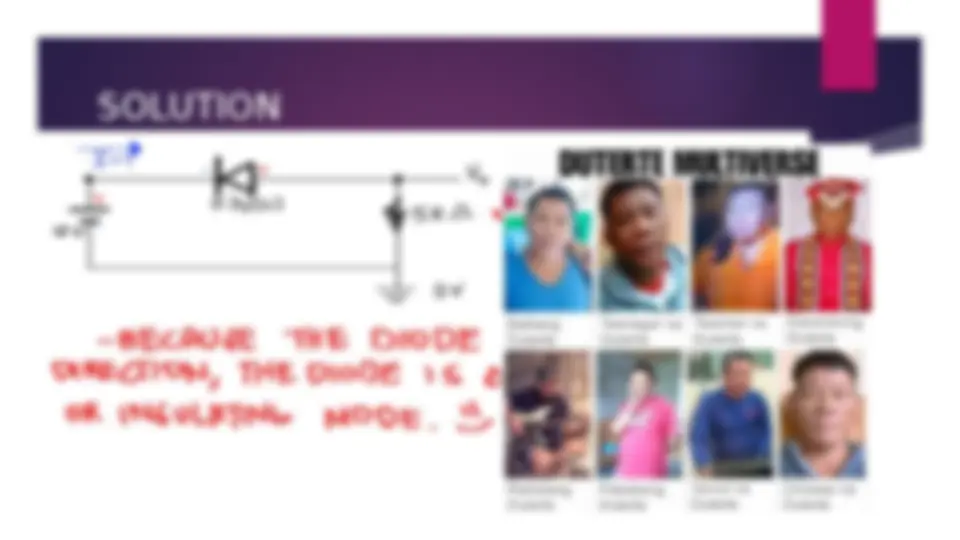
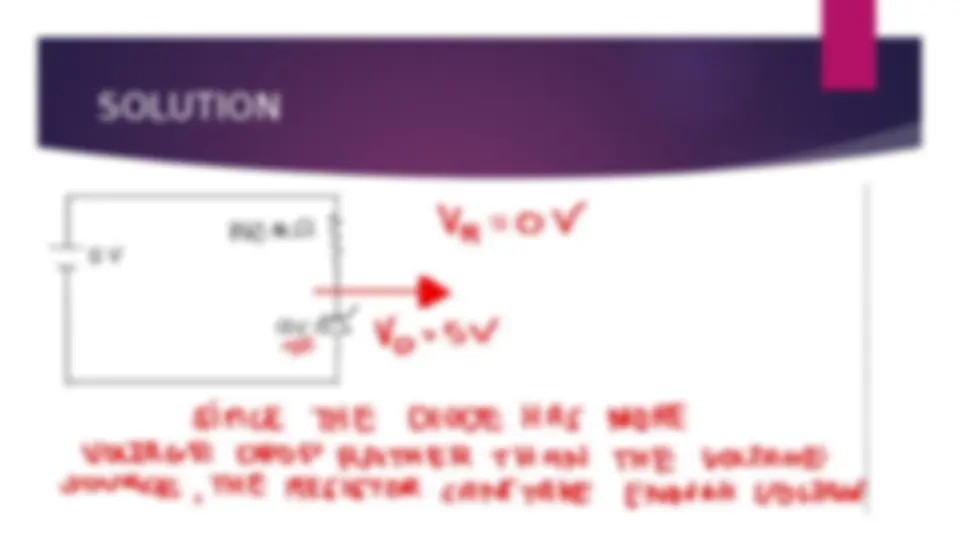
An introduction to diodes, including their parts, types, and uses. It explains the function of diodes in forward and reverse biased conditions and provides examples of different types of diodes, including PN junction diodes, Zener diodes, Schottky diodes, light-emitting diodes, photodiodes, and step recovery diodes. The document also includes examples of problem-solving with diodes using Ohm's law.
Typology: Slides
1 / 28

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!





















(^) a semiconductor device with two terminals, typically allowing the flow of current in one direction only.(wikipedia) (^) An electrical component that allows the flow of current in only one direction. In circuit diagrams, a diode is represented by a triangle with a line across one vertex.(Britannica)
ANODE (+) - Positive Terminal of the diode CATHODE (-) - Negative Terminal of Diode INSULATING COAT(RESIN) – COVERS THE BODY OF DIODE POSITIVE MATERIAL JUNCTION (P) – A SILICON TYPE WITH ALUMINUM JUNCTION. NEGATIVE MATERIAL JUNCTION (N) – A SILICON TYPE WITH PHOSPHORUS JUNCTION.
(^) GUNN DIODE – USE TO PRODUCE MICROWAVE SIGNALS FROM 10 GHz to THz. It is a Negative Differential Resistance device – also called as transferred electron device oscillator – which is a tuned circuit consisting of Gunn diode with DC bias voltage applied to it.
(^) LASER DIODE - Laser diodes are the most common type of lasers produced, with a wide range of uses that include fiber optic communications, barcode readers, laser pointers, CD/DVD/Blu- ray disc reading/recording, laser printing, laser scanning and light beam illumination.
(^) PHOTODIODE - is a semiconductor device with a P-N junction that converts photons (or light) into electrical current. The P layer has an abundance of holes (positive), and the N layer has an abundance of electrons (negative). It also in reserved biased condition.
(^) STEP RECOVERY DIODE – It is a type of microwave diode use to generate pulses at the very high frequency. It s also called snap-off diode or charge-storage diode. The applications of these diodes are in higher order multipliers and in pulse shaper circuits. The cut-off frequency of these diodes is very high which are nearly at Giga hertz order.