Download Design Options for Transportation and Distribution Network and more Lecture notes Business Management and Analysis in PDF only on Docsity!
DESIGN OPTIONS FOR
TRANSPORTATION AND
DISTRIBUTION
NETWORK
GROUP 4
DESIGN OPTIONS FOR
TRANSPORTATION NETWORK
- (^) DIRECT SHIPPING NETWORK
- (^) DIRECT SHIPPING WITH MILK RUNS
- (^) ALL SHIPMENTS VIA CENTRAL DC
- (^) SHIPPING VIA DC USING MILK RUNS
- (^) TAILORED NETWORK
DIRECT SHIPPING WITH MILK RUNS
- (^) A milk run is a route on which a truck either delivers product from a single supplier to multiple retailers or goes from multiple suppliers to a single buyer location.
- (^) A supplier delivers directly to multiple buyer locations on a truck or a truck picks up deliveries destined for the same buyer location from many suppliers.
- (^) Major decision supply chain manager has to decide on the routing of each milk run. Advantage: ✓ Eliminates intermediate warehouses. Lower transportation cost and increases utilization by consolidating shipments to multiple locations on a single truck.
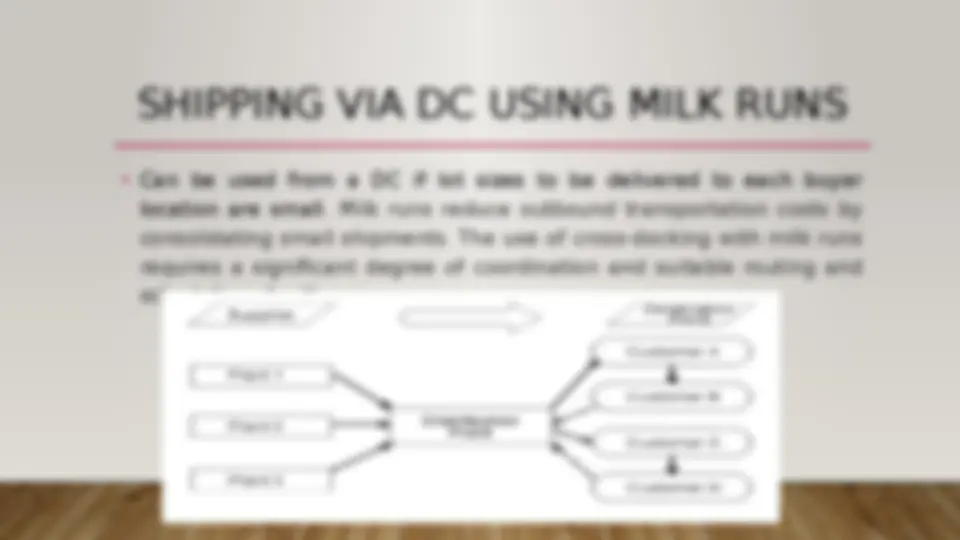
SHIPPING VIA DC USING MILK RUNS
- (^) Can be used from a DC if lot sizes to be delivered to each buyer location are small. Milk runs reduce outbound transportation costs by consolidating small shipments. The use of cross-docking with milk runs requires a significant degree of coordination and suitable routing and scheduling of milk runs.
DESIGN OPTIONS FOR DISTRIBUTION NETWORK
- (^) MANUFACTURER STORAGE WITH DIRECT SHIPPING NETWORK
- (^) MANUFACTURER STORAGE WITH DIRECT SHIPPING AND IN TRANSIT MERGE
- (^) DISTRIBUTOR STORAGE WITH CARRIER DELIVERY
- (^) DISTRIBUTOR STORAGE WITH LAST MILE DELIVERY
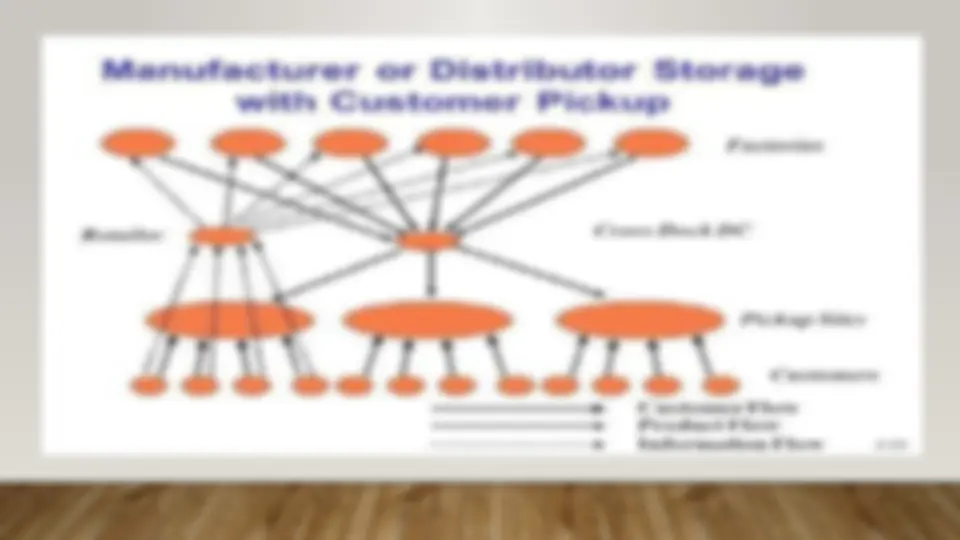
- (^) MANUFACTURER OR DISTRIBUTOR STORAGE WITH CONSUMER PICK UP
- (^) RETAIL STORAGE WITH CUSTOMER PICK UP
MANUFACTURER STORAGE WITH
DIRECT SHIPPING NETWORK
- In this option, product is shipped directly from the manufacturer to the end customer, bypassing the retailer (who takes the order and initiates the delivery request). This option is also referred to as drop shipping. All inventories are stored at the manufacturer. ✓ Products are shipped directly to the consumer from the manufacturer ✓ Retailer is an information collector ✓ Passes orders to the manufacturers ✓ It does not hold product inventory ✓ Inventory is centralize at manufacturers ✓ Drop shipping offers the manufacturer the opportunity to postpone customization ✓ Effective for high value, large variety, low demand products ✓ High transportation cost
Unlike pure drop-shipping, under which each product in the order is sent directly from its manufacturer to the end customer, in-transit merge combines pieces of the order coming from different locations so that the customer gets a single delivery ✓ In-transit merge has been used by direct sellers such as Dell ✓ Best suited for low- to medium-demand, high-value items the retailer is sourcing from a limited number of manufacturers. ✓ Best implemented if there are no more than four or five sourcing locations.
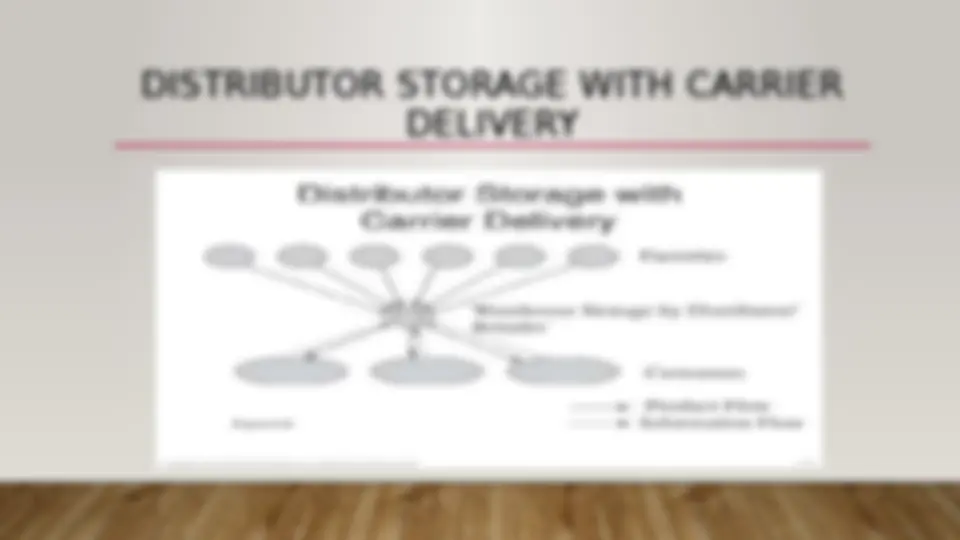
DISTRIBUTOR STORAGE WITH CARRIER
DELIVERY
DISTRIBUTOR STORAGE WITH LAST
MILE DELIVERY
- (^) Last-mile delivery refers to the distributor/retailer delivering the product to the customer's home instead of using a package carrier.
- (^) Can only be justified if there is a large customer segment willing to pay for this convenience. Hence, used if customer orders are large enough to provide economies of scale.
- (^) Distributor storage with the last-mile delivery requires higher levels of inventory than the other options (except for retail stores) because of its lower level of aggregation.
- (^) From inventory perspective, warehouse storage with last-mile delivery is suitable for the FMCG items, as they are needed quickly and some level of aggregation is beneficial for them.
RETAIL STORAGE WITH CUSTOMER PICKUP
- (^) Most traditional types of Supply Chain
- (^) Inventory stored locally at retail store
- (^) Suitable for fast moving items