







Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An examination paper for the control engineering unit of the beng (hons) electrical & electronic engineering program at manchester metropolitan university for the session 2005/2006. The examination covers various topics such as differential equations, transfer functions, laplace transforms, and system stability. Students are required to answer all questions in section a and two questions from section b.
Typology: Exams
1 / 10

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!







Examination for the BEng (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING YEAR/STAGE TWO
Thursday 18 May 2006
9.30 am to 11.30 am
Instructions to Candidates
Answer ALL questions in SECTION A and TWO questions from SECTION B.
Students are permitted to use their own calculators subject to Faculty Guidelines.
The following are provided at the end of this examination:
Answer BOTH questions in this section. (Total 50 Marks)
2
2 Kx t dt
dxt Kyt B dt
dyt B dt
d yt M + + = + [4]
(b) Given that the suspension system constants in question 1(a) are M=10^3 kg , B=2x10^3 N/m/s , K=10^4 N/m, show that the transfer function relating output displacement Y(s) to input displacement X(s) is given by
x(t)
FIGURE Q1(a) Vehicle Suspension system
Vehicle Mass M
y(t)
s s
s X s
Y s [3]
(c) The transfer function that relates output voltage V(s) of a thermocouple (measured in mV) to temperature T(s) (measured in 0 C) is given by
T s s
V s
. What is the steady state gain and time constant of the
thermocouple? [3]
(d) For the thermocouple in question 1(c) use the Laplace tables provided to find the time domain expression for the output voltage, v(t), when there is a step change in temperature of 4^0 C. [4]
11/07/2006 S165 Question 1 continued overleaf
function ( )
G s s
at a frequency of 3 rad/s. [4]
(b) Estimate the gain and phase of a system for the system described by
the transfer function ( )
G s s s
at low and high frequencies,
and sketch the Nyquist diagram. State, with reasons, whether the system is open loop stable or not. [4]
(c) Define what is meant by “phase margin” and “gain margin” in the context of frequency response analysis. [4]
(d) What is the gain and phase margins for the system whose frequency response is shown in Figure Q2(c). [4]
(e) Briefly explain what is meant by “scanning process” in the operation of a PLC. [3]
(f) Explain what is meant by “regulatory” control or “servo” control and state, with reasons, which of the two categories do the following problems fall into.
(i) Cruise control system (ii) Antenna tracking system [6]
0
50
100
Magnitude (dB)
10 -2^10 -1^100 101
Phase (deg)
Bode Diagram
Frequency (rad/sec)
FIGURE Q2(c)
11/07/2006 S165 continued
Answer TWO questions in this section. (25 marks each)
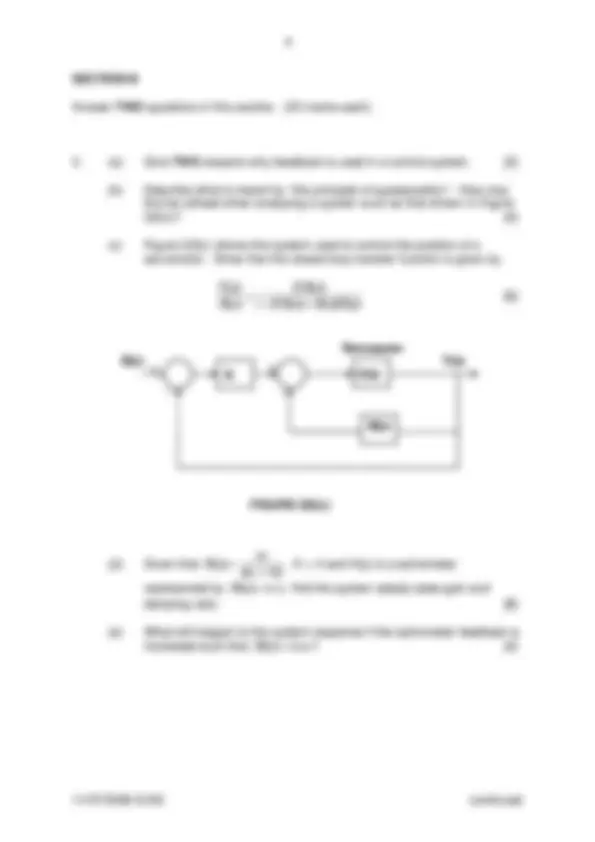
(b) Describe what is meant by “the principle of superposition”. How may this be utilised when analysing a system such as that shown in Figure Q3(c)? [4]
(c) Figure Q3(c) shows the system used to control the position of a servomotor. Show that the closed loop transfer function is given by
KGs GsH s
KGs Rs
Y s 1 + +
Y(s)
Servomotor
H(s)
R(s)
FIGURE Q3(c)
G(s)
(d) Given that ( )
ss
G s , K = 4 and H(s) is a tachometer
represented by find the system steady state gain and damping ratio. [8]
H ( s ) = 0. 1 s
(e) What will happen to the system response if the tachometer feedback is increased such that H ( s ) = 0. 6 s? [4]
11/07/2006 S165 continued
(b) Figures Q5(b)(i) – (b)(iii) show three Nyquist plots.
(i) ( 1 )( 2 )( 3 )
s s s
Gs
(ii)
-0.4 -1.5 -1 -0.5 0
-0.
-0.
-0.
0
( 1 )
s s
G s n
(iii)
-0.5 0 0.5 1
-0.
-0.
-0.
-0.
0
-0.5^ -1 0 0.5 1 1.
-0.
0
FIGURE Q5b(i)
FIGURE Q5b(ii)
FIGURE Q5b(iii)
(i) State the value for K for Fig. Q5(i). (ii) State the value for n for (ii). (iii) Give the form of the transfer function for (iii) [6]
11/07/2006 S165 Question 5 continued overleaf
Question 5 continued
(c) A subset of data obtained from a frequency response test on a process is shown in Table T5. Using this data:
(i) Determine the gain margin and phase margin of the system. (ii) Comment on the relative stability of the system in unity feedback closed-loop control configuration. (iii) Comment on the nature of the closed-loop response to a unit step input. [6]
(d) If a proportional controller is introduced into the forward path of the closed-loop system, determine the controller gain such that the closed- loop system will have a phase margin of 40o. What will be the new gain margin? Comment on the stability of the closed-loop system with the proportional controller included. [7]
Frequency (rad/s)
Gain 2.46 1.74 1.30 1.00 0.73 0. Phase (deg)
(b) Explain how the main processor in a PLC is protected from potential surges from a field device. [4]
(c) What are the main functions of the executive program in a PLC? [3]
(d) Give examples of TWO input field devices in a typical industrial environment using PLC-based control. [2]
11/07/2006 S165 Question 6 continued overleaf
Second order time domain relationships
per unit overshoot = ⎟
exp ζ
ζπ
n
tr
n
ζω