

Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
cheat sheet - stats: probability and decision tree, Cheat Sheet of Statistics
stats cheat sheet for descriptive stats course. conditional probabilities and decision tree
Typology: Cheat Sheet
Uploaded on 06/25/2023
1 document
1 / 1

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!

Related documents
Partial preview of the text
Download cheat sheet - stats: probability and decision tree and more Cheat Sheet Statistics in PDF only on Docsity!
0<P(E)<1 ; P(E) =E/S GENERAL ADDITION RULE P(A)+P(B)-P(A&B) – (OVERLAP): P(A^ or^ B)^ COMPLEMENT RULE P(not E) =1 – P(E) Quality 10-19 20-29 30-39 40- Goo d 0.140 0.133 0.007 0.000 0. Very Go od 0.113 0.213 0.153 0.020 0. Excellent 0.007 0.047 0.093 0.073 0. Total 0.260 0.393 0.253 0.093 1.
Price Range Total Joint Pr (2 E simultaneously): (Good & 10-19=0.140;
Union P: (Good or 10-19) = .26+.28-.14=.40 (Elim doub count)
Marginal P: P(Good)=0.28; P(10- 19 )=0.26 *unconditional Pr
Conditional Probability: Pr of Event GIVEN another event is true: P(G|10-19)=0.14/0.26=0.538; P(10-19|G) = 0.14/0.28 = 0. Allows us to create Pr distributions from subsets of contingeny table
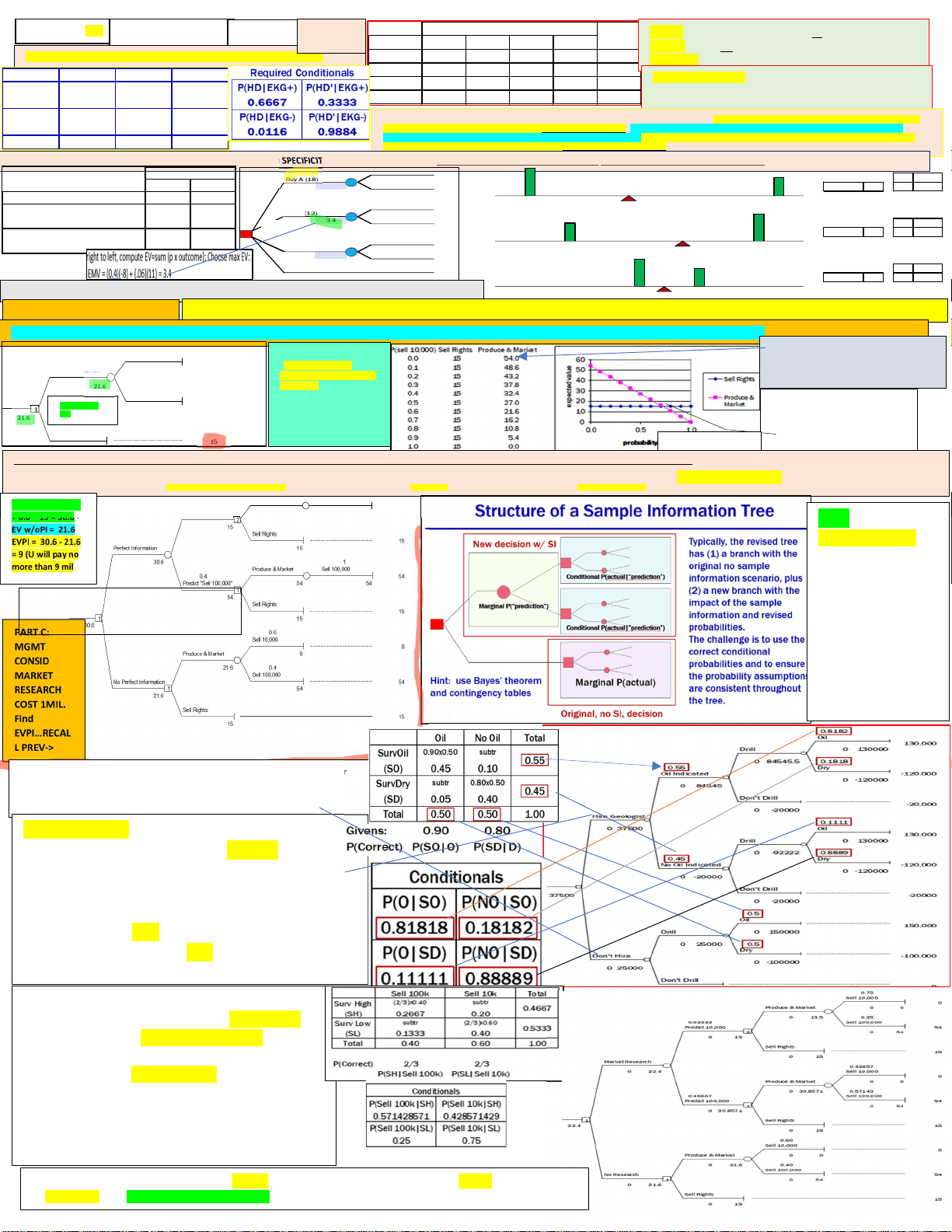
P(EKG+/HD )= 0 .9; P(EKG-/HD) = 0 .1; P(EKG-/HD’) = 0 .95; P(EKG+/HD’) = 0.
P(HD) = 0. P(HD’) = 0. HD HD' Totals (.1)(.9) subtract Σ across 0.09 0.045 0. subtract (.9)(.95) Σ across 0.01 0.855 0. Totals 0.10 0.90 1.
EKG+
EKG- What we want is the probability of having heart disease given the patient’s test result P(HD) = 0.10 and P(HD’) = 0.90, are called PRIOR PROBABILITIES..The role of Bayes Theorem is to revise these probabilities base on new…The unconditional probabilities we start with initially^ – information, which is typically a test, like the EKG in our example…The probabilities derived from the use of Bayes Theorem, which is new conditional probability distribution, are called POSTERIOR PROBABILITIES P(EKG+/HD) = SENSITIVITY; P(EKG-/HD) = FALSE NEG; -- P(EKG-/HD’) = SPECIFICITY; P(EKG+/HD’) = FALSE POS;; POSITIVE PREDICTIVE VALUE P(HD/EKG+); NEGATIVE PREDICTIVE VALUE P(HD’/EKG-) A B Current purchase price $18 $ Present value of future cash flows if hotel and airport ARE built at this location $31 $ Present value of future sale of parcel if airport IS NOT built at this location $6 $ (Amounts are in millions) Parcel of Land Location Buy A (18)^31 0. -2.0 6 0. Buy B (12) (^) 3.4 234 0.40. Buy A & B (30) 1.4 3529 0.40. Buy Neither 5
- 0 A B 13
11 A B A MAX = EMV^ B Don’t “expect” to get expected value. It’s simply prob-weighted avg outcome. repeat, ev would be long-term avg. -15 -12 -10 -5 0 5 10 13 15 -15 -10 -8 -5 0 5 10 11 15 -15 -10 -5 -1 0 5 10 15
EV 1. Range 6 σ 1. EV -2. EV 3. Range 19 σ 3. Range 25 σ 4. NPV NPV NPV A B A&B 0.
-2.
Comparing Risk profile shows A has greatest risk, widest range, and A&B the lowest risk, narrowest range; It also shows that while B has a higher EV than A&B, it also has more than 3x the risk
PART A: BELOW Draw & Solve dec. tree to help silicon w/ problem. Assuming prob of 2 level of sales 0.6 (10k) & 0,4 (100k), which alt should be chosen (600 per device)
PART A (^) Sell 10,0000.6 (10K)(600) Produce & Market 0 0 0 –^ 6MM= 0 0 21.6 (^) Sell 100,0000.4 (100K)(600) 1 0 54 54 = 54MM–^ 6MM
Sell Rights 15 00.6+540.4 =
PART B: DEVELOP ->
*It is unclear what the probabilities of the two levels of sales are. *GRAPGH THAT PLOTS EXPECTED PAYOFFOF EACH ALT VS PROB OF SELLING 10K COMP. *SOLVE FOR INTERSEC PT. EXPLAIN SIGNIFICANCE
P0+(1-P)54 = 15
54 – 54*P = 15
39 = 54P
Intersection/ break even point P = 39/54 = 0.
P*0 + (1-P) * 54 = EV
We will change P to find the EV
The VALUE of the information is the DIFFERENCE between value WITH the information and the value WITHOUT the information…{The value WITHOUT the information is what we already CALCULATED (THE EV)]. EVPI places an upper bound what we would pay for add info. EVPI is MAX you should pay to learn the future… EVw/PI = Value with Perfect Information (sometimes called EPPI=Exp profit/ perfect ingo); EVw/oPI = Value without Perfect Information (this is just EV of original) ….. EVPI = VOPI = EVw/PI – EVw/oP: W/PI, Residens Inns’ expected paoff would be: EV with PI = 0.4$13 + 0.6$11 = $11. 8 (take the best from A nd B); W/O PI, EMV was 3. 4 …the expected value of perfect info is: EVPI – 11. 8 – 3.4= 8.
PART C:
MGMT
CONSID
MARKET
RESEARCH
COST 1MIL.
Find
EVPI…RECAL
L PREV->
EV w/ PI = 0.4*
- 0.6 * 15 = 30.6 - EV w/oPI = 21. EVPI = 30.6 - 21. = 9 (U will pay no more than 9 mil Produce & Market Sell 10,000^1 Predict "Sell 10,000"^ 0.6^0 152 Sell Rights 15 Perfect Information 15 30.6 (^) Produce & Market Sell 100,000 1 Predict "Sell 100,000"^ 0.4^54 541 Sell Rights 15 30.6^1 Sell 10,000^ 0. Produce & Market 0 0 21.6 (^) Sell 100,0000. No Perfect Information 1 54 54
Sell Rights 15 15
VOSI (or EVSI) =
EVw/SI – EVw/oI
1)revised sample info;
2)fill in table w/ revised
data 3)bayes theorem for
conditional prob *ensure
proper order of P*
- use a probability table to apply Bayes Theorem
- fill table, start with givens; calculate -bottom margin prob stay the same*
- new sample daat on left column -new dec tree branch. Same struct as orig dec, but w/ diff P and values -survey cost is reflected in payoffs EXERCISE 1 (Complete EV & EVPI: An Alberta oil company routinely seeks new sites for oil drilling. With no other information, there is a 50-50 chance of striking oil. If oil is found, a profit of $150,000 is realized. If the site is dry, a loss of $100,000 is incurred. Find the optimal strategy and the EVPI.

