































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
The concepts of friction and deformation in the context of solid mechanics. Topics include the types of friction, friction coefficients, deformation of rings and hoops, tension of ropes, and applications of friction. The document also includes equations and calculations for determining forces, deformations, and changes in length.
What you will learn
Typology: Lecture notes
1 / 42

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!



































Friction
Types of friction
Types of friction
Typical friction coefficients
Surface μ
s
μ
k
Velcro on Velcro 6.0 5.
avg tire-on-dry pavement 0.9 0.
Grooved tire-on-dry pavement 0.8 0.
Glass on glass 0.9 0.
Metal on metal (dry) 0.6 0.
Metal on metal (lubricated) 0.1 0.
Steel on teflon 0.05 0.
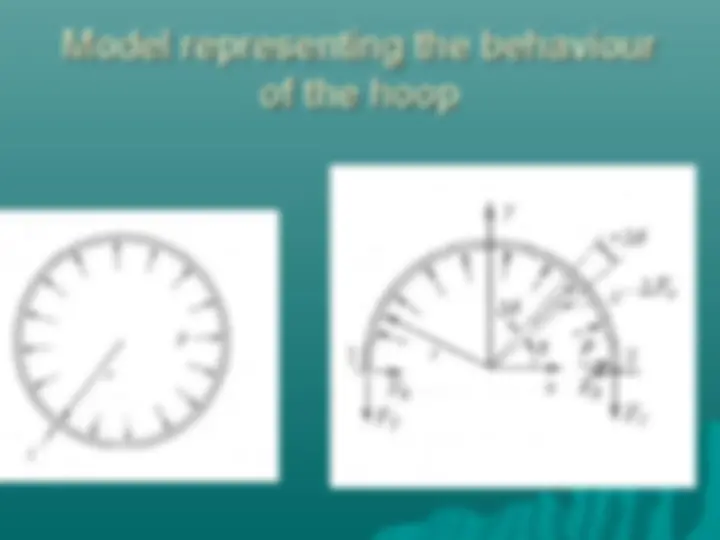
Ring subjected to uniform pressure
Ring subjected to uniform pressure
A thin ring of
A thin ring of
internal radius r,
internal radius r,
thickness t and
thickness t and
width b is
width b is
subjected to an
subjected to an
internal pressure p
internal pressure p
Determine the
Determine the
forces in the ring
forces in the ring
and the
and the
deformation of the
deformation of the
ring
ring
Force equilibrium equations
Force equilibrium equations
∑
∑
y
y
T
T
T
T
Force Deformation Relation
Force Deformation Relation
The increase in circumference can be
The increase in circumference can be
obtained from the relation:
obtained from the relation:
δ
δ = PL/AE
The change in circumference of the hoop
The change in circumference of the hoop
is thus:
is thus:
δ
δ
TT
TT
π
π (r+t/2) /(bt)E
(r+t/2) /(bt)E
Where F
Where F
T
T
= prb
= prb
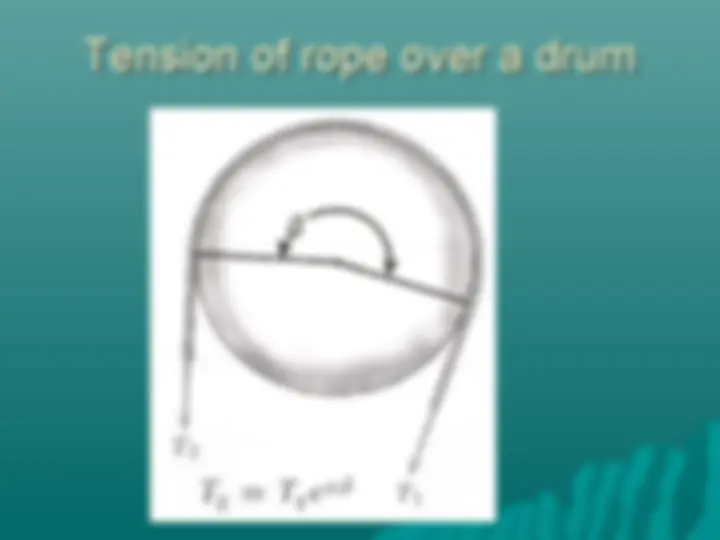
Tension of rope over a drum
Tension of rope over a drum
Frictional forces
Frictional forces
Load is applied on one end of the rope
Load is applied on one end of the rope
while the other end is anchored in a
while the other end is anchored in a
support.
support.
By increasing the total applied force at the
By increasing the total applied force at the
same (maximum) power setting, the
same (maximum) power setting, the
motor rpm will decrease.
motor rpm will decrease.
Rpm can be measured by a tachometer or
Rpm can be measured by a tachometer or
stroboscope.
stroboscope.
Thus torque versus rpm characteristics can
Thus torque versus rpm characteristics can
be obtained.
be obtained.
To torque a smooth bar, use plenty of
To torque a smooth bar, use plenty of
turns of rope to get a grip.
turns of rope to get a grip.
Apply the torque using a lever. To maintain
Apply the torque using a lever. To maintain
the surface finish, you can also use a
the surface finish, you can also use a
cushioning material.
cushioning material.