Download Introduction to Mechanics: Free Body Diagrams, Equilibrium, and Force Analysis and more Lecture notes Mechanics in PDF only on Docsity!
ESO202A-204:ESO202A-204:
Mechanics of Solids Mechanics of Solids
Introduction Introduction
S.Kamle S.Kamle
Aerospace Engg. Department Aerospace Engg. Department
Outline of Today’s lectureOutline of Today’s lecture
About the courseAbout the course
Review of physics concepts- Force,Review of physics concepts- Force,
Moment, vectors Moment, vectors
Introduction to Mechanics- FreeIntroduction to Mechanics- Free
Body Diagram Body Diagram
About ESO202A-ESO204About ESO202A-ESO
The course is being developed as a webThe course is being developed as a web
based course. All Home Work sheets, based course. All Home Work sheets,
Quiz / Exam. solutions will be posted on Quiz / Exam. solutions will be posted on
Brihaspati. Brihaspati.
Course content available on-line at Course content available on-line at
Brihaspati: Brihaspati:
http://brihaspati.nmeict.in/brihaspati/servlet/b http://brihaspati.nmeict.in/brihaspati/servlet/b
You can login As guest (The password isYou can login As guest (The password is
also guest). also guest).
Course ContentsCourse Contents
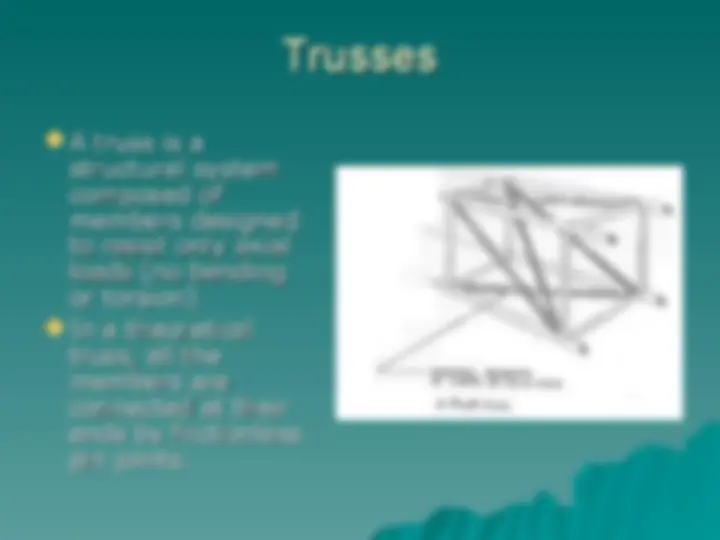
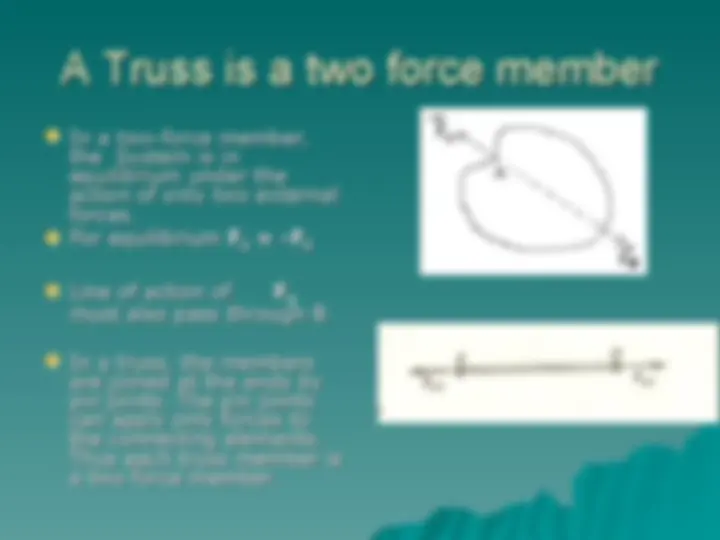
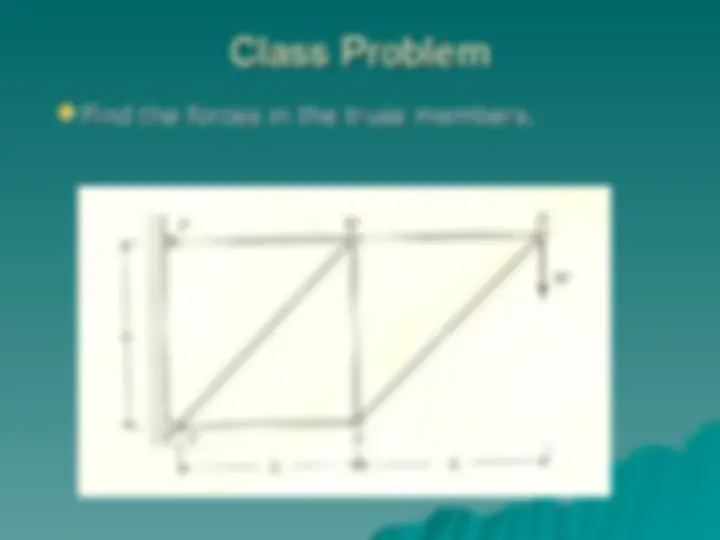
Free body diagram, Modeling ofFree body diagram, Modeling of
supports, Conditions for equilibrium, supports, Conditions for equilibrium,
friction. friction.
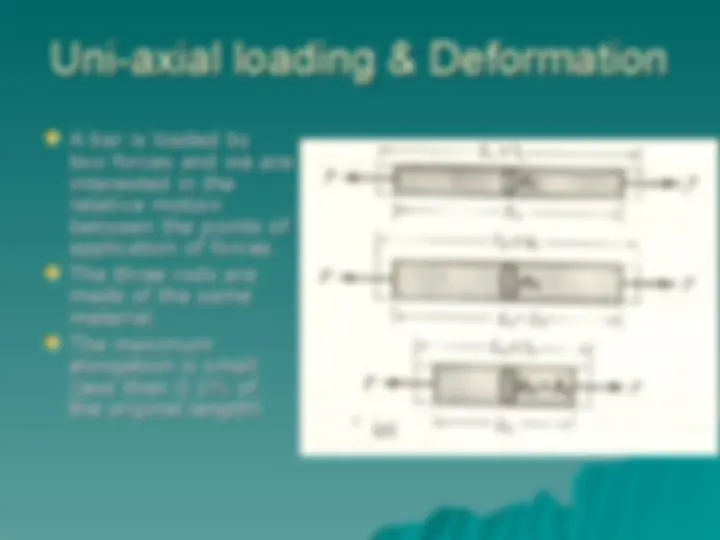
Force-deformation relationship andForce-deformation relationship and
geometric compatibility (for small geometric compatibility (for small
deformations) with illustrations deformations) with illustrations
through simple problems on axially through simple problems on axially
loaded members and thin-walled loaded members and thin-walled
pressure vessels pressure vessels
Course ContentsCourse Contents
(^) Discussion of experimental results on 1-D stress-Discussion of experimental results on 1-D stress- strain curve, Concepts of isotropy, orthotropy, strain curve, Concepts of isotropy, orthotropy, anisotropy, Generalized Hooke's law (without and anisotropy, Generalized Hooke's law (without and with thermal strains), Complete equations of with thermal strains), Complete equations of elasticity, elasticity, (^) Torsion of circular shafts and thin-walled tubesTorsion of circular shafts and thin-walled tubes (plastic analysis and rectangular shafts not to be (plastic analysis and rectangular shafts not to be discussed). discussed). (^) Bending of beams with symmetric cross sectionBending of beams with symmetric cross section (Normal and shear stresses) (shear center and (Normal and shear stresses) (shear center and plastic analysis not to be discussed). plastic analysis not to be discussed).
Course ContentsCourse Contents
Combined stresses, Yield criteria.Combined stresses, Yield criteria.
Deflection due to bending,Deflection due to bending,
Integration of the moment-curvature Integration of the moment-curvature
relationship for simple boundary relationship for simple boundary
conditions, Superposition principle conditions, Superposition principle
(singularity functions not to be (singularity functions not to be
used). used).
BooksBooks
Text BookText Book
S.H.Crandall, N.C.Dahl and T.J.Lardner,S.H.Crandall, N.C.Dahl and T.J.Lardner,
"An introduction to the mechanics of "An introduction to the mechanics of
solids", second edition with SI units, solids", second edition with SI units,
McGraw Hill 1978 McGraw Hill 1978
Reference Books Reference Books
Shames I.H., "Engineering MechanicsShames I.H., "Engineering Mechanics
Statics and Dynamics", Prentice Hall of Statics and Dynamics", Prentice Hall of
India, 1996 India, 1996
Popov E.G. "Engineering mechanics ofPopov E.G. "Engineering mechanics of
soilds", Prentice Hall of India, 1993 soilds", Prentice Hall of India, 1993
Grade Break-upGrade Break-up
Method Of evaluation Weightage
Mid. Sem. Exam.15 Feb 30%
End Sem. Exam.18 April 40%
Quiz(best 3 of 4 quizzes) 15%
Home Work 8%
Attendance 7%
Vector AnalysisVector Analysis
(^) Vectors have aVectors have a starting point at one starting point at one end (tail) and an end (tail) and an arrow at the opposite arrow at the opposite end (head). The tail is end (head). The tail is located at the point of located at the point of origin. origin. (^) Component vectorsComponent vectors can be determined by can be determined by plotting them on a plotting them on a rectangular coordinate rectangular coordinate system system
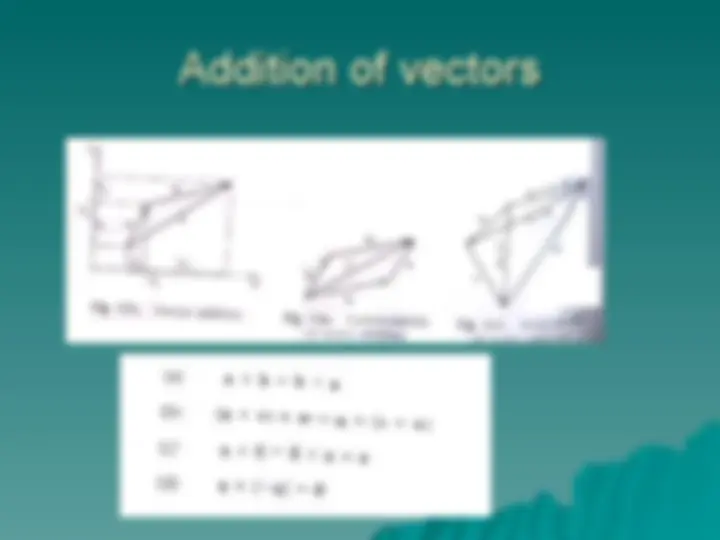
Addition of vectorsAddition of vectors
When twoWhen two or more vectors are added theyor more vectors are added they
yield the sum or resultant vector. yield the sum or resultant vector.
Vector operationsVector operations
Dot ProductDot Product
Projection of a vectorProjection of a vector
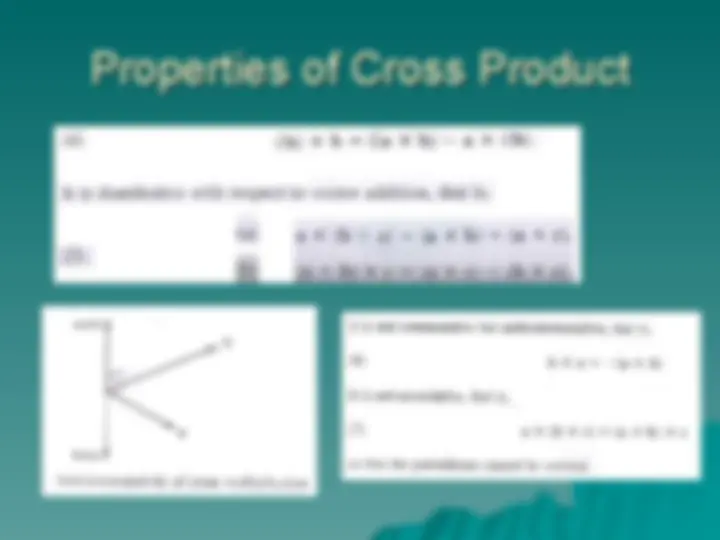
Cross ProductCross Product