


























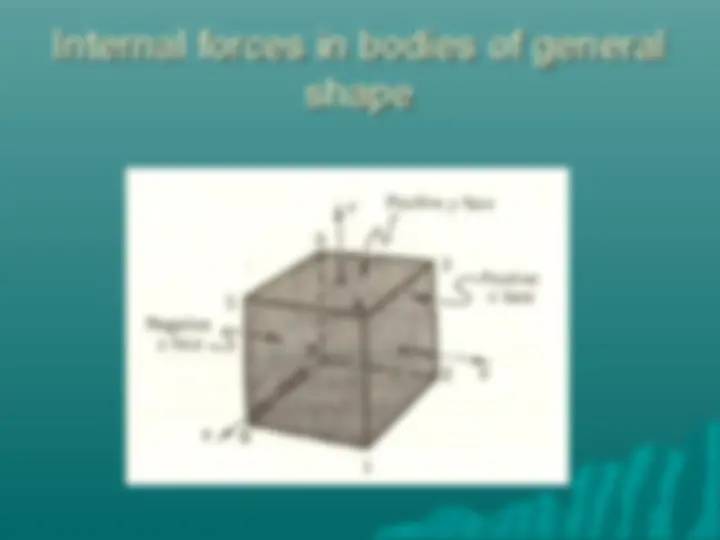


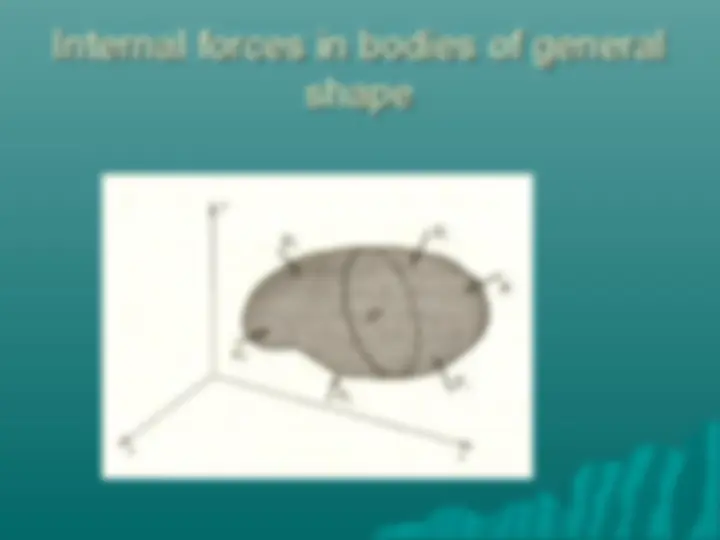
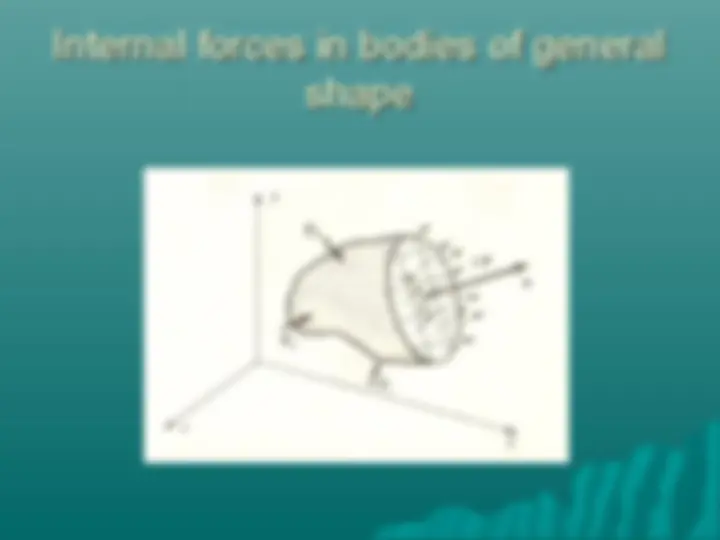
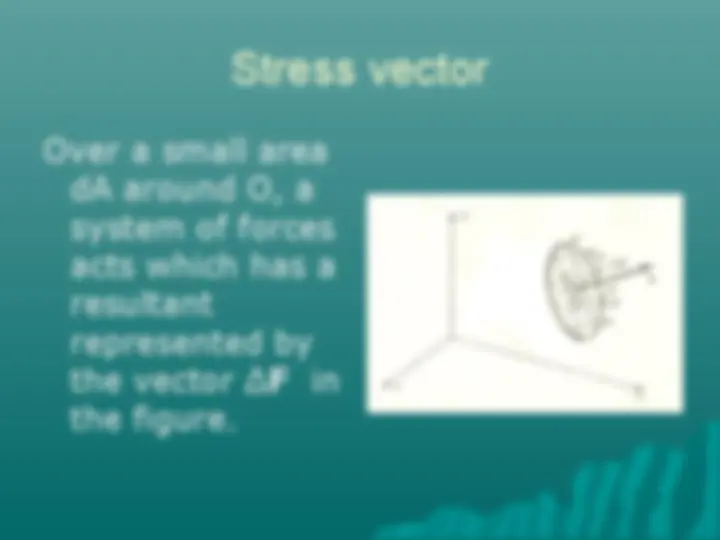















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
beam bending,deflection,buckling,mechanics of solid
Typology: Lecture notes
1 / 64

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!

























































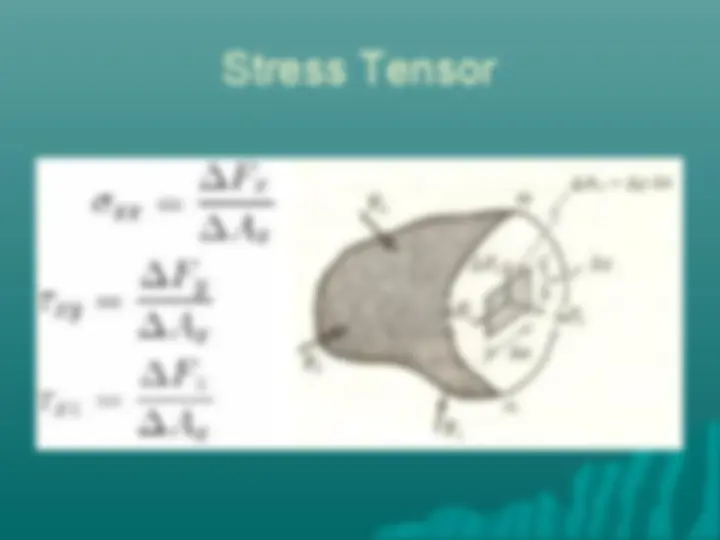
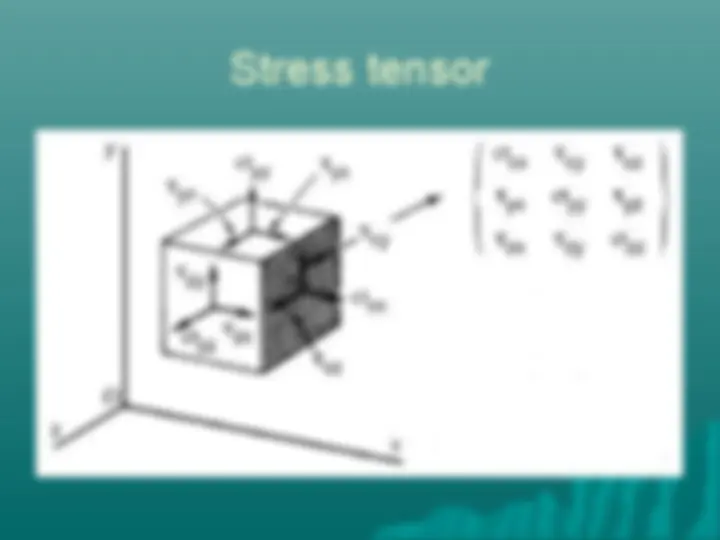
What is AxialWhat is Axial stress? stress? Axial Stress = Load/Axial Stress = Load/ AreaArea Axial Strain = Change in length per unitAxial Strain = Change in length per unit length length Modulus of elasticity = Stress/StrainModulus of elasticity = Stress/Strain We will generalize the definition of stressWe will generalize the definition of stress and define stress equal to force/area and define stress equal to force/area
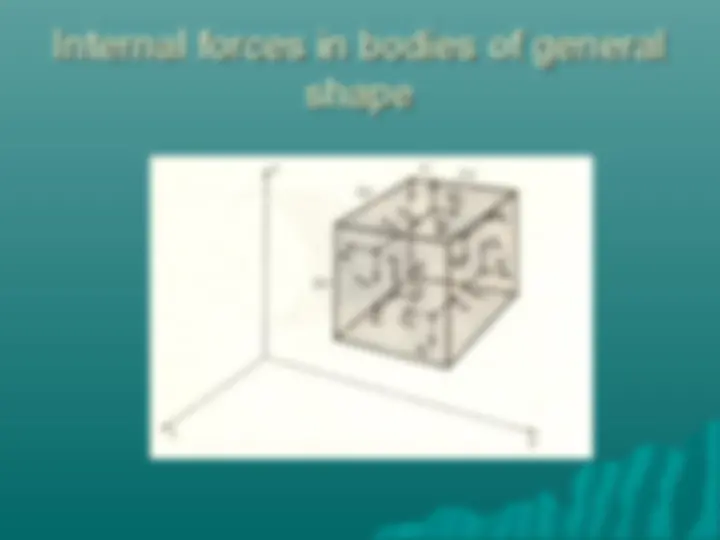
Shear Stress Shear stress acts tangential to the surface of a material element Shear stress results in a shape change
Shearing stresses Bolt in Single shear Shearing stresses commonly found in bolts and rivets
Shearing stresses Bolt in Double shear Shearing stresses commonly found in bolts and rivets
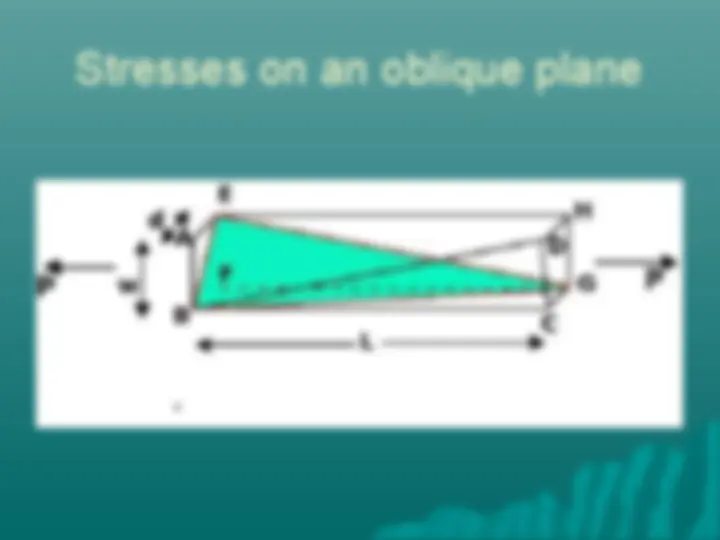
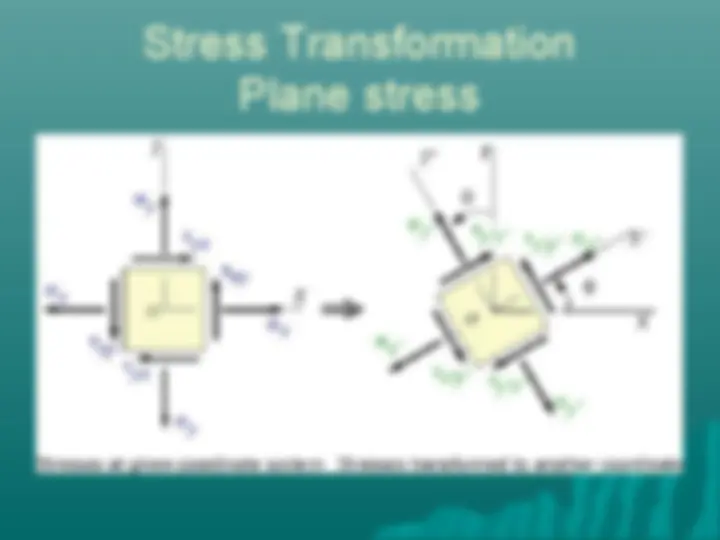
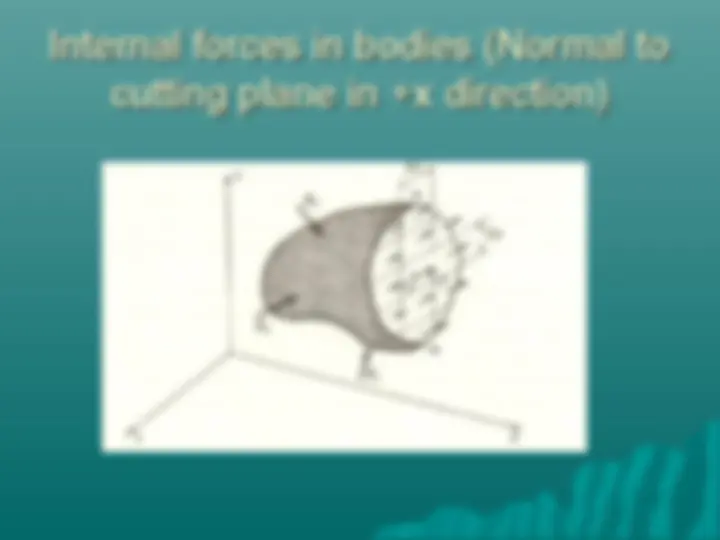
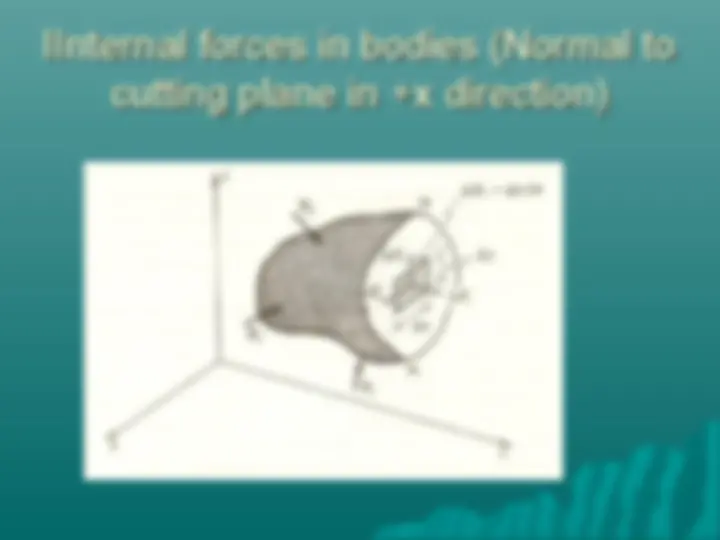
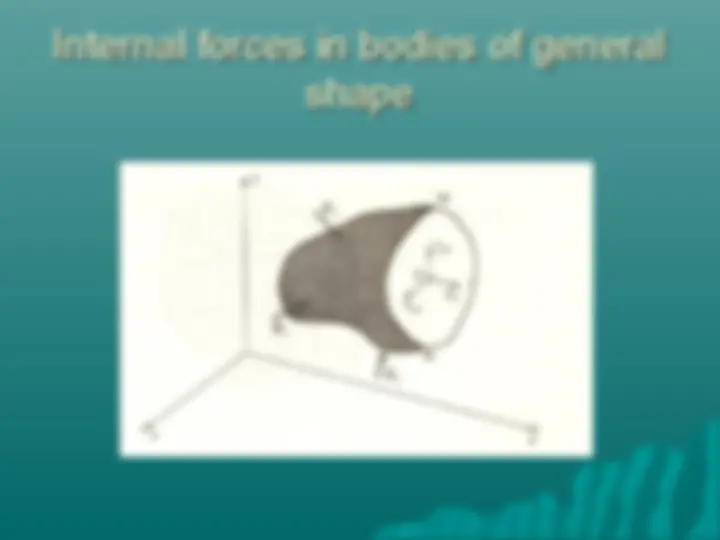
Stresses on an oblique plane Axial forces cause both normal and shearing stresses on planes which are not perpendicular to the axis.
Stresses on an oblique plane Magnitude of Normal Stress σ= Q/A θ Or, σ= (P/ A 0 )cos 2 (θ) Magnitude of Shear stress τ = V/A θ Or, τ = (P/ A 0 )cos(θ)sin(θ)
Stress on an oblique plane
Stresses on an oblique plane Consider the special case when angle θ= Axis x' coincides with x axis Axis y' coincides with y axis Normal stress σ xx
0
Or, σ x'x' = σ xx cos 2 (θ) Similarly, τ x'y' =- σ xx cos(θ)sin(θ)
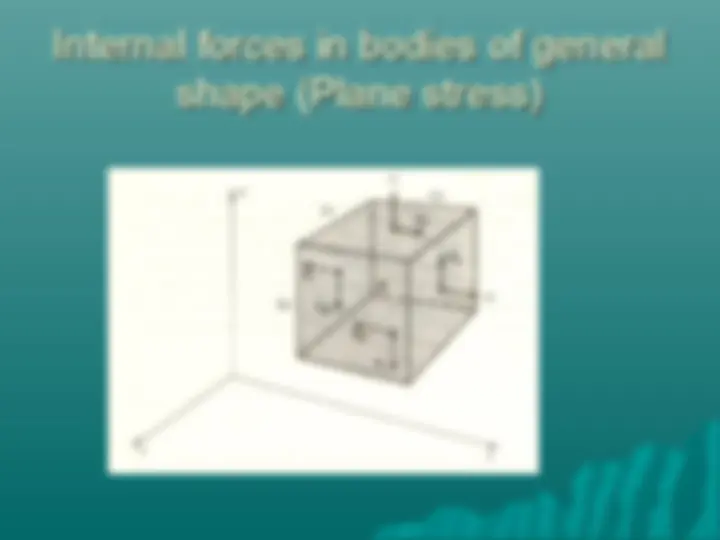
Stresses on an oblique plane Normal force applied to a bar on an inclined sction produces a combination of shear and normal stresses.
Stresses on an oblique plane
Stresses on an oblique plane
Stresses on an oblique plane
Stresses on an oblique plane