

Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
A reviewer for the final exam in Anatomy and Physiology, specifically focusing on the digestive system. It covers the functions of the digestive system, the parts of the gastrointestinal tract and accessory glands, the histology of the GI tract, and the regulation of stomach secretions. It also discusses the small and large intestines, the accessory glands (liver, gall bladder, and pancreas), and the male and female reproductive systems.
Typology: Lecture notes
1 / 6

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!




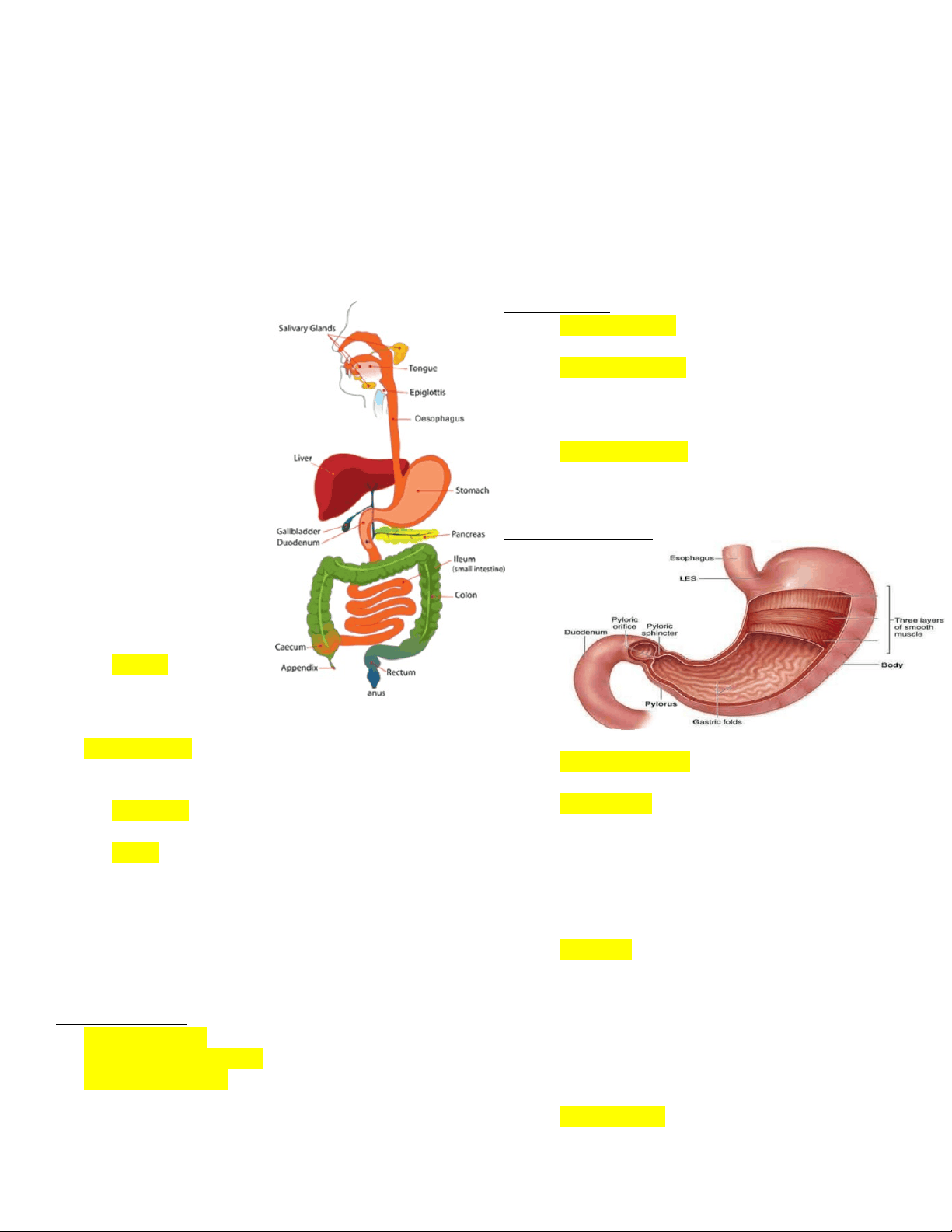
2 PARTS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
GI/ DIGESTIVE TRACT
GI TRACT HISTOLOGY
Parts : Lips & Cheeks – mastication and speech Tongue (7th^ Cranial Nerve)– speech, taste, mastication, & swallowing SALIVARY GLANDS
Connects pharynx to the stomach Upper esophageal sphincter Lower esophageal sphincter (cardiac sphincter/ gastroesophageal sphincter )
3 Wall Muscle Layers Longitudinal Circular Oblique
SMALL INTESTINE
- major site for absorption Goblet cells & duodenal glands - produces mucus Most of the absorption occurs in the duodenum and jejunum. PARTS OF THE SMALL INTESTINE 1. Duodenum – “First Part” has ligaments of troits which keeps the small intestine fix. 2. Jejunum 3. Ileum *APPENDIX
LARGE INTESTINE Function : water absorption & feces production Ileocecal junction/valve – is a one-way valve in waste secretion. It separates the small intestine’s ileum and large intestine’s ascending colon.
PARTS OF THE LARGE INTESTINE
ACCESSORY GLANDS
LIVER Has 4 lobes Production of BILE – which helps in the digestion of fats and lipids It stores and processes nutrients and detoxifies molecules
GALL BLADDER (Storage for bile concentrations) It stores, concentrates and secretes the BILE.
CYSTIC DUCT – connected to common hepatic duct forming the common bile duct. EXIT : Ampulla of Vater
PANCREAS
Amylase – digest carbohydrates Lipase – digest lipids Protease – digest proteins Trypsin
ADDITION INFO:
URETERS 25-30cm It collects the urine that is secreted by the kidneys and propel it to the bladder by peristaltic waves.
URINARY BLADDER Hollow, spherical, collapsible bag of smooth muscles. Reservoir for urine: 200-300cc: first urge 500-600cc: mod full 1000-1800cc: max capacity Influenced by the Autonomic Nervous System.
URETHRA Female: 3-5 cm Male: 20cm
ADDITIONAL INFO:
GAMETES (Sex cells) – basic structural and functional unit of the reproductive system. EXOCRINE FUNCTION – Gametes ENDOCRINE FUNCTION – Hormones
TESTES (Male Gonads) “Golf Ball” Primary reproductive organ of the male. Surrounded by Tunica Albuginea (white coat). – inner most layer and Tunica Vaginalis (outermost layer). SPERMATIC CORD – connects testes to the trunk and it contains blood vessels. DUCTUS/VAS DEFERENS – passage for sperm. SEMINIFEROUS TUBULES – creates/ produces sperm; it brings the sperm to rete testis to the duct system. SEMEN – protects the sperm (2-5ml) 1tbsp.
DUCT SYSTEM (Accessory Gland) EPIDIDYMIS – temporary storage for immature sperm to mature (20 days to mature) DUCTUS/VAS DEFERENS – upward tube through spermatic cord
URETHRA – “terminal duct” the urine and semen would never pass at the same time. ASPERMIA – absence of sperm but has semen.
ACCESSORY GLANDS:
SCROTUM “Pouch” PENIS Deliver sperm into the female reproductive tract. Glans Penis – enlarged tips Prepuce/ foreskin – sleeves around the glans. SPERMATOGENESIS Occurs in the seminiferous tubules of testes. SPERM PARTS:
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) – stimulates seminiferous tubules tio produce sperm. Luteinizing Hormone (LH) – stimulates interstitial cells of Leydig to produce testosterone. TESTOSTERONE “Masculinizing Hormone” Primary sec characteristic (Libido, reproductive organ development) Secondary sex characteristics (Voice deepening, Body hair growth, bon growth)
OVARIES (female Gonads) -almond shape Production, menstruation, secretion Contains sac-like ovarian follicles which contains immature egg cells (oocytes). OVULATION – releases mature egg cells on the 14th^ day of menstrual cycle Produces estrogen and progesterone Order of cycle:
Uterine Tubes Uterus Vagina
FALLOPIAN TUBE (uterine) 4 PARTS: