









Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
A compilation of lectures and activities
Typology: Slides
1 / 14

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!









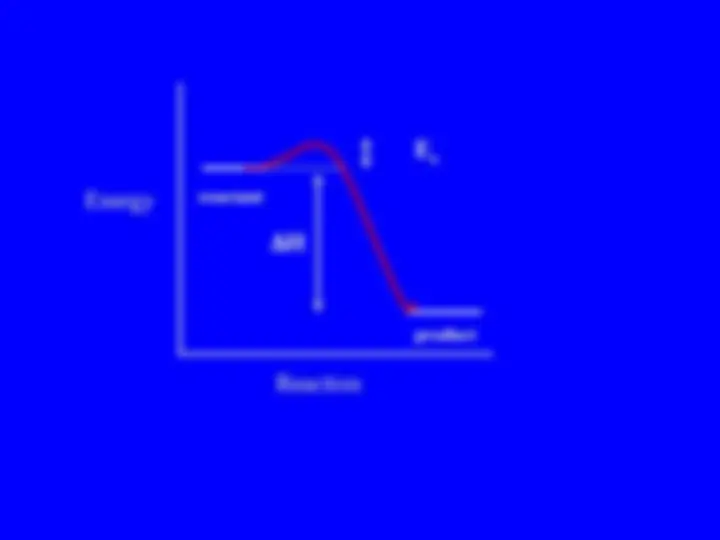
The Difference Between Equilibrium and Kinetics?
Energy
Reaction
NO!
reactant
product
Energy
Reaction
reactant
product
E a
H
aA + bB cC + dD
K = [C]
c [D]
d
[A]
a [B]
b
= constant if at equilibrium
Became interested in the conditions
needed for equilibrium in chemical
reactions after examining some
unexpected results at a mine's furnace.
In 1888, he stated what became known as the
Le Chatelier principle: every change in one of
the factors of an equilibrium occasions a
rearrangement of the system in such direction
that the factor in question experiences a
change in the sense opposite to the original
change.
Fe 2
O 3
Fe 2
O 3
C Fe + CO 2
CO
CO 2
C + CO
Fe 2
O 3
The reaction was thought to be:
Henri noticed CO was also made:
EUREKA!
The CO 2
was in equilibrium
o
o
o
- -32. - +6. - -20. - -33. Gibbs Free Energy Changes
Rxn# Enzyme
G°'
(kJ/mol)
1 Citrate synthase -32.
2 Aconitase +6.
3 Isocitrate dehydrogenase -20.
4
a-Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
complex
5 Succinyl-CoA synthetase -2.
6 Succinate dehydrogenase 0.
7 Fumerase -3.
8 Malate dehydrogenase +29.
Overall free energy -57.6 kJ/mol
Biochemical Energetics