




Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
this contains discussion about amino acids and proteins
Typology: Lecture notes
1 / 5

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!




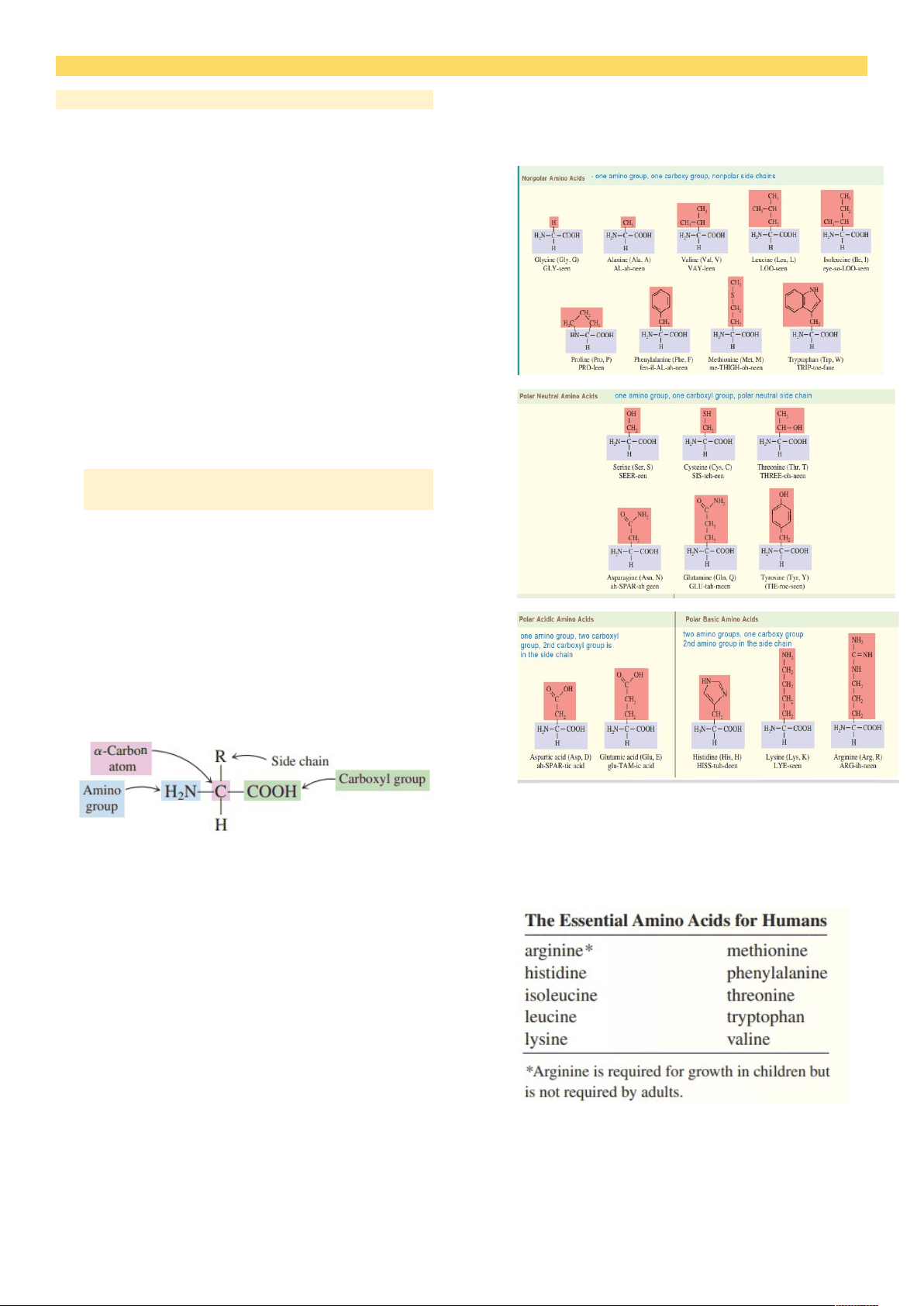
Account for 15% of a cell’s overall mass Contain CHON/S (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur) Nitrogen is always present in protein, unlike in carbohydrates and lipids Nitrogen content: 15.4 % Specialized proteins like casein and hemoglobin contain phosphorus and iron, respectively Naturally occurring, unbranched polymer Monomer units: amino acids I. AMINO ACIDS: THE BUILDING BLOCKS FOR PROTEINS An organic compound Contains an amino group(-NH 2 ) and carboxyl group(-COOH) amino acids found in proteins are always a-amino acids a-amino acids
- (-NH 2 ) & (-COOH) are always attached to a-carbon atom General formula: R-GROUP
BASIC Higher than 6. ACIDIC Lower than 4. ELECTROPHORESIS
based on how many PEPTIDE CHAIN PRESENT MONOMERIC Only one peptide chain present MULTIMERIC More than one peptide chain present based on CHEMICAL COMPOSITION SIMPLE Only amino acid residues are present CONJUGATED Non-amino acids (prosthetic) + peptide chains based on SHAPE FIBROUS Molecules are elongated shape; linear “Water-insoluble” GLOBULAR Molecules are folded into spherical or globular shape “Water-soluble” MEMBRANE protein that is found associated with a membrane system of a cell. “Water-insoluble” based on FUNCTION Class Function examples CATALYTIC
- catalyze biochemical reactions in the cells - Participate in metabolic reactions in the body Enzymes – biochemical catalyst Sucrase Trypsin DEFENSE Recognize and destroy foreign substances Immunoglobulins Antibodies TRANSPORT carry essential substances throughout the body Hemoglobin Lipoprotein MESSENGER Transmit signals to different parts of the body Insulin Glucagon Human growth hormone CONTRACTILE Move muscles Actin Myosin STRUCTURAL Provide structural component Collagen keratin TRANSMEMBRANE Control movement of small molecules and ion through the cell membrane STORAGE Store nutrients Ferritin myoglobin REGULATORY Control enzymatic actions rhodopsin NUTRIENT Nourish and provide immunological Casein Ovalbumin
protection for young PROTEIN HYDROLYSIS