
































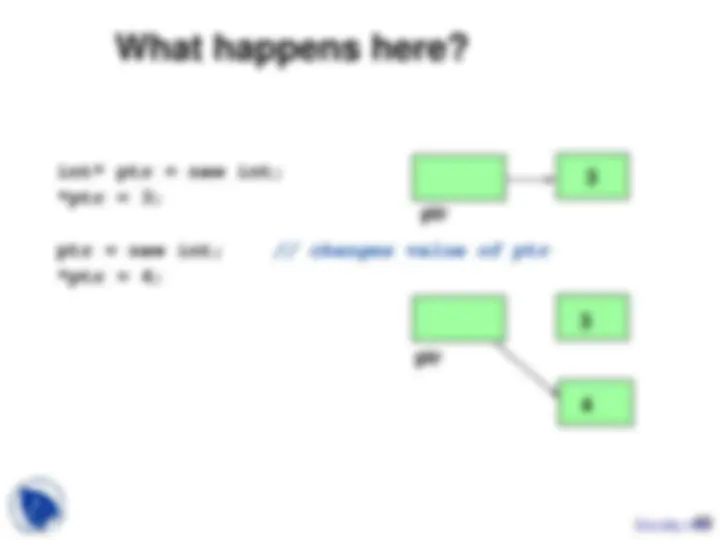

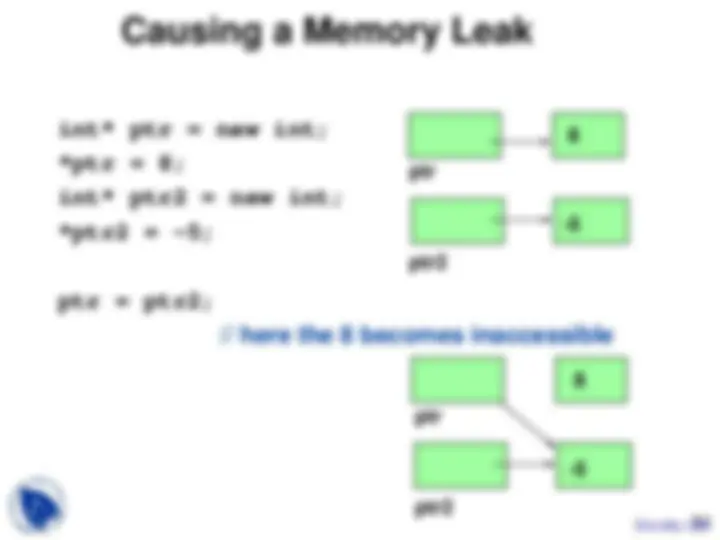


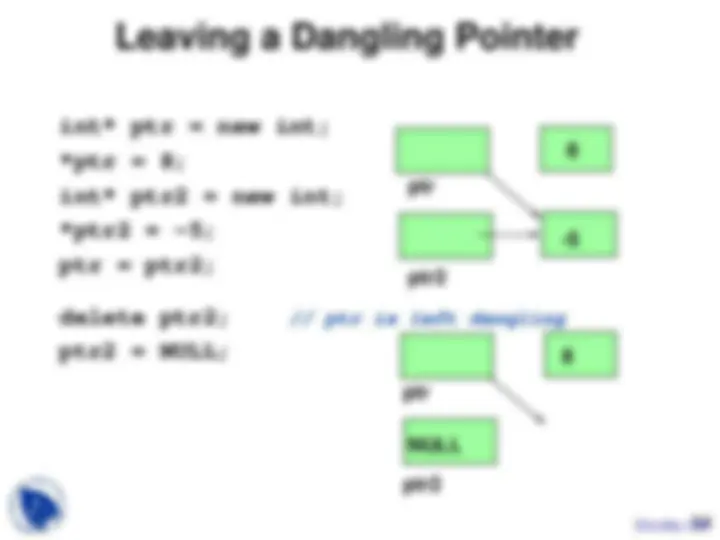















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
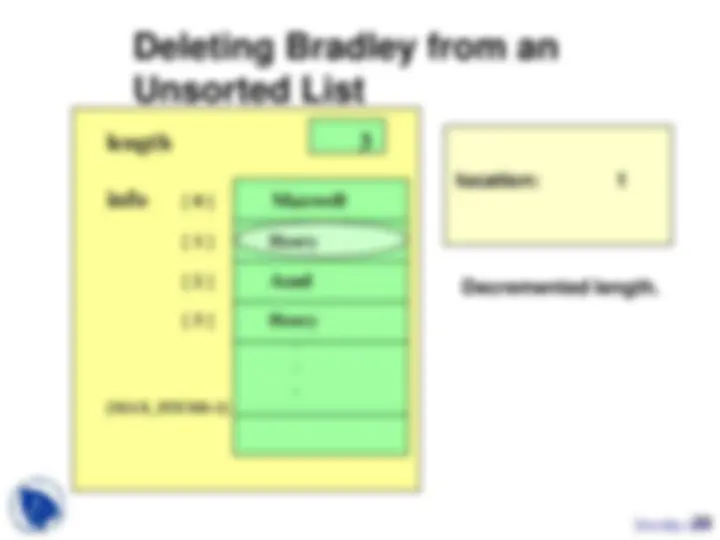
In the subject of the Data Structures, the key concept and the main points, which are very important in the context of the data structures are listed below:Adt Unsorted List, Linear Relationship, List Definitions, Each Element, Unique Predecessor, Length, Unique Successor, Number of Items, Unsorted List, Sorted List
Typology: Slides
1 / 75

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!




































































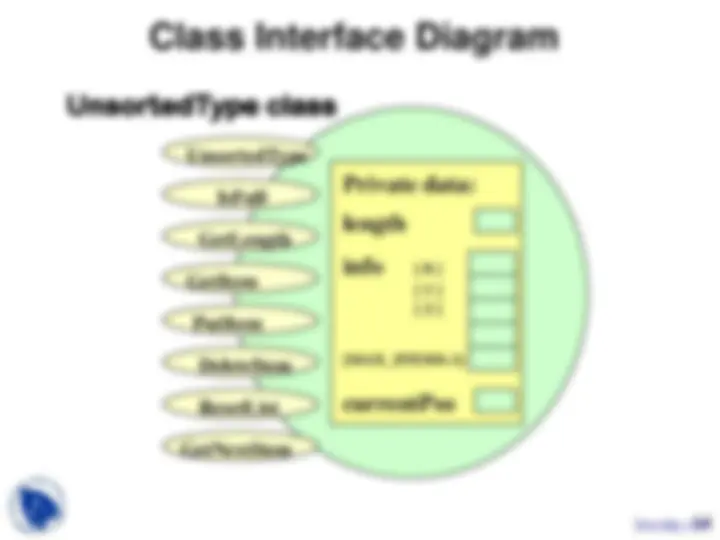
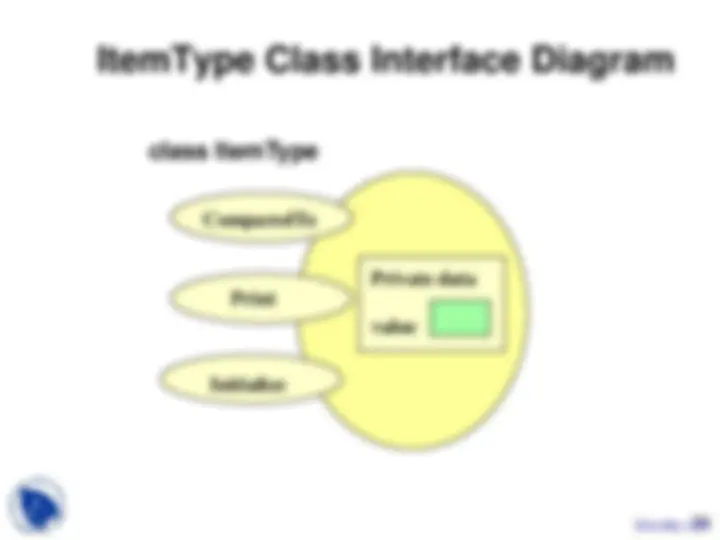
// SPECIFICATION FILE ( unsorted.h ) #include “ItemType.h”
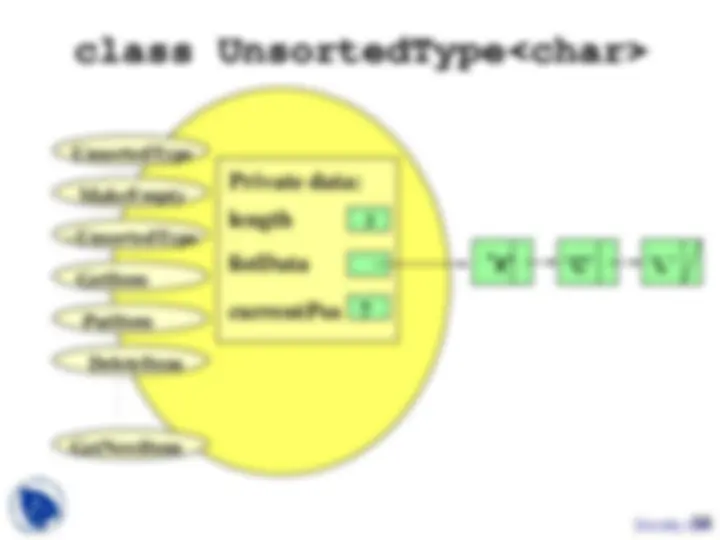
class UnsortedType // declares a class data type { public : // 8 public member functions void UnsortedType ( ); bool IsFull ( ) const; int GetLength ( ) const ; // returns length of list ItemType GetItem ( ItemType item, bool& found); void PutItem ( ItemType item ); void DeleteItem ( ItemType item ); void ResetList ( ); ItemType GetNextItem ();
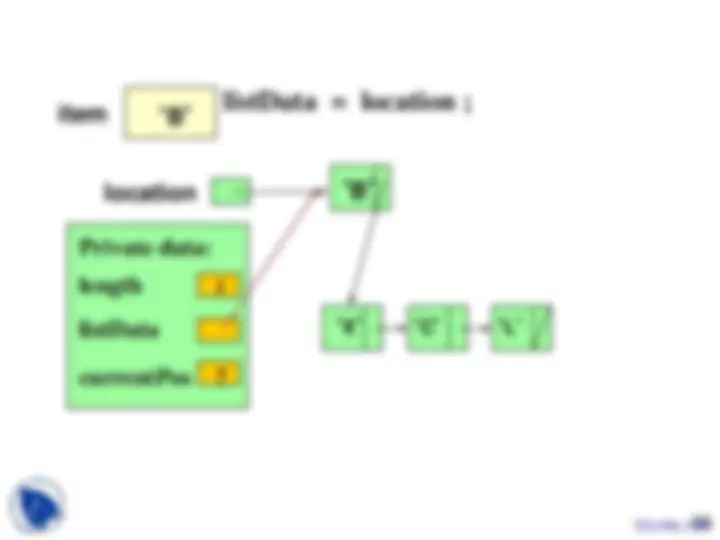
private : // 3 private data members int length; ItemType info[MAX_ITEMS]; int currentPos; };
[ 1 ] [ 2 ]
[MAX_ITEMS-1]
[MAX_ITEMS-1]
[MAX_ITEMS-1]
19
ItemType UnsortedType::GetItem ( ItemType item, bool& found ) // Pre: Key member of item is initialized. // Post: If found, item ’ s key matches an element ’ s key in the list // and a copy of that element is returned; // otherwise, input item is returned. { bool moreToSearch; int location = 0;
found = false; moreToSearch = ( location < length ); while ( moreToSearch && !found ) { switch ( item.ComparedTo( info[location] ) ) { case LESS : case GREATER : location++; moreToSearch = ( location < length ); break; case EQUAL : found = true; item = info[ location ]; break; } } return item; } (^) Docsity.com 19
[MAX_ITEMS-1]